Abstract
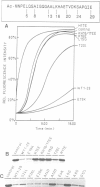
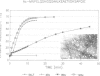
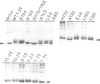
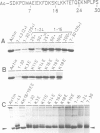
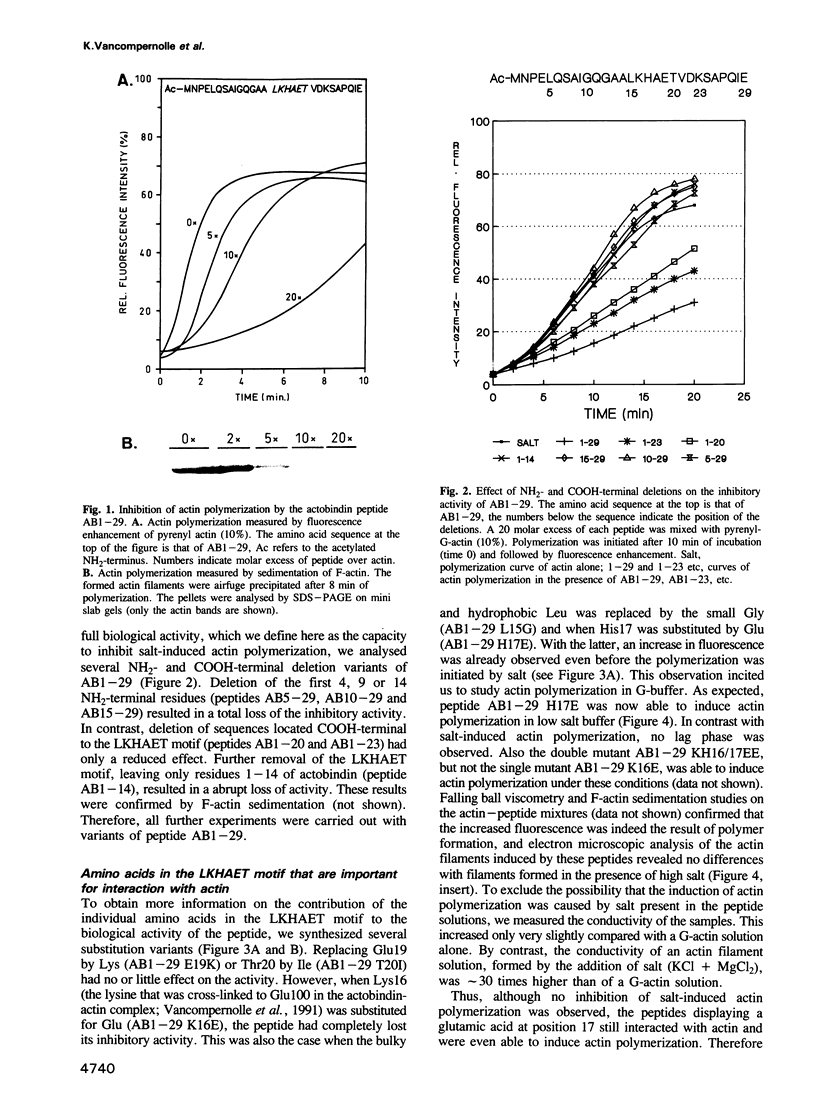
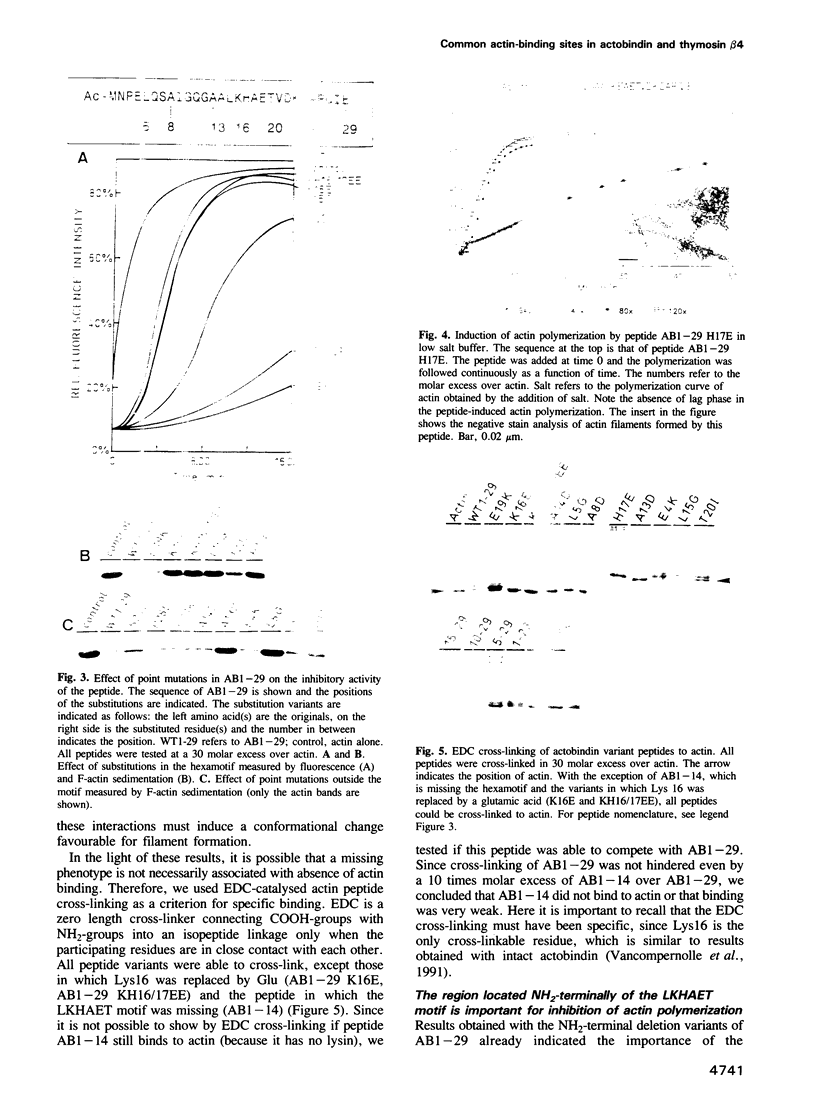
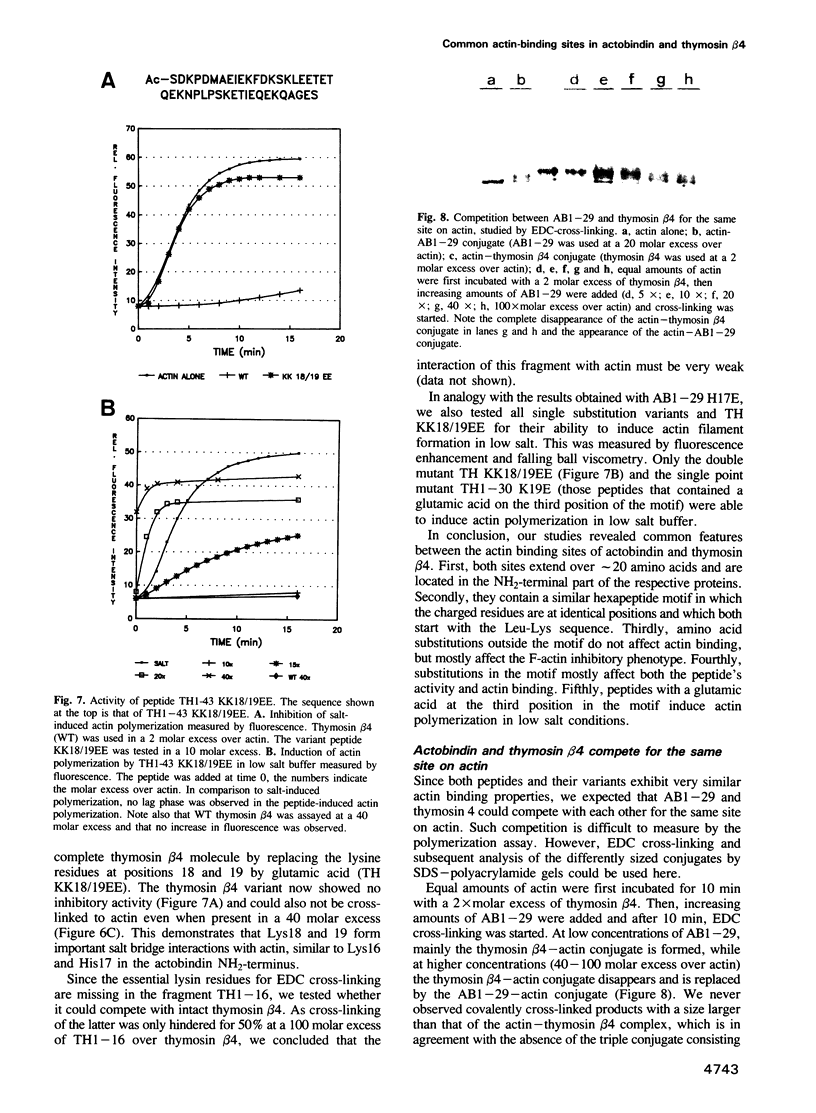
The actin binding sites of actobindin and thymosin beta 4, two small polypeptides that inhibit actin polymerization by interacting with monomeric actin, have been localized using peptide mimetics. Both sites are functionally similar and extend over 20 residues and are located in the NH2-terminus of the polypeptides. They can be dissected into two functional entities: a conserved hexapeptide motif (LKHAET or LKKTET), which forms the major contact site through electrostatic interactions with actin, and a non-conserved NH2-terminal segment preceding the motif, which exerts the inhibitory activity on actin polymerization probably by steric hindrance. The introduction of a glutamic acid at the third position in the motif, creating LKEAET or LKETET sequences, which are similar to those found in some F-actin binding proteins, converts the peptide's inhibitory phenotype into an F-actin stimulatory property. These results allow the proposal of a simple model for G- to F-actin modulation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauw G., De Loose M., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Alterations in the phenotype of plant cells studied by NH(2)-terminal amino acid-sequence analysis of proteins electroblotted from two-dimensional gel-separated total extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4806–4810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. On the mechanism of actin monomer-polymer subunit exchange at steady state. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5013–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. S., Spudich J. A. Nucleation of polar actin filament assembly by a positively charged surface. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):499–504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Imai M., Lee R., Moore P., Cook R. G., Lin W. G. Cloning and expression of a smooth muscle caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13873–13879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Sundkvist I., Markey F., Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Blum J. D., Williams R. C., Jr, Pollard T. D. Purification and characterization of actophorin, a new 15,000-dalton actin-binding protein from Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):477–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Vancompernolle K., Huet C., Goethals M., Finidori J., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. An actin-binding site containing a conserved motif of charged amino acid residues is essential for the morphogenic effect of villin. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90535-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano K. A., Khatib F. A., Hayden S. M., Daoud E. W., Adams M. E., Amorese D. A., Bernstein B. W., Bamburg J. R. Properties of purified actin depolymerizing factor from chick brain. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8931–8938. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Kwiatkowski D. J. Actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal A. A., Korn E. D. Reinvestigation of the inhibition of actin polymerization by profilin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10132–10138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambooy P. K., Korn E. D. Inhibition of an early stage of actin polymerization by actobindin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12836–12843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambooy P. K., Korn E. D. Purification and characterization of actobindin, a new actin monomer-binding protein from Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17150–17155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. G., Cote G. P., Mak A. S., Smillie L. B. Amino acid sequence of equine platelet tropomyosin. Correlation with interaction properties. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 13;156(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80511-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Hu S. K., Goldstein A. L. Complete amino acid sequence of bovine thymosin beta 4: a thymic hormone that induces terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity in thymocyte populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1162–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi I. An actin-depolymerizing protein (depactin) from starfish oocytes: properties and interaction with actin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1612–1621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S. D., Pollard T. D. Viscometric analysis of the gelation of Acanthamoeba extracts and purification of two gelation factors. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):414–428. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Iida K., Yonezawa N., Koyasu S., Yahara I., Sakai H. Cofilin is a component of intranuclear and cytoplasmic actin rods induced in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5262–5266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Muneyuki E., Maekawa S., Ohta Y., Sakai H. An actin-depolymerizing protein (destrin) from porcine kidney. Its action on F-actin containing or lacking tropomyosin. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6624–6630. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebar R. W., Miyake A., Low T. L., Goldstein A. L. Thymosin stimulates secretion of luteinizing hormone-releasing factor. Science. 1981 Nov 6;214(4521):669–671. doi: 10.1126/science.7027442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichstein E., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba profilin. A protein of low molecular weight from Acanpthamoeba castellanii that inhibits actin nucleation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6174–6179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D., Elzinga M., Nachmias V. T. Thymosin beta 4 and Fx, an actin-sequestering peptide, are indistinguishable. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4029–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. C., Goldstein A. L., Wang Y. L. Thymosin beta 4 (Fx peptide) is a potent regulator of actin polymerization in living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Wright R. W., Swingle D. M. Enhancement by N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide of water-soluble carbodiimide-mediated coupling reactions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):220–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vancompernolle K., Vandekerckhove J., Bubb M. R., Korn E. D. The interfaces of actin and Acanthamoeba actobindin. Identification of a new actin-binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15427–15431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Van Damme J., Vancompernolle K., Bubb M. R., Lambooy P. K., Korn E. D. The covalent structure of Acanthamoeba actobindin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12801–12805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Vancompernolle K. Structural relationships of actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90056-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. L., Wang L. W., Xu S. A., Lu R. C., Saavedra-Alanis V., Bryan J. Localization of the calmodulin- and the actin-binding sites of caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9166–9172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbock J., Oschkinat H., Hannappel E., Kalbacher H., Voelter W., Holak T. A. Solution conformation of thymosin beta 4: a nuclear magnetic resonance and simulated annealing study. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7814–7821. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]