Abstract
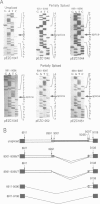
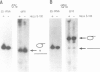
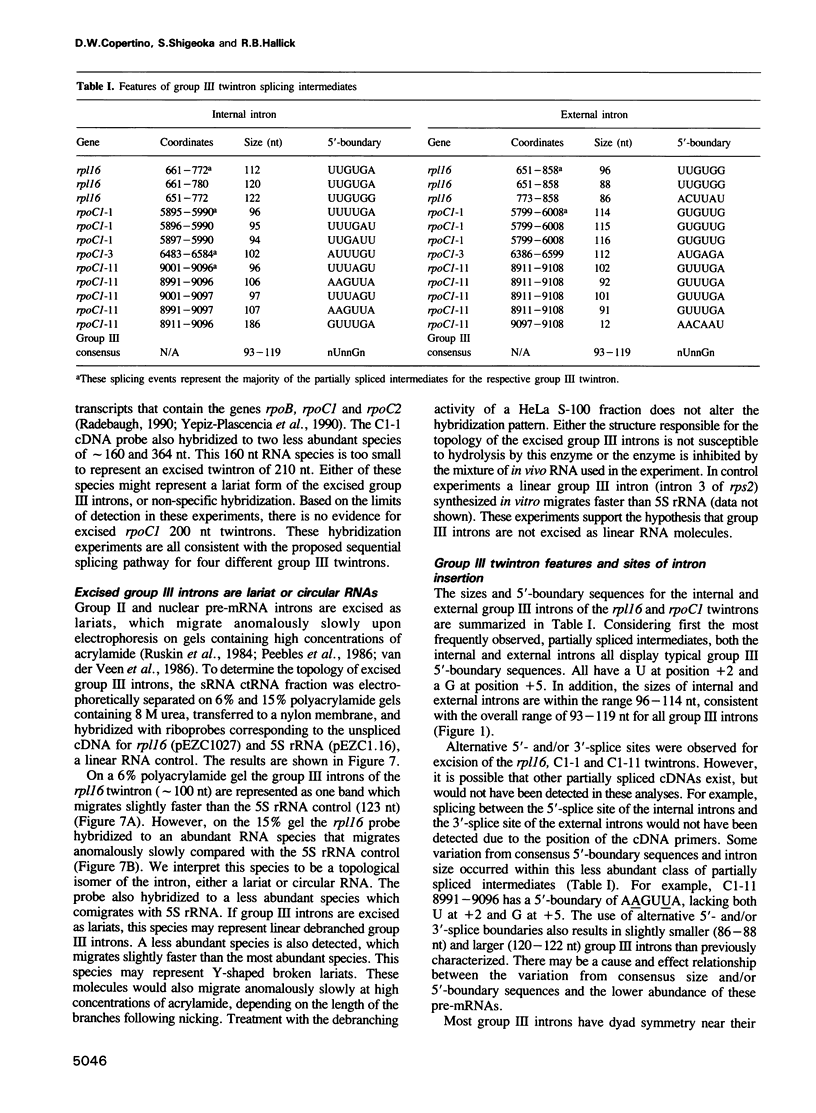
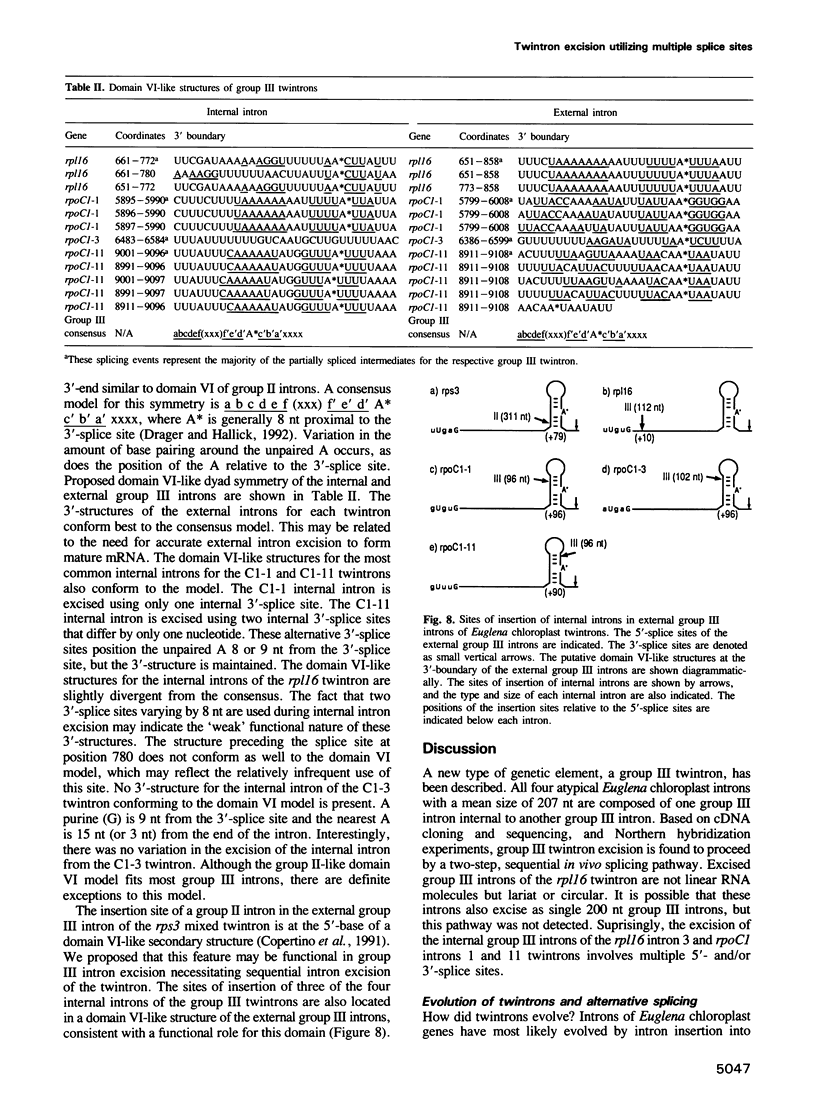
The chloroplast genes of Euglena gracilis contain more than 60 group II and 47 group III introns. Some Euglena chloroplast genes also contain twintrons, introns-within-introns. Two types of twintrons have previously been described, a group II twintron and a mixed group II/group III twintron. We report that four introns, three within the RNA polymerase subunit gene rpoC1 and one within ribosomal protein gene rpl16, with mean lengths twice typical group III introns, are a new type of twintron. The group III twintrons are composed of group III introns within other group III introns. The splicing of the twintrons was analyzed by PCR amplification, cloning and sequencing of cDNAs, and Northern hybridization. Excision of each group III twintron occurs by a two-step, sequential splicing pathway. Removal of the internal introns precedes excision of the external introns. Splicing of internal introns in three of the four group III twintrons involves multiple 5'- and/or 3'-splice sites. With two of the twintrons the proximal 5'-splice site can be spliced to an internal 3'-splice site, yielding alternative 'pseudo' fully spliced mRNAs. Excised group III introns of the rpl16 twintron are not linear RNA molecules but either lariat or circular RNAs, probably a lariat. The origins of alternative splicing and a possible evolutionary relationship between group II, group III and nuclear pre-mRNA introns are discussed.
