Abstract
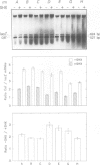
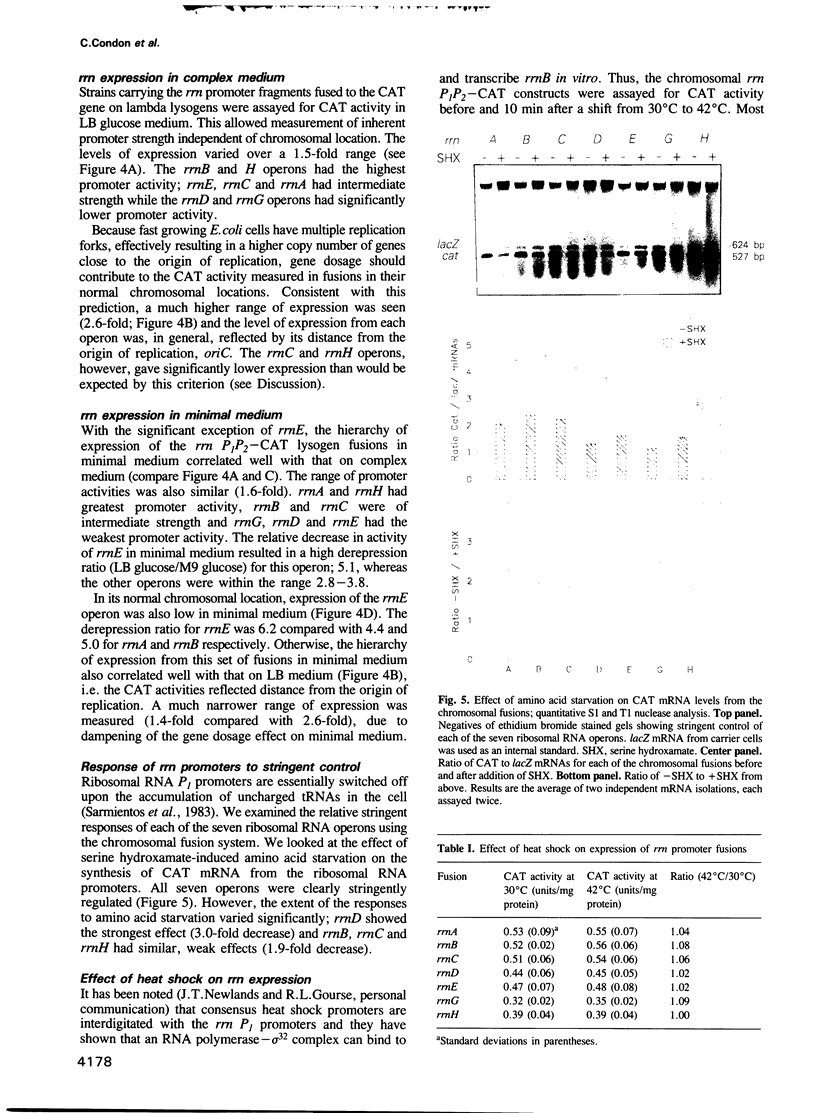
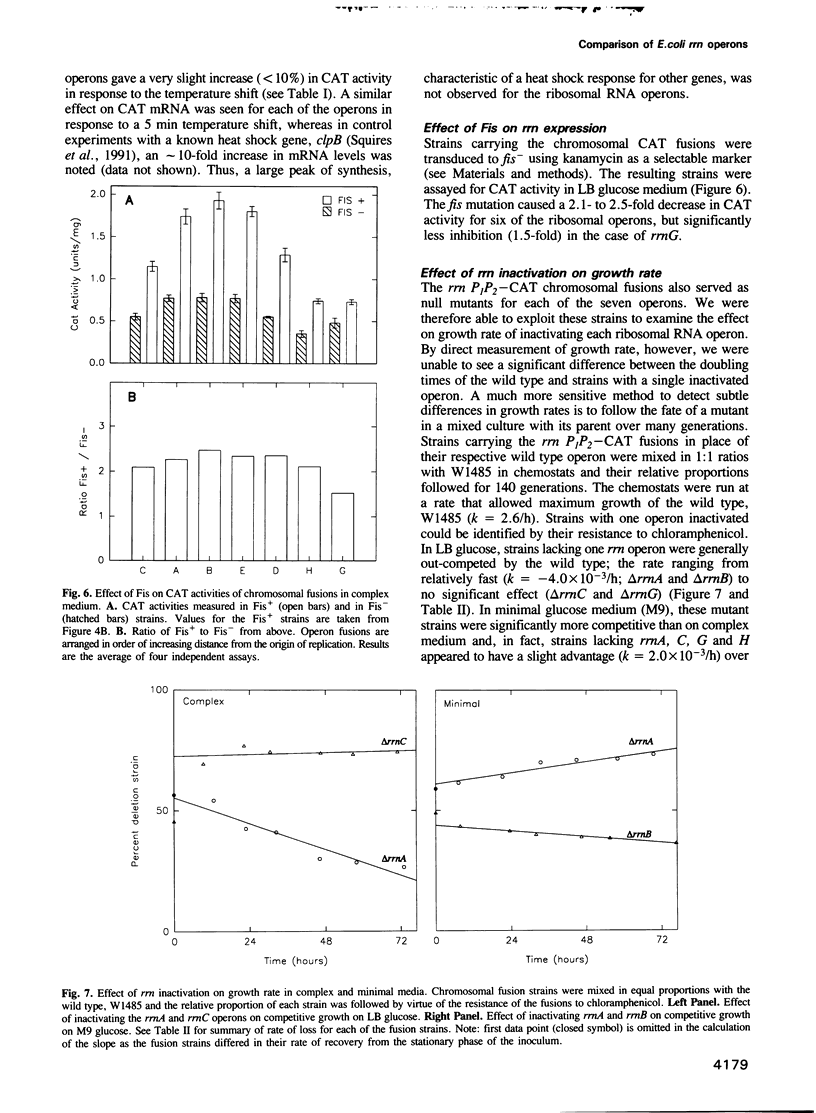
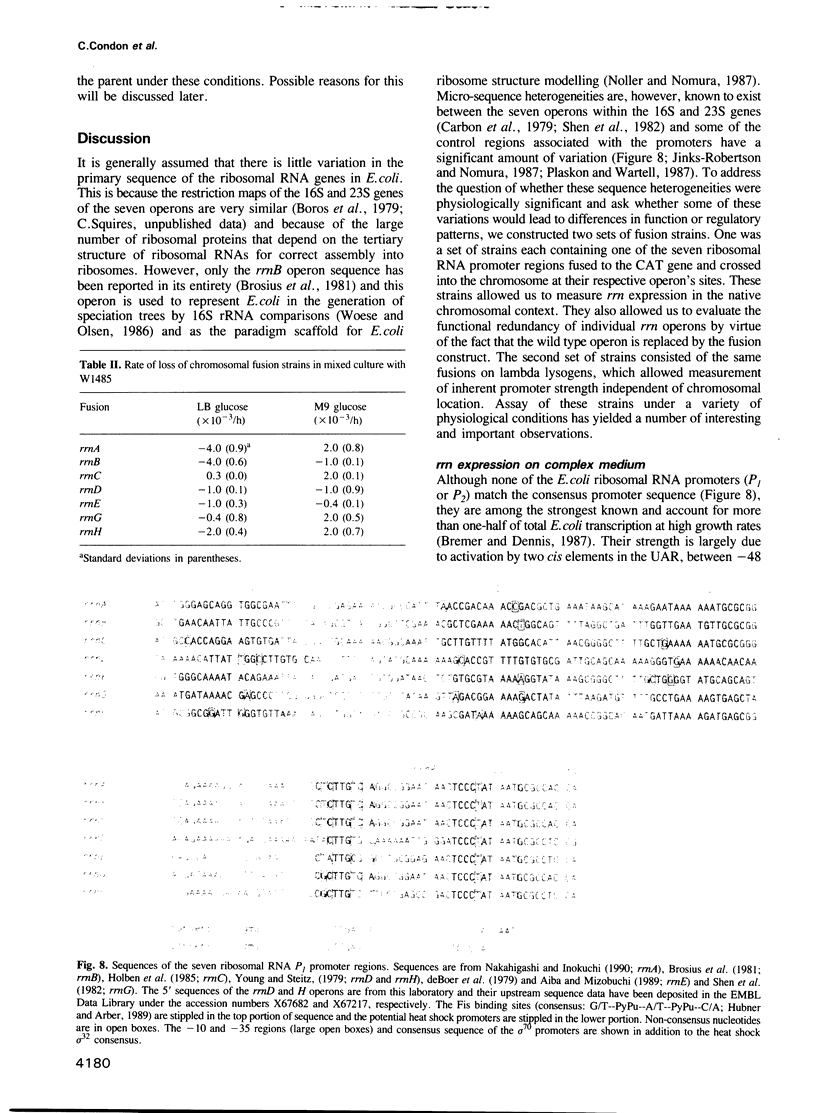
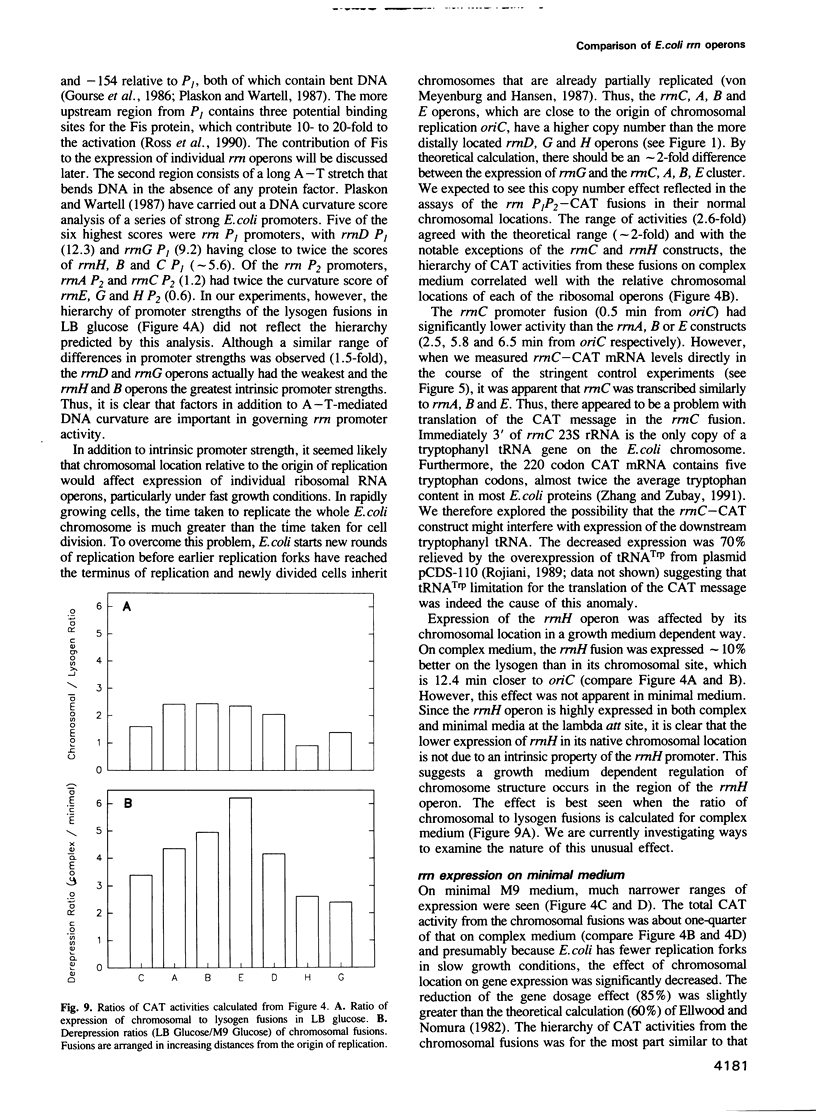
We have compared the expression of the seven ribosomal RNA operons (rrn) of Escherichia coli and their responses to a variety of physiological and genetic perturbations. We used a set of rrn promoter fusion constructs in their native chromosomal positions to examine effects of chromosomal location on rrn operon expression and the same set of fusions on lambda lysogens to assay intrinsic promoter strengths independent of chromosome context. In its native chromosomal location, expression of the rrnH operon was significantly lower than expected. This effect was not attributable to weak promoter activity and was dependent on the growth medium. The rrnE operon had reduced promoter activity relative to the other ribosomal operons in minimal medium and thus appears to have abnormal growth rate regulation. The ribosomal RNA operons showed varied responses to amino acid starvation; expression of rrnD was inhibited most. There was only a slight increase in rrn transcription in response to a temperature shift (30 degrees C to 42 degrees C) and the differences between individual operons was very small. The rrnG operon showed a significantly lower response than the other ribosomal RNA operons to a depletion of the rrn transcription activator, Fis, and thus appears to have decreased Fis-mediated transactivation. Finally, the chromosomal fusion strains were used to study the effect on growth rate of inactivating each rrn operon. In fast growth conditions, loss of certain rrn operons caused subtle decreases in growth rate on complex medium.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba A., Mizobuchi K. Nucleotide sequence analysis of genes purH and purD involved in the de novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21239–21246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy S., Squires C. L., Squires C. Evidence for antitermination in Escherichia coli RRNA transcription. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.260-264.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy S., Squires C. L., Squires C. Translational coupling of the trpB and trpA genes in the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):363–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.363-367.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arps P. J., Winkler M. E. Structural analysis of the Escherichia coli K-12 hisT operon by using a kanamycin resistance cassette. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1061–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1061-1070.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
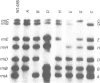
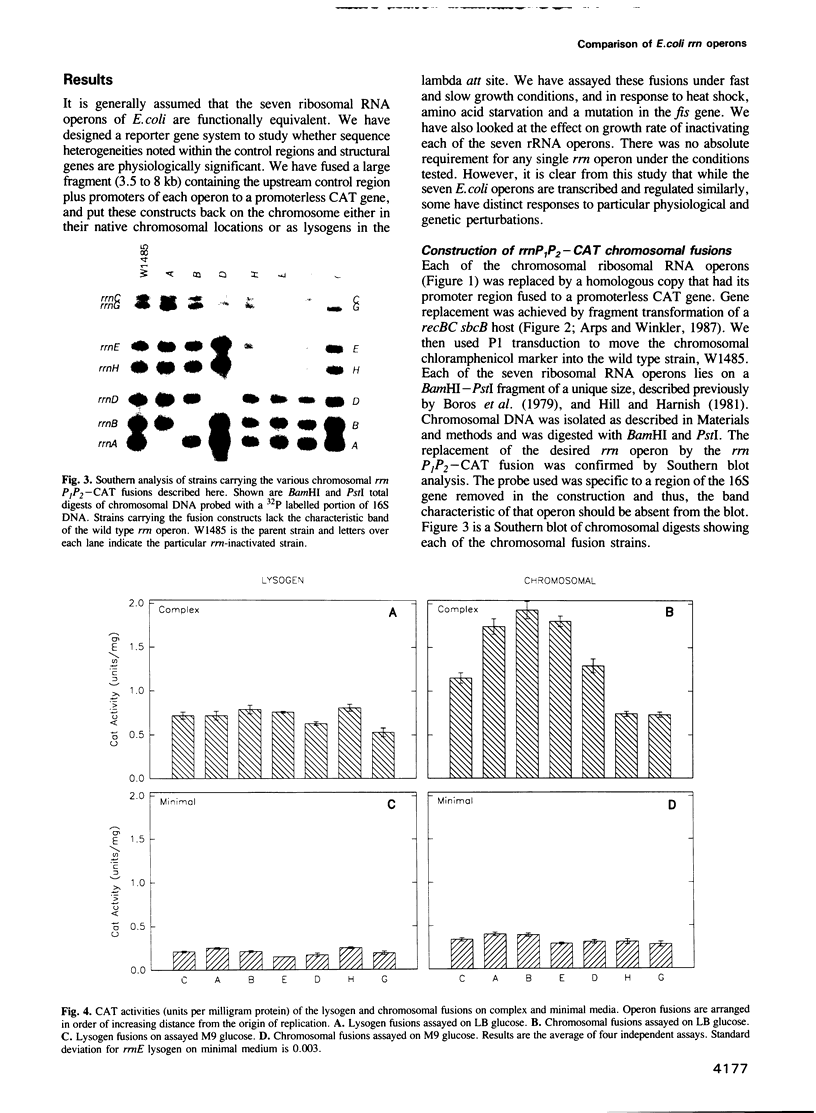
- Boros I., Kiss A., Venetianer P. Physical map of the seven ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1817–1830. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Plasmid vectors for the selection of promoters. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Ebel J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal 16-S RNA from Excherichia coli. Experimental details and cistron heterogeneities. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):399–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M., Nomura M. Chromosomal locations of the genes for rRNA in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):458–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.458-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M., Nomura M. Deletion of a ribosomal ribonucleic acid operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1077–1080. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1077-1080.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimberg J., Maguire S., Belluscio L. A simple method for the preparation of plasmid and chromosomal E. coli DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8893–8893. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., Sogin M. L., Wollett G., Hollingdale M., de la Cruz V. F., Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Structurally distinct, stage-specific ribosomes occur in Plasmodium. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):933–937. doi: 10.1126/science.3672135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Hill C. W., Squires C., Squires C. L. Loss of the spacer loop sequence from the rrnB operon in the Escherichia coli K-12 subline that bears the relA1 mutation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1235–1238. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1235-1238.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. W., Harnish B. W. Inversions between ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7069–7072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben W. E., Prasad S. M., Morgan E. A. Antitermination by both the promoter and the leader regions of an Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5073–5077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui I., Dennis P. P. Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene clusters in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner P., Arber W. Mutational analysis of a prokaryotic recombinational enhancer element with two functions. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):577–585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ball C. A., Pfeffer D., Simon M. I. Isolation of the gene encoding the Hin recombinational enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josaitis C. A., Gaal T., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Sequences upstream of the-35 hexamer of rrnB P1 affect promoter strength and upstream activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Kahmann R. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli host factor required for inversion of the G segment in bacteriophage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15673–15678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFauci G., Widom R. L., Eisner R. L., Jarvis E. D., Rudner R. Mapping of rRNA genes with integrable plasmids in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):204–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.204-214.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirmo S., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. I. Kinetic analysis of the roles of the upstream activator region and supercoiling on transcription of the rrnB P1 promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):555–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Squires C. L., Squires C. Antitermination of E. coli rRNA transcription is caused by a control region segment containing lambda nut-like sequences. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Pizer L. I. Regulation of phospholipid synthesis in Escherichia coli by guanosine tetraphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):355–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.355-366.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Ward D. F. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning with BamHI and Sau3A. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahigashi K., Inokuchi H. Nucleotide sequence between the fadB gene and the rrnA operon from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6439–6439. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaskon R. R., Wartell R. M. Sequence distributions associated with DNA curvature are found upstream of strong E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):785–796. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojiani M. V., Jakubowski H., Goldman E. Effect of variation of charged and uncharged tRNA(Trp) levels on ppGpp synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6493–6502. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6493-6502.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Thompson J. F., Newlands J. T., Gourse R. L. E.coli Fis protein activates ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3733–3742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmientos P., Sylvester J. E., Contente S., Cashel M. Differential stringent control of the tandem E. coli ribosomal RNA promoters from the rrnA operon expressed in vivo in multicopy plasmids. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1337–1346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W. F., Squires C., Squires C. L. Nucleotide sequence of the rrnG ribosomal RNA promoter region of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3303–3313. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires C. L., Pedersen S., Ross B. M., Squires C. ClpB is the Escherichia coli heat shock protein F84.1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4254–4262. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4254-4262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek H., Nilsson L., Baliko G., Bosch L. Potential binding sites of the trans-activator FIS are present upstream of all rRNA operons and of many but not all tRNA operons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom R. L., Jarvis E. D., LaFauci G., Rudner R. Instability of rRNA operons in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):605–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.605-610.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Olsen G. J. Archaebacterial phylogeny: perspectives on the urkingdoms. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Tandem promoters direct E. coli ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. Transcriptional control of the S10 ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli after a shift to higher temperature. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):140–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.140-147.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. P., Zubay G. The peculiar nature of codon usage in primates. Genet Eng (N Y) 1991;13:73–113. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3760-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Gilbert S. F., Nomura M. DNA sequences of promoter regions for rRNA operons rrnE and rrnA in E. coli. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]