Abstract
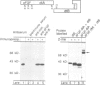
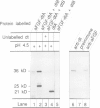
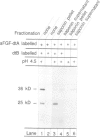
A fusion protein of acidic fibroblast growth factor and diphtheria toxin A-fragment was disulfide-linked to the toxin B-fragment. The complex bound specifically to diphtheria toxin receptors, and subsequent exposure to low pH induced the fusion protein to translocate to the cytosol. Heparin, inositol hexaphosphate and inorganic sulfate strongly increased the trypsin resistance of the growth factor part of the fusion protein, indicating tight folding, and they prevented translocation of the fusion protein to the cytosol. The data indicate that only a more disordered form of the growth factor is translocation competent.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Effect of diphtheria toxin on protein synthesis: inactivation of one of the transfer factors. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland R. A., Ji H., Halfpenny A. J., Williams R. W., Thompson K. C., Herber W. K., Thomas K. A., Bruner M. W., Ryan J. A., Marquis-Omer D. The structure of human acidic fibroblast growth factor and its interaction with heparin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Aug 15;289(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90441-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabora J. M., Sanyal G., Middaugh C. R. Effect of polyanions on the refolding of human acidic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23637–23640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont M. E., Richards F. M. The pH-dependent conformational change of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2087–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schatz G. Binding of a specific ligand inhibits import of a purified precursor protein into mitochondria. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):228–232. doi: 10.1038/322228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Cousens L. S., Weaver L. H., Matthews B. W. Three-dimensional structure of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3441–3445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Protein sorting to mitochondria: evolutionary conservations of folding and assembly. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):930–938. doi: 10.1126/science.2406905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Kato I., Hayaishi O. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis by diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4251–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Engleka K., Zhan X., Tokita Y., Forough R., Roeder D., Jackson A., Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Recovery of mitogenic activity of a growth factor mutant with a nuclear translocation sequence. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.1699274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Small G. M., Lazarow P. B. Translocation of acyl-CoA oxidase into peroxisomes requires ATP hydrolysis but not a membrane potential. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2915–2922. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Howk R., Burgess W., Ricca G. A., Chiu I. M., Ravera M. W., O'Brien S. J., Modi W. S., Maciag T., Drohan W. N. Human endothelial cell growth factor: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):541–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3523756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill S., Stenmark H., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Membrane interactions of diphtheria toxin analyzed using in vitro synthesized mutants. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2843–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Morimoto T., Rifkin D. B. Basic fibroblast growth factor released by single, isolated cells stimulates their migration in an autocrine manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11007–11011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaug J. O., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Cell-mediated reduction of the interfragment disulfide in nicked diphtheria toxin. A new system to study toxin entry at low pH. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10339–10345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaug J. O., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Low pH-induced release of diphtheria toxin A-fragment in Vero cells. Biochemical evidence for transfer to the cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2518–2525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaug J. O., Stenmark H., Olsnes S. Insertion of diphtheria toxin B-fragment into the plasma membrane at low pH. Characterization and topology of inserted regions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2652–2659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesch A., Hartmann E., Rohde K., Rubartelli A., Sitia R., Rapoport T. A. A novel pathway for secretory proteins? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90186-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan L., Warder E., McNeil P. L. Basic fibroblast growth factor is efficiently released from a cytolsolic storage site through plasma membrane disruptions of endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Moskaug J. O., Stenmark H., Sandvig K. Diphtheria toxin entry: protein translocation in the reverse direction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Sep;13(9):348–351. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Sandvig K. How protein toxins enter and kill cells. Cancer Treat Res. 1988;37:39–73. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-1083-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Stenmark H., McGill S., Hovig E., Collier R. J., Sandvig K. Formation of active diphtheria toxin in vitro based on ligated fragments of cloned mutant genes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12747–12751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega S., Schaeffer M. T., Soderman D., DiSalvo J., Linemeyer D. L., Gimenez-Gallego G., Thomas K. A. Conversion of cysteine to serine residues alters the activity, stability, and heparin dependence of acidic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5842–5846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain D., Kanwar Y. S., Blobel G. Identification of a receptor for protein import into chloroplasts and its localization to envelope contact zones. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):232–237. doi: 10.1038/331232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Rassow J., Guiard B., Söllner T., Hartl F. U., Neupert W. Energy requirements for unfolding and membrane translocation of precursor proteins during import into mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16324–16329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon L., Moll T., Vestweber D., Marshallsay B., Schatz G. Protein import into mitochondria: ATP-dependent protein translocation activity in a submitochondrial fraction enriched in membrane contact sites and specific proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2603–2616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassow J., Hartl F. U., Guiard B., Pfanner N., Neupert W. Polypeptides traverse the mitochondrial envelope in an extended state. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81469-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi K., Yanagishita M., Takeuchi Y., Aurbach G. D. Identification of heparan sulfate proteoglycan as a high affinity receptor for acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF) in a parathyroid cell line. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7270–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Entry of the toxic proteins abrin, modeccin, ricin, and diphtheria toxin into cells. I. Requirement for calcium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7495–7503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Rapid entry of nicked diphtheria toxin into cells at low pH. Characterization of the entry process and effects of low pH on the toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9068–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz P., Meyer D. I. Signal recognition particle (SRP) stabilizes the translocation-competent conformation of pre-secretory proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3553–3557. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03232.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G. 17th Sir Hans Krebs lecture. Signals guiding proteins to their correct locations in mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi E., Kan M., Xu J. M., McKeehan W. L. 16-kilodalton heparin binding (fibroblast) growth factor type one appears in a stable 40-kilodalton complex after receptor-dependent internalization. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5774–5779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerjanc I. S., Sheffield W. P., Randall S. K., Silvius J. R., Shore G. C. Import of precursor proteins into mitochondria: site of polypeptide unfolding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9444–9451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark H., Afanasiev B. N., Ariansen S., Olsnes S. Association between diphtheria toxin A- and B-fragment and their fusion proteins. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):619–625. doi: 10.1042/bj2810619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark H., Moskaug J. O., Madshus I. H., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Peptides fused to the amino-terminal end of diphtheria toxin are translocated to the cytosol. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1025–1032. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. NMR spectra and proposed structures of ribosyl-diphthamide and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10710–10716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Lemire B. D. Tight folding of a passenger protein can interfere with the targeting function of a mitochondrial presequence. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1491–1495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Blobel G. Cytosolic factor purified from Escherichia coli is necessary and sufficient for the export of a preprotein and is a homotetramer of SecB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. D., Cousens L. S., Barr P. J., Sprang S. R. Three-dimensional structure of human basic fibroblast growth factor, a structural homolog of interleukin 1 beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3446–3450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Komiya H., Chirino A., Faham S., Fox G. M., Arakawa T., Hsu B. T., Rees D. C. Three-dimensional structures of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):90–93. doi: 10.1126/science.1702556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]