Full text
PDF
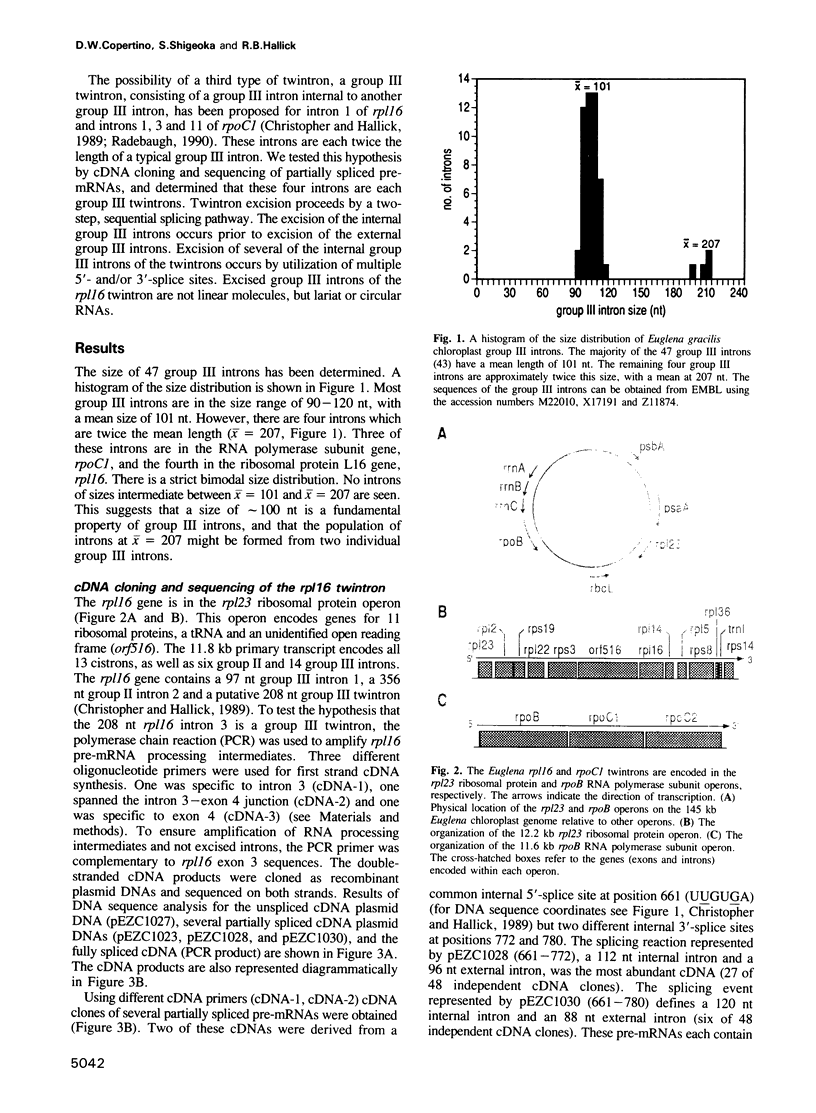




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avvedimento V. E., Vogeli G., Yamada Y., Maizel J. V., Jr, Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Correlation between splicing sites within an intron and their sequence complementarity with U1 RNA. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Splicing a spliceosomal RNA. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):14–15. doi: 10.1038/337014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. L., Pannetier C., Jaulin C., Kourilsky P. Optimal conditions for directly sequencing double-stranded PCR products with sequenase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4028–4028. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
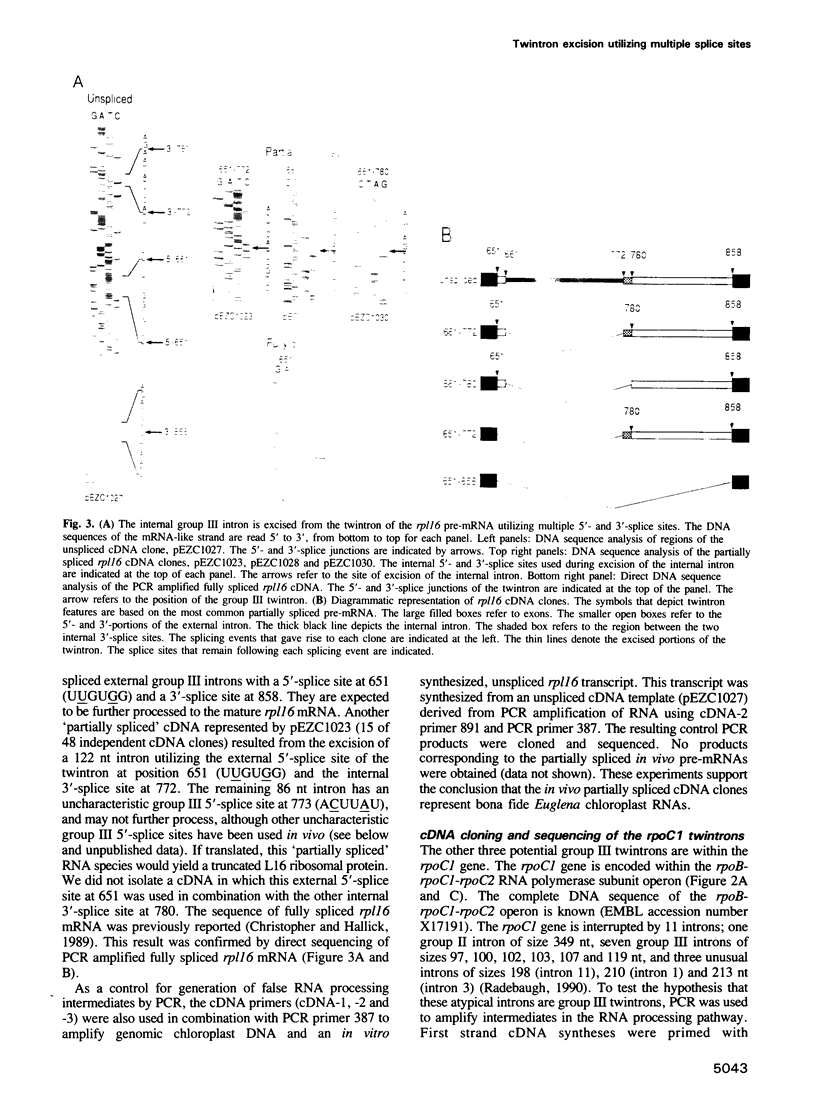
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Complex RNA maturation pathway for a chloroplast ribosomal protein operon with an internal tRNA cistron. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):659–671. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein operon: a new chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L5 and description of a novel organelle intron category designated group III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7591–7608. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copertino D. W., Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. A mixed group II/group III twintron in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein S3 gene: evidence for intron insertion during gene evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6491–6497. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copertino D. W., Hallick R. B. Group II twintron: an intron within an intron in a chloroplast cytochrome b-559 gene. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):433–442. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07965.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingrich J. C., Hallick R. B. The Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. I. Complete DNA sequence and analysis of the nine intervening sequences. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16156–16161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Choquet Y., Girard-Bascou J., Michel F., Schirmer-Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. A small chloroplast RNA may be required for trans-splicing in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90415-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B. M., Narita J. O., DeLuca-Flaherty C., Gruissem W., Rushlow K. A., Hallick R. B. Evidence for two RNA polymerase activities in Euglena gracilis chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14880–14887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Jacquesson-Breuleux N. Splice site selection and role of the lariat in a group II intron. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):415–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Base-pairing interactions involving the 5' and 3'-terminal nucleotides of group II self-splicing introns. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):437–447. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Michel F. Multiple exon-binding sites in class II self-splicing introns. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90658-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A. Self-splicing group II and nuclear pre-mRNA introns: how similar are they? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90075-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. A., Dietrich R. C., Perlman P. S. Group II intron domain 5 facilitates a trans-splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J. L., Boulanger S. C., Dib-Hajj S. D., Hebbar S. K., Perlman P. S. Group II introns deleted for multiple substructures retain self-splicing activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):1950–1958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Gingrich J. C., Stiegler G. L., Farley M. A., Delius H., Hallick R. B. Nine introns with conserved boundary sequences in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M. C., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast rpoA, rpoB, and rpoC genes specify at least three components of a chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase active in tRNA and mRNA transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14302–14307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Umesono K., