Abstract
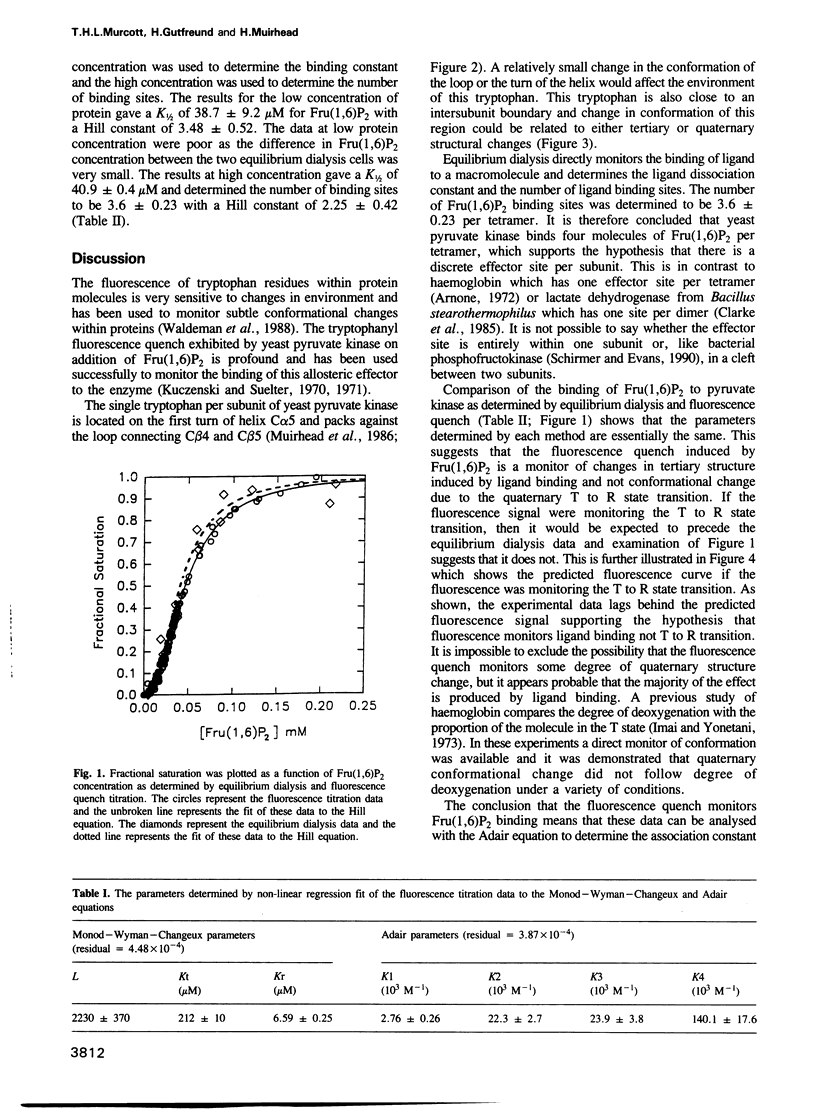
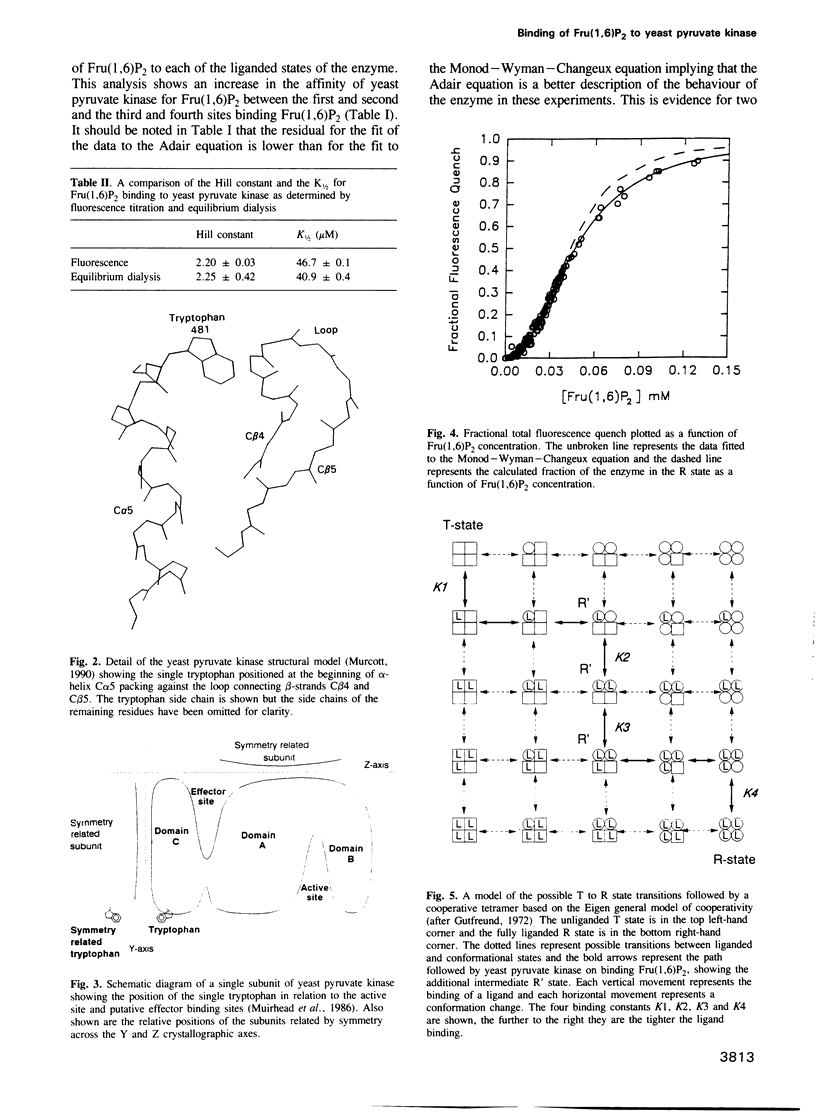
The cooperative binding of the allosteric activator fructose-1,6-bisphosphate [Fru(1,6)P2] to yeast pyruvate kinase was investigated by equilibrium dialysis and fluorescence quench titration. The results show that yeast pyruvate kinase binds four molecules of Fru(1,6)P2 per tetramer and the observed fluorescence quench follows the binding of the ligand and not the cooperative T to R state transition. Additionally it is shown that the binding of Fru(1,6)P2 to yeast pyruvate kinase is compatible with the model of cooperativity that has been proposed and incorporates an intermediate state, R', with properties between those of the T and R states.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnone A. X-ray diffraction study of binding of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate to human deoxyhaemoglobin. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):146–149. doi: 10.1038/237146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeckel R., Hess B., Lauterborn W., Wüster K. H. Purification and allosteric properties of yeast pyruvate kinase. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 May;349(5):699–714. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1968.349.1.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Yonetani T. Non-linear relationships between oxygen saturation and magnitude of fine structure of ultraviolet oxy versus deoxy difference spectrum in human hemoglobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1055–1060. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinderlerer J., Ainsworth S., Morris C. N., Rhodes N. The regulatory properties of yeast pyruvate kinase. Effect of pH. