Abstract
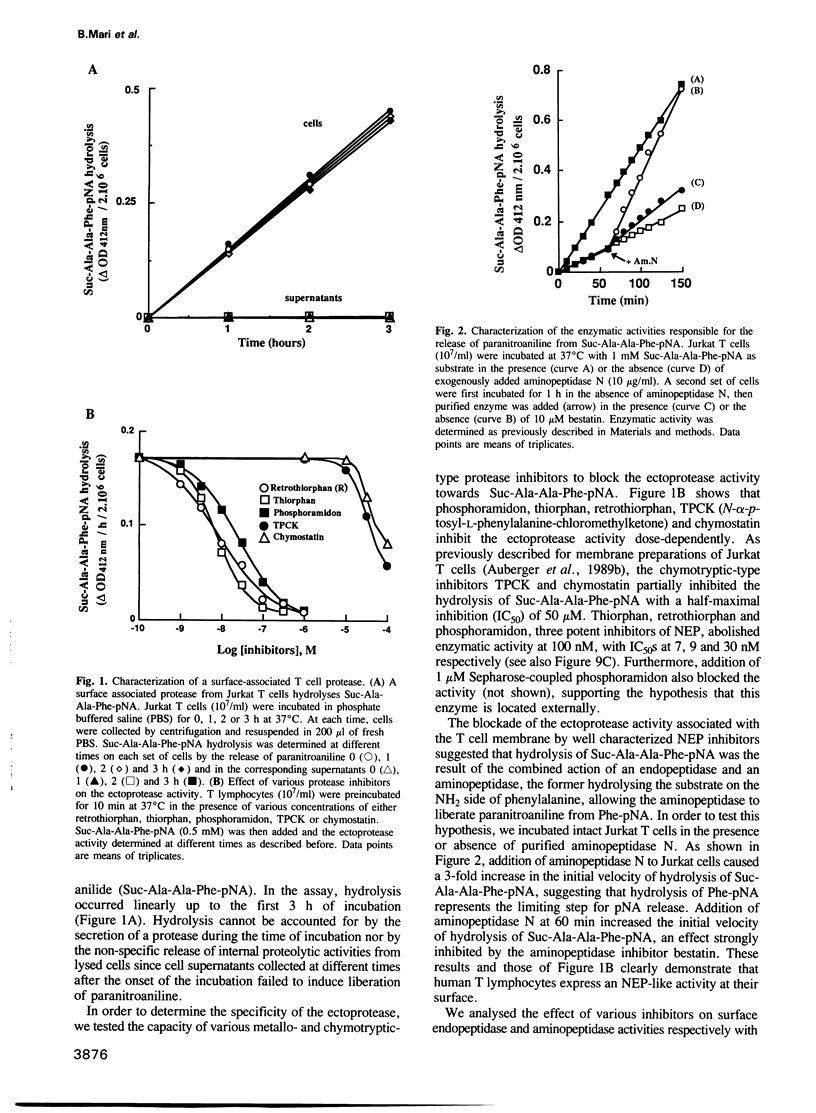
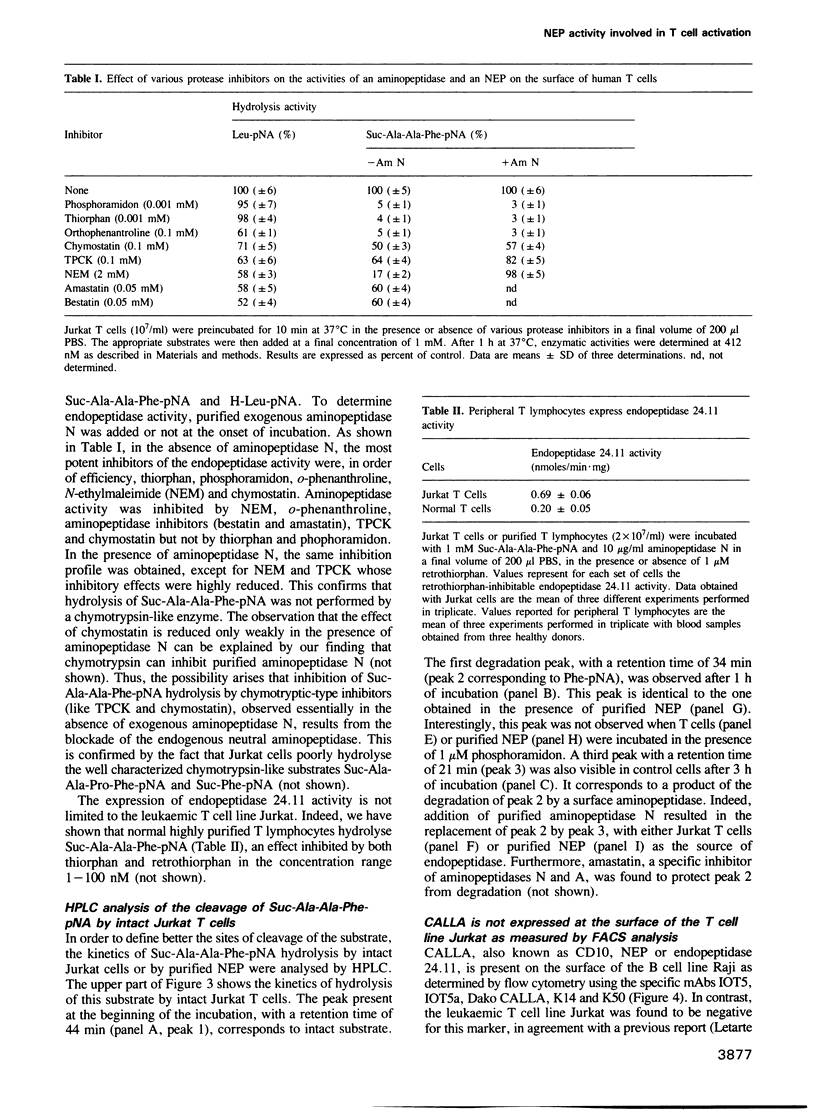
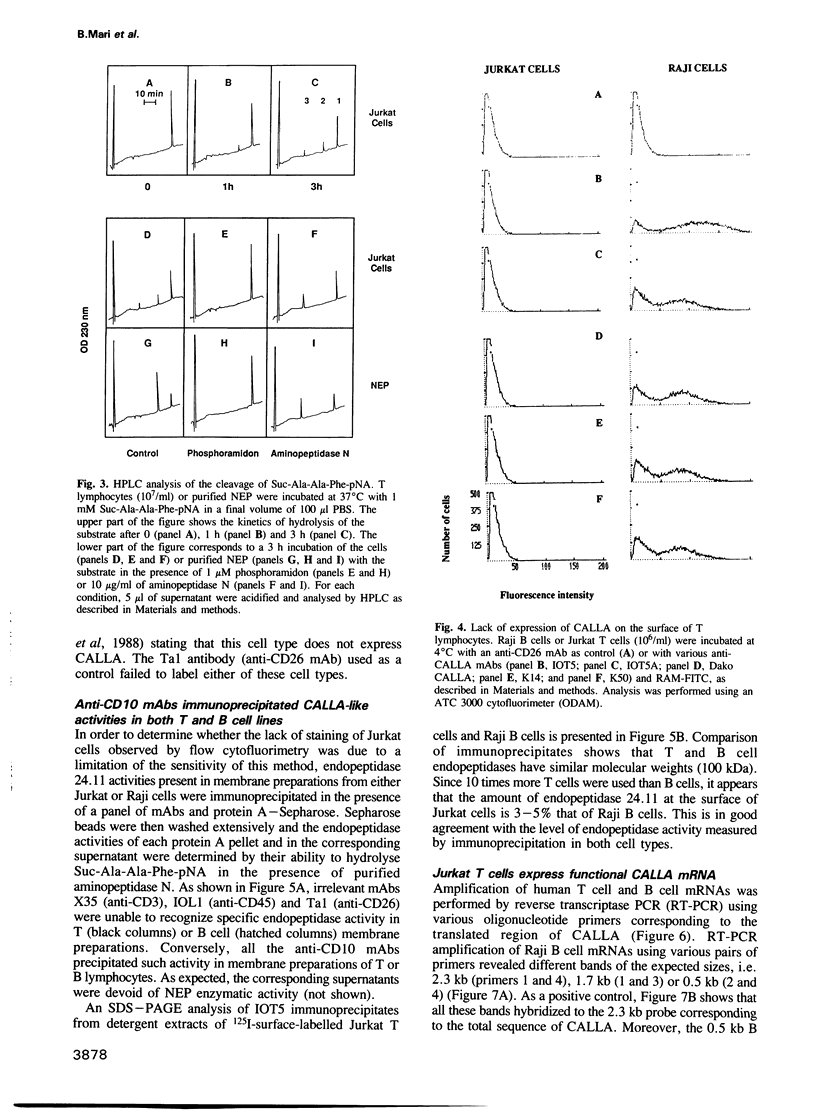
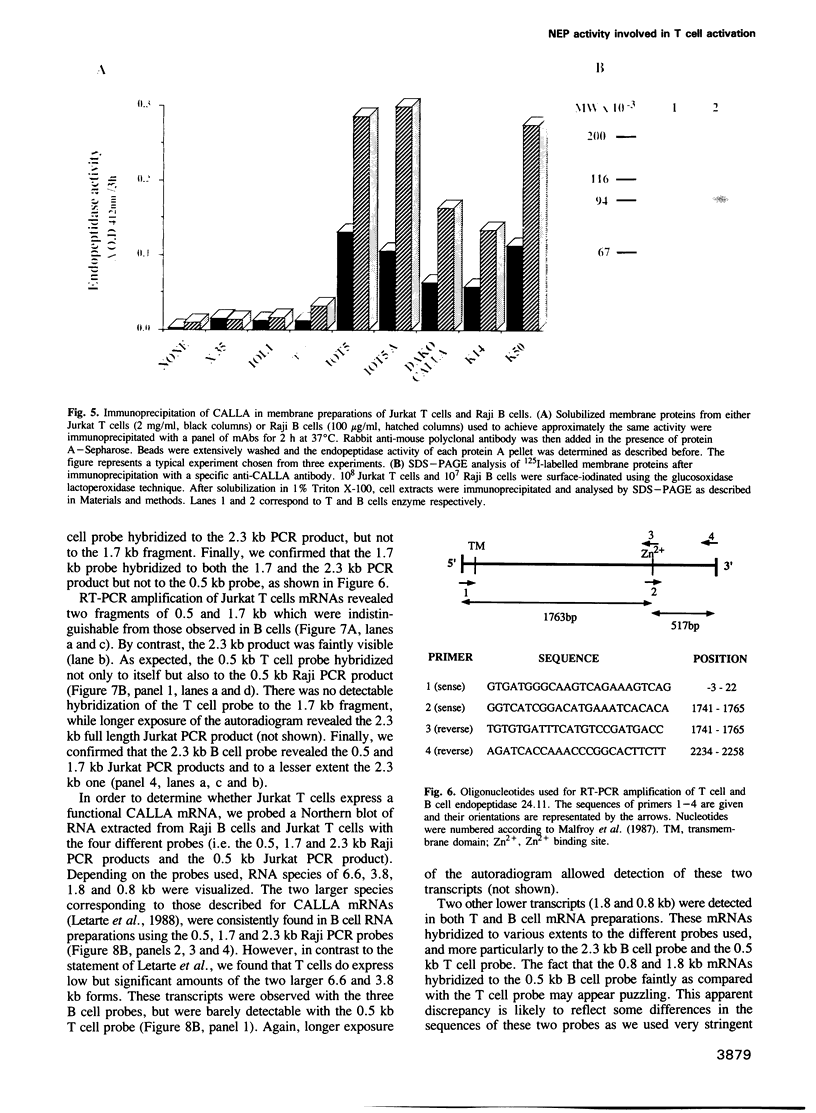
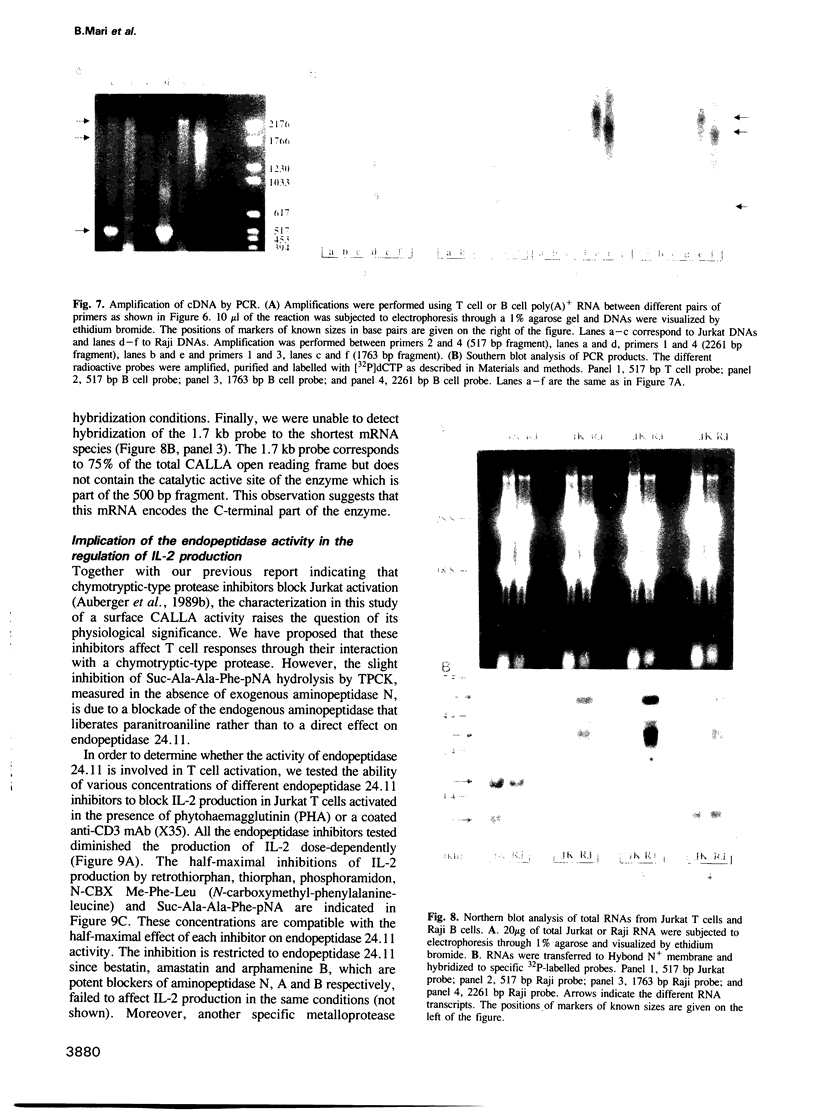
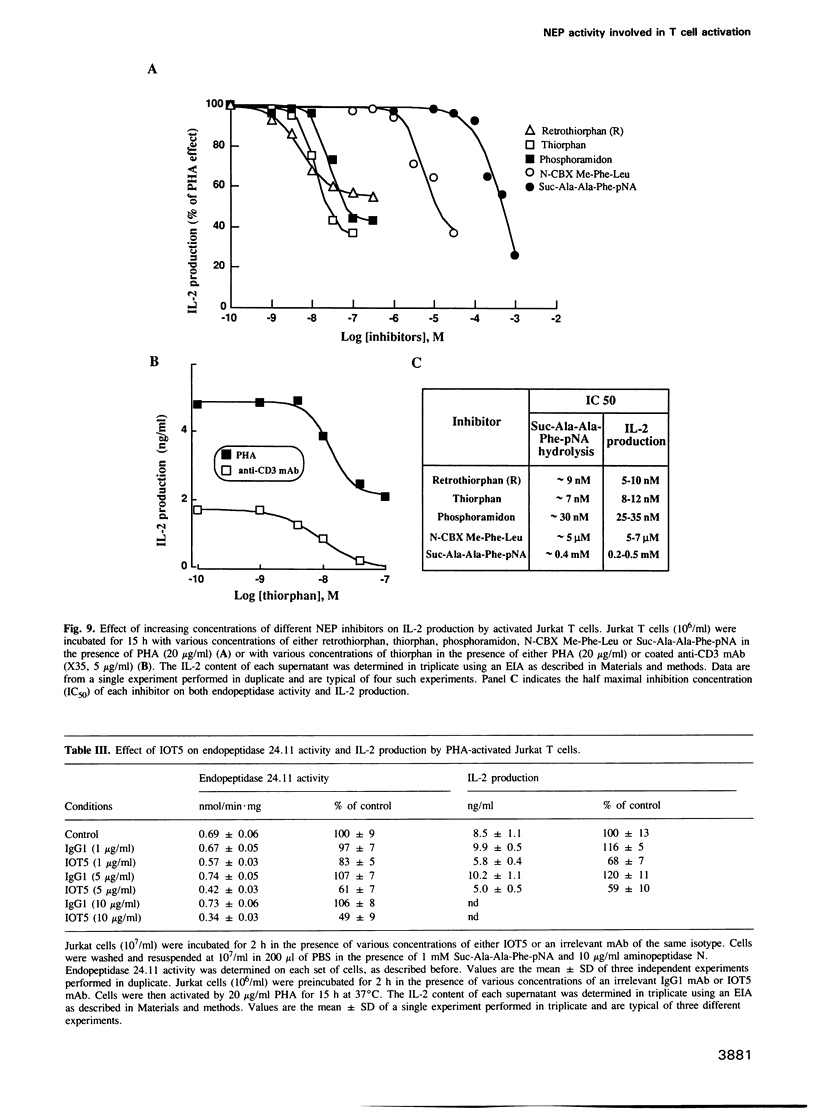
We have characterized a T lymphocyte endopeptidase activity that hydrolyses succinyl-alanine-alanine-phenylalanine-paranitroanilide (Suc-Ala-Ala-Phe-pNa). Hydrolysis of this substrate by intact Jurkat T cells was markedly enhanced when exogenous aminopeptidase N was added to the incubation medium. It thus appears that the release of paranitroaniline from Suc-Ala-Ala-Phe-pNA results from the combination of two distinct enzymatic activities: (i) an endopeptidase activity that cleaves the substrate at the alanyl bond and (ii) an aminopeptidase activity that ultimately cleaves the phenylalanyl bond. This cleavage was further confirmed by HPLC analysis. Specific endopeptidase 24.11 inhibitors were shown to inhibit the endopeptidase activity. These features are reminiscent of the characteristics of neutral endopeptidase (NEP, also known as endopeptidase 24.11, CALLA or CD10). Anti-CD10 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognized the CD10+ B cell line Raji, but not Jurkat cells as assessed by FACS analysis. This is probably due to a lack of sensitivity of this method, the level of NEP activity in Jurkat T cells being 3-5% of that measured in B cell lines. Anti-CD10 mAbs immunoprecipitated endopeptidase 24.11 activities in both Jurkat T cells and Raji B cells, demonstrating that T lymphocytes express a CALLA-related endopeptidase. We also demonstrate that T and B cell endopeptidases have the same molecular weight, that T cells express less functional CALLA mRNA than B cells and that there are at least two shorter transcripts (1.8 and 0.8 kb) in both T and B cells.