Abstract
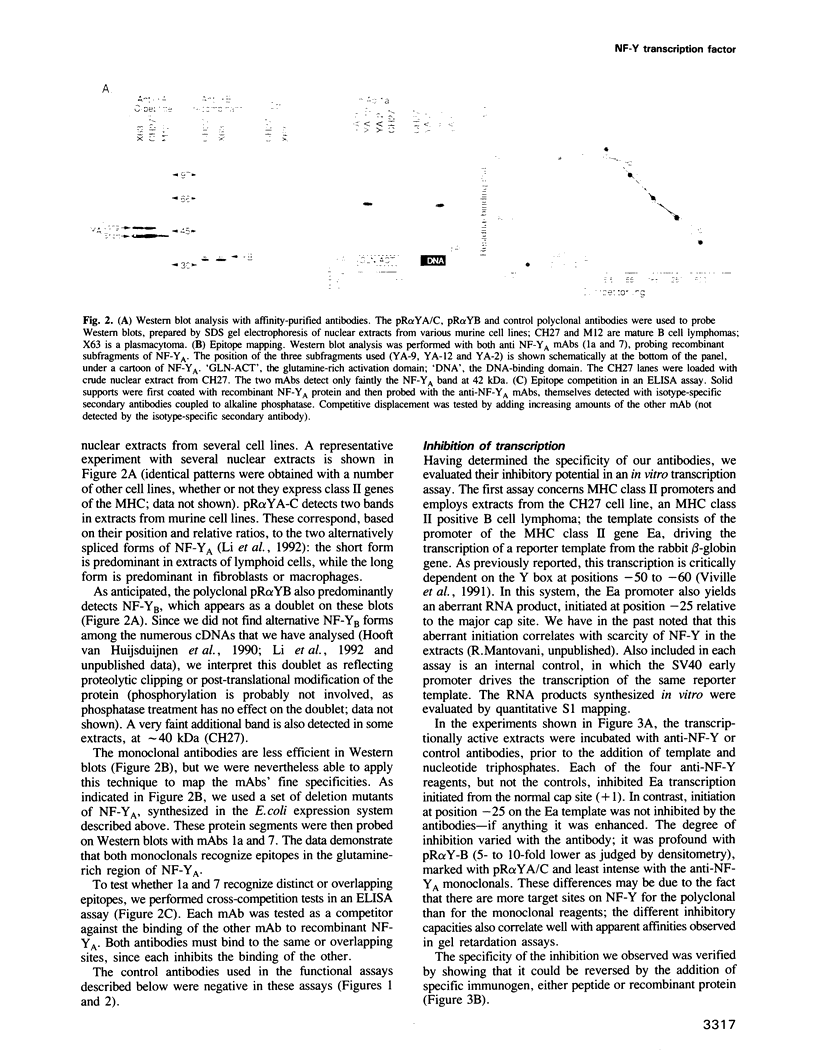
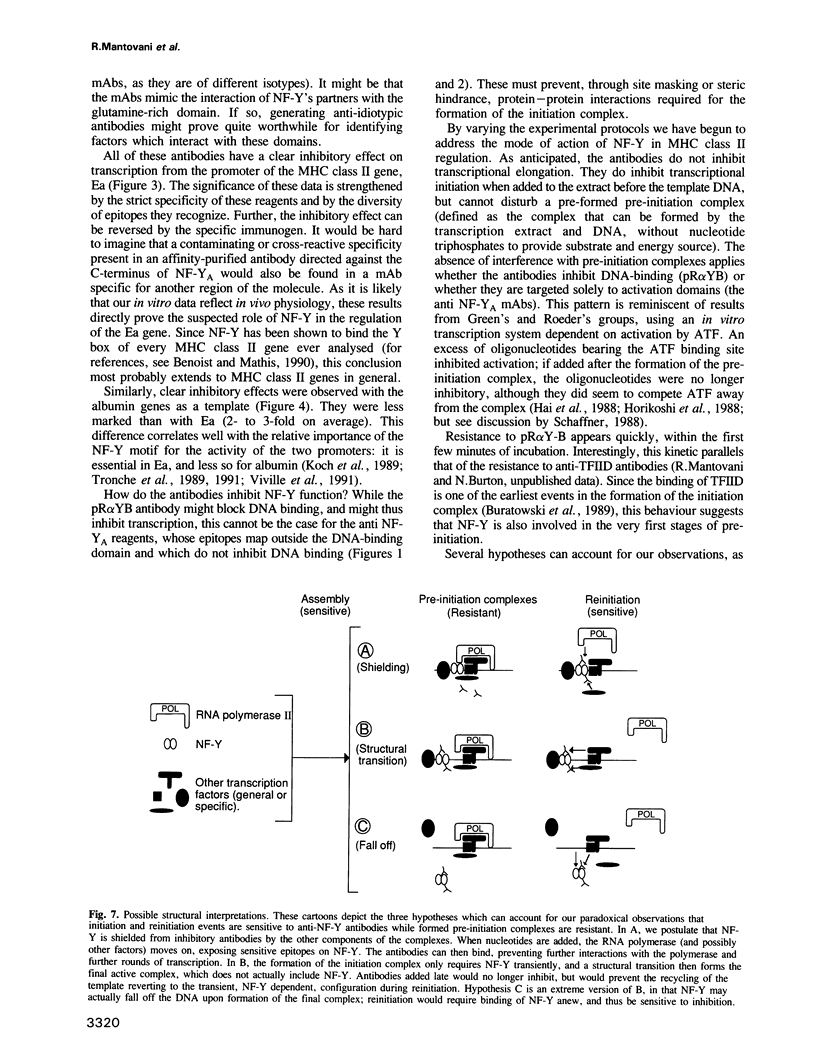
NF-Y is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein which, as a heterodimer, recognizes CCAAT motifs in a variety of transcriptional promoters. We have generated a panel of monoclonal and affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies directed against various epitopes of NF-Y. These reagents are highly specific for either of the A or B subunits; we have mapped the epitopes recognized by the monoclonal antibodies to the glutamine-rich activation domain of NF-YA. The antibodies inhibit in vitro transcription from the promoters of the albumin gene and of Ea, a class II gene of the major histocompatibility complex. These data definitively demonstrate the role of NF-Y in regulating the transcription of two tissue-specific genes whose expression patterns do not overlap. Interestingly, the antibodies cannot inhibit a formed pre-initiation complex, but do block reinitiation of subsequent rounds of transcription from the same templates.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didier D. K., Schiffenbauer J., Woulfe S. L., Zacheis M., Schwartz B. D. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a protein binding to the major histocompatibility complex class II Y box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7322–7326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostatni N., Lambert P. F., Sousa R., Ham J., Howley P. M., Yaniv M. The functional BPV-1 E2 trans-activating protein can act as a repressor by preventing formation of the initiation complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1657–1671. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Green M. R. Analysis of the role of the transcription factor ATF in the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Functional steps in transcription initiation and reinitiation from the major late promoter in a HeLa nuclear extract. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3452–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Separation and partial characterization of three functional steps in transcription initiation by human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8163–8172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Li X. Y., Black D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Co-evolution from yeast to mouse: cDNA cloning of the two NF-Y (CP-1/CBF) subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3119–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Glimcher L. H. In vivo footprinting of MHC class II genes: bare promoters in the bare lymphocyte syndrome. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.1902592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Benoist C., Mathis D. Anatomy of a new B-cell-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):303–311. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. Y., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Mantovani R., Benoist C., Mathis D. Intron-exon organization of the NF-Y genes. Tissue-specific splicing modifies an activation domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8984–8990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maity S. N., Golumbek P. T., Karsenty G., de Crombrugghe B. Selective activation of transcription by a novel CCAAT binding factor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):582–585. doi: 10.1126/science.3399893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen J., Hatamochi A., de Crombrugghe B. Separate binding sites for nuclear factor 1 and a CCAAT DNA binding factor in the mouse alpha 2(I) collagen promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11064–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Gene regulation. A hit-and-run mechanism for transcriptional activation? Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):427–428. doi: 10.1038/336427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmay M. N., Sawadogo M. Transcription factor requirement for multiple rounds of initiation by human RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10691–10695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Bach I., Weiss M. C., Yaniv M. The rat albumin promoter: cooperation with upstream elements is required when binding of APF/HNF1 to the proximal element is partially impaired by mutation or bacterial methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4759–4766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Sourdive D., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. NFY or a related CCAAT binding factor can be replaced by other transcriptional activators for co-operation with HNF1 in driving the rat albumin promoter in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 5;222(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90735-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sawadogo M. DNA-binding and transcriptional properties of human transcription factor TFIID after mild proteolysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3415–3420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viville S., Jongeneel V., Koch W., Mantovani R., Benoist C., Mathis D. The E alpha promoter: a linker-scanning analysis. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3211–3217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Brou C., Wu J., Lutz Y., Moncollin V., Chambon P. The acidic transcriptional activator GAL-VP16 acts on preformed template-committed complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2229–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J., Mueller C., Schibler U. A ubiquitous CCAAT factor is required for efficient in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):865–874. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90341-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeleznik-Le N. J., Azizkhan J. C., Ting J. P. Affinity-purified CCAAT-box-binding protein (YEBP) functionally regulates expression of a human class II major histocompatibility complex gene and the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1873–1877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









