Abstract
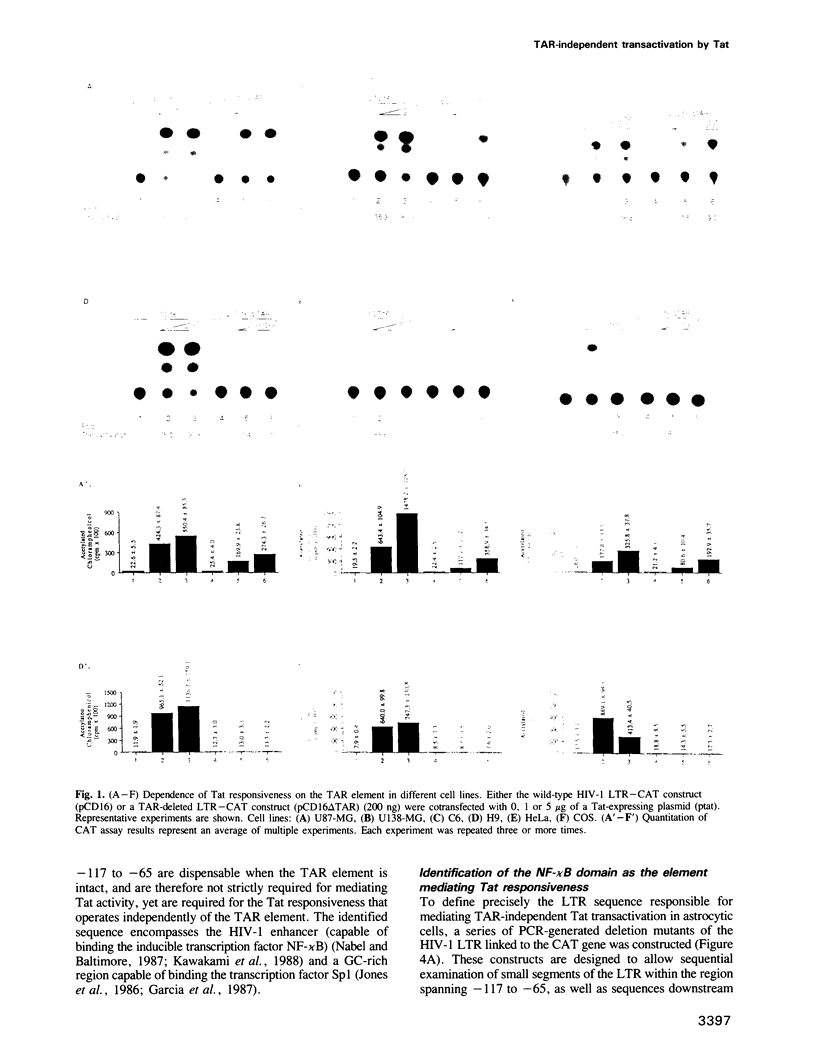
The Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is essential for productive infection and is a potential target for antiviral therapy. Tat, a potent activator of HIV-1 gene expression, serves to greatly increase the rate of transcription directed by the viral promoter. This induction, which seems to be an important component in the progression of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), may be due to increased transcriptional initiation, increased transcriptional elongation, or a combination of these processes. Much attention has been focused on the interaction of Tat with a specific RNA target termed TAR (transactivation responsive) which is present in the leader sequence of all HIV-1 mRNAs. This interaction is believed to be an important component of the mechanism of transactivation. In this report we demonstrate that in certain CNS-derived cells Tat is capable of activating HIV-1 through a TAR-independent pathway. A Tat-responsive element is found upstream within the viral promoter that in glial-derived cell lines allows transactivation in the absence of TAR. Deletion mapping and hybrid promoter constructs demonstrate that the newly identified Tat-responsive element corresponds to a sequence within the viral long terminal repeat (LTR) previously identified as the HIV-1 enhancer, or NF-kappa B domain. DNA band-shift analysis reveals NF-kappa B binding activity in glial cells that differs from that present in T lymphoid cells. Further, we observe that TAR-deleted mutants of HIV-1 demonstrate normal late gene expression in glial cells as evidenced by syncytia formation and production of viral p24 antigen.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Rabson A. B., Jeang K. T. TAR-independent activation of the HIV-1 LTR: evidence that tat requires specific regions of the promoter. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Silverman R. H., Jeang K. T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Tidor B., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Arginine-mediated RNA recognition: the arginine fork. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1167–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein: an RNA sequence-specific processivity factor? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Sakai K., Bresser J., Stevenson M., Evinger-Hodges M. J., Volsky D. J. Persistent productive infection of human glial cells by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and by infectious molecular clones of HIV. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3774–3782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3774-3782.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Sharer L. R., Joshi V. V., Fojas M. M., Koenigsberger M. R., Oleske J. M. Progressive encephalopathy in children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1985 May;17(5):488–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H. Neurologic disorders associated with HIV infections. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Jun;22(6 Pt 2):1232–1236. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70168-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Wu F. K., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Interactions of cellular proteins involved in the transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3761–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Vaca K., Noonan C. A. Secretion of neurotoxins by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1593–1596. doi: 10.1126/science.2148832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyorkey F., Melnick J. L., Gyorkey P. Human immunodeficiency virus in brain biopsies of patients with AIDS and progressive encephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):870–876. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. TAR independent activation of the human immunodeficiency virus in phorbol ester stimulated T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4417–4423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the trans-activation-responsive region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):673–679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.673-679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Schooley R. T., Kaplan J. C., Allan J. D., Groopman J. E., Resnick L., Felsenstein D., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Isolation of HTLV-III from cerebrospinal fluid and neural tissues of patients with neurologic syndromes related to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1493–1497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Khoury G., Brady J. Spacing between simian virus 40 early transcriptional control sequences is important for regulation of early RNA synthesis and gene expression. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):935–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.935-942.