Abstract
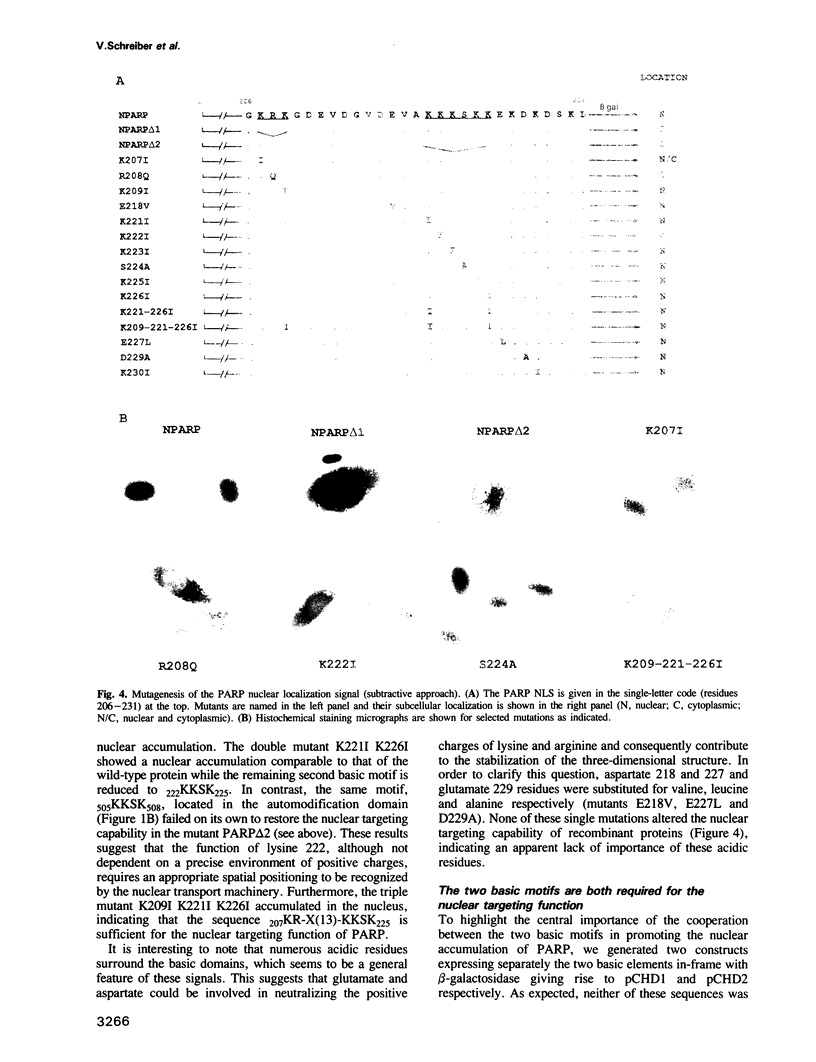
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP, EC 2.4.2.30) is a zinc finger DNA-binding protein involved in DNA repair processes in eukaryotes. By deletion and extensive site-directed mutagenesis, its DNA-binding domain fused to the N-terminus of beta-galactosidase was shown to contain a nuclear localization signal (NLS) of the form KRK-X(11)-KKKSKK (residues 207-226). In vitro, both the DNA-binding capacity and the polymerizing activity of PARP are independent of the nuclear location function. Each basic cluster is essential but not sufficient on its own for this function, while both motifs together are. Crucial basic amino acids (K207, R208 and K222) in each of these two motifs are required for nuclear homing. The results presented here support the concept that the human PARP NLS is an autonomous functional element and belongs to the class of bipartite NLSs. We show that the linear distance between the two basic clusters is not crucial. Insertional mutation analysis leading to a partial reversion of the cytoplasmic phenotype displayed by the mutant K222I highlights the crucial positioning of this lysine. The structure-function relationship of the second cluster of basic residues is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Althaus F. R., Richter C. ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Enzymology and biological significance. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1987;37:1–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. I., Buki K. G., Hakam A., Kun E. Macromolecular association of ADP-ribosyltransferase and its correlation with enzymic activity. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):17–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2700017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt P. B., Groeneveld H., Teubel W. J., van de Putte P., Backendorf C. Construction and properties of an Epstein-Barr-virus-derived cDNA expression vector for human cells. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):407–417. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. C., Gill D. M. Poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. A comparison of DNA molecules containing different types of strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10502–10508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buki K. G., Kun E. Polypeptide domains of ADP-ribosyltransferase obtained by digestion with plasmin. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):5990–5995. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Ralph R., Jonak G. Sequence requirements for synthetic peptide-mediated translocation to the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2487–2492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M., Buchwalder A., Tessier L. H., Jaye M., Benavente A., Balland A., Kohli V., Lathe R., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. High-level production of biologically active human alpha 1-antitrypsin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C. Transport across the nuclear envelope: enigmas and explanations. Bioessays. 1991 May;13(5):213–218. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson H. J., Rance M., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A., Wright P. E. Folding of immunogenic peptide fragments of proteins in water solution. I. Sequence requirements for the formation of a reverse turn. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):161–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Kallenbach E., Schultz N. Movement of a karyophilic protein through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J., Heitman J., Hall M. N. Nuclear protein localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):83–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90013-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradwohl G., Ménissier de Murcia J. M., Molinete M., Simonin F., Koken M., Hoeijmakers J. H., de Murcia G. The second zinc-finger domain of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase determines specificity for single-stranded breaks in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2990–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Lescop P., Christin-Maitre S., Loosfelt H., Perrot-Applanat M., Milgrom E. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the progesterone receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3851–3859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04954.