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):699–703. doi: 10.1042/bj2340699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczenski R. T., Suelter C. H. Effect of temperature and effectors on the conformations of yeast pyruvate kinase. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):939–945. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczenski R. T., Suelter C. H. Interactions of Fructose 1,6-diphosphate, substrates, and monovalent cations with yeast pyruvate kinase monitored by changes in enzyme fluorescence. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 20;10(15):2862–2866. doi: 10.1021/bi00791a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirhead H., Clayden D. A., Barford D., Lorimer C. G., Fothergill-Gilmore L. A., Schiltz E., Schmitt W. The structure of cat muscle pyruvate kinase. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):475–481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murcott T. H., McNally T., Allen S. C., Fothergill-Gilmore L. A., Muirhead H. Purification, characterisation and mutagenesis of highly expressed recombinant yeast pyruvate kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 1;198(2):513–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes N., Morris C. N., Ainsworth S., Kinderlerer J. The regulatory properties of yeast pyruvate kinase. Effects of NH4+ and K+ concentrations. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):705–715. doi: 10.1042/bj2340705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer T., Evans P. R. Structural basis of the allosteric behaviour of phosphofructokinase. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):140–145. doi: 10.1038/343140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun S. L., Aust A. E., Suelter C. H. A revised preparation of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) pyruvate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