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. M., Flomerfelt F. A., Ghrayeb J. Expression of the art/trs protein of HIV and study of its role in viral envelope synthesis. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):837–840. doi: 10.1126/science.3033827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. Synergy between HIV-1 Tat and adenovirus E1A is principally due to stabilization of transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2397–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J., Hollander H., Mills J., Kaminsky L. Isolation of AIDS-associated retroviruses from cerebrospinal fluid and brain of patients with neurological symptoms. Lancet. 1985 Sep 14;2(8455):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. L., Moudgil T., Vinters H. V., Ho D. D. CD4-independent, productive infection of a neuronal cell line by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1383–1387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1383-1387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels J., Sharer L. R., Epstein L. G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the nervous system: a review. Immunodefic Rev. 1988;1(1):71–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Okamoto T., Reuter P., Ugarkovic D., Schröder H. C. Functional characterization of Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Evidence that Tat links viral RNAs to nuclear matrix. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3803–3808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Price R. W. The acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia complex as the presenting or sole manifestation of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jan;44(1):65–69. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520130051017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Benter T., Josephs S. F., Sadaie M. R., Wong-Staal F. Transcriptional activation from the long-terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):606–614. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90526-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S., Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Wiley C., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. High levels of unintegrated HIV-1 DNA in brain tissue of AIDS dementia patients. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):85–89. doi: 10.1038/343085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasabapathy R., Sheldon M., Johal L., Hernandez N. The HIV-1 long terminal repeat contains an unusual element that induces the synthesis of short RNAs from various mRNA and snRNA promoters. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2061–2074. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. H., Ward J. M., Walker D. L., Ross A. A. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and retroviral encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1207–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hennighausen L., Siebenlist U. Inducible nuclear factor binding to the kappa B elements of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells can be blocked by cyclosporin A in a signal-dependent manner. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4037–4041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4037-4041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Peterlin B. M. Trans-activation by HIV-1 Tat via a heterologous RNA binding protein. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90121-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. Location of the trans-activating region on the genome of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2990041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C. D., Green M. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein activates transcription from an upstream DNA-binding site: implications for Tat function. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2496–2507. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Activation of transcription by HIV-1 Tat protein tethered to nascent RNA through another protein. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):640–642. doi: 10.1038/345640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornatore C., Nath A., Amemiya K., Major E. O. Persistent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in human fetal glial cells reactivated by T-cell factor(s) or by the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6094–6100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6094-6100.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., O'Leary T. J., Baskin G. B., Benveniste R., Harris C. A., Nara P. L., Rhodes R. H. Immunohistochemical localization of human and simian immunodeficiency viral antigens in fixed tissue sections. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):199–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]