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haymerle H., Herz J., Bressan G. M., Frank R., Stanley K. K. Efficient construction of cDNA libraries in plasmid expression vectors using an adaptor strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8615–8624. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppi K., Bhatia K., Siwarski D., Klinman D., Cherney B., Smulson M. Sequence and organization of the mouse poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3387–3401. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittel M. E., Garnier J. M., Jeltsch J. M., Niedergang C. P. Chicken poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase: complete deduced amino acid sequence and comparison with mammalian enzyme sequences. Gene. 1991 Jun 30;102(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda Z., Taniguchi T., Shizuta Y. Poly (ADP-Ribose) synthetase. Separation and identification of three proteolytic fragments as the substrate-binding domain, the DNA-binding domain, and the automodification domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4770–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazen A., Menissier-de Murcia J., Molinete M., Simonin F., Gradwohl G., Poirier G., de Murcia G. Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase: a novel finger protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4689–4698. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménissier-de Murcia J., Molinete M., Gradwohl G., Simonin F., de Murcia G. Zinc-binding domain of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase participates in the recognition of single strand breaks on DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihs H. P., Jans D. A., Fan H., Peters R. The rate of nuclear cytoplasmic protein transport is determined by the casein kinase II site flanking the nuclear localization sequence of the SV40 T-antigen. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):633–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihs H. P., Peters R. Nuclear transport kinetics depend on phosphorylation-site-containing sequences flanking the karyophilic signal of the Simian virus 40 T-antigen. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1479–1484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. The effect of protein context on nuclear location signal function. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. Nuclear location signal-mediated protein transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 14;1008(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Hatakeyama K., Kido T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Ueda K. Cloning of a full-length cDNA encoding bovine thymus poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase: evolutionarily conserved segments and their potential functions. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90187-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonin F., Briand J. P., Muller S., de Murcia G. Detection of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase in crude extracts by activity-blot. Anal Biochem. 1991 Jun;195(2):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90321-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonin F., Ménissier-de Murcia J., Poch O., Muller S., Gradwohl G., Molinete M., Penning C., Keith G., de Murcia G. Expression and site-directed mutagenesis of the catalytic domain of human poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in Escherichia coli. Lysine 893 is critical for activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19249–19256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Whytock S., Mills A. D. Association of gold-labelled nucleoplasmin with the centres of ring components of Xenopus oocyte nuclear pore complexes. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida K., Morita T., Sato T., Ogura T., Yamashita R., Noguchi S., Suzuki H., Nyunoya H., Miwa M., Sugimura T. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for human fibroblast poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):617–622. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Murcia G., Ménissier-de Murcia J., Schreiber V. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: molecular biological aspects. Bioessays. 1991 Sep;13(9):455–462. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]