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amoscato A. A., Alexander J. W., Babcock G. F. Surface aminopeptidase activity of human lymphocytes. I. Biochemical and biologic properties of intact cells. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auberger P., Didier M., Didier J., Aussel C., Fehlmann M. A chymotryptic-type protease inhibitor decreases interleukin 2 synthesis and induces prostaglandin production in Jurkat T cells. Cell Signal. 1989;1(3):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auberger P., Mary D., Breittmayer J. P., Aussel C., Fehlmann M. Chymotryptic-type protease inhibitors block the increase in Ca2+ and Il-2 production in activated Jurkat T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1253–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont A., Brouet J. C., Roques B. P. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 and angiotensin converting enzyme like activity in CALLA positive and CALLA negative lymphoid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1323–1329. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes M. A., Kenny A. J. An immunohistochemical study of endopeptidase-24.11 and aminopeptidase N in lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1987 Feb;60(2):247–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd-Bartlett Y., Troll W. Murine lymphocyte cell surface proteolytic activity is strain related. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):600–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90822-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Eisen H. N. Effects of N alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethylketone on the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly J. C., Skidgel R. A., Schulz W. W., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 in human neutrophils: cleavage of chemotactic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Sugita K., Daley J. F., Schow P., Prado C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cell surface modulation of CD26 by anti-1F7 monoclonal antibody. Analysis of surface expression and human T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):3963–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrua B., Aussel C., Fehlmann M. Human interleukin 2. Detection at the picomolar level by sandwich enzyme immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Mar 12;97(2):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Vivier I., Naquet P., Brekelmans P., Rigal A., Pierres M. Characterization of the neutral aminopeptidase activity associated to the mouse thymocyte-activating molecule. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2899–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski J. K., Mukherji B., Cohen S. The role of cytoplasmic intermediates in IL 2-induced T cell growth. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3068–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegen M., Niedobitek G., Klein C. E., Stein H., Fleischer B. The T cell triggering molecule Tp103 is associated with dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV activity. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann D., Vischer T. L. Immunomodulation by alpha 2-macroglobulin and alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complexes: the effect on the human T lymphocyte response. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):755–760. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. I. Enzymatic iodination of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):438–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta T., Okubo H., Kudo J., Ishibashi H., Inoue T. Alpha 1-antitrypsin synthesis by human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1509–1516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janković B. D., Veljić J., Pesić G., Marić D. Enkephalinase-inhibitors modulate immune responses. Int J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;59(1-3):45–51. doi: 10.3109/00207459108985448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett M., Seed T. M., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes and intact nuclei from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2134–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Kikutani H., Nishizawa Y., Sakaguchi N., Yamamura Y. Involvement of anti-Ig-activated serine protease in the generation of cytoplasmic factor(s) that are responsible for the transmission of Ig-receptor-mediated signals. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku G. S., Quigley J. P., Sultzer B. M. The inhibition of the mitogenic stimulation of B lymphocytes by a serine protease inhibitor: commitment to proliferation correlates with an enhanced expression of a cell-associated arginine-specific serine enzyme. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2494–2499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorens-Cortes C., Giros B., Schwartz J. C. A novel potential metallopeptidase derived from the enkephalinase gene by alternative splicing. J Neurochem. 1990 Dec;55(6):2146–2148. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb05810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W., Paetkau V. H., Bleackley R. C. Novel serine proteases encoded by two cytotoxic T lymphocyte-specific genes. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):858–861. doi: 10.1126/science.3518058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schofield P. R., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Henzel W. J. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of rat enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mary D., Aussel C., Ferrua B., Fehlmann M. Regulation of interleukin 2 synthesis by cAMP in human T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1179–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Nabholz M., Estrade C., Tschopp J. Granules of cytolytic T-lymphocytes contain two serine esterases. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1595–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Torimoto Y., Levinson G., Rudd C. E., Schrieber M., Dang N. H., Letvin N. L., Schlossman S. F. 1F7, a novel cell surface molecule, involved in helper function of CD4 cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3430–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Dukes R., Sullivan J., Carter R., Erdös E. G., Johnson A. R. Function of neutral endopeptidase on the cell membrane of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9456–9461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Verret C. R., Liu M. A., Eisen H. N. Serine esterase in cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):740–743. doi: 10.1038/322740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. M., Ejlersen E., Moestrup S. K., Jensen P. H., Sand O., Sottrup-Jensen L. Immunosuppressive properties of electrophoretically "slow" and "fast" form alpha 2-macroglobulin. Effects on cell-mediated cytotoxicity and (allo-) antigen-induced T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P. Inhibiteurs d'enképhalinase et exploration moléculaire des différences entre sites actifs de l'enképhalinase et de l'enzyme de conversion de l'angiotensine. J Pharmacol. 1985;16 (Suppl 1):5–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Lucas-Soroca E., Chaillet P., Costentin J., Fournié-Zaluski M. C. Complete differentiation between enkephalinase and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition by retro-thiorphan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Jahn S., Kiessig S. T., Demuth H. U., Neubert K., Barth A., Von Baehr R., Ansorge S. The role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocyte activation. Inhibitors and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1821–1826. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Vijayaraghavan J., Schmidt E. V., Masteller E. L., D'Adamio L., Hersh L. B., Reinherz E. L. Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is active neutral endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase"): direct evidence by cDNA transfection analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya N., Nakanishi M. A serine protease triggers the initial step of transmembrane signalling in cytotoxic T cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16514–16517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Louvard D., Maroux S., Desnuelle P. Structural and topological homology between porcine intestinal and renal brush border aminopeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier I., Marguet D., Naquet P., Bonicel J., Black D., Li C. X., Bernard A. M., Gorvel J. P., Pierres M. Evidence that thymocyte-activating molecule is mouse CD26 (dipeptidyl peptidase IV). J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. L., Gutowski J. K., Katz M., Goldfarb R. H., Cohen S. Induction of DNA synthesis in isolated nuclei by cytoplasmic factors: inhibition by protease inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Wall D. A., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and characterization of a serine esterase from cytolytic T cell granules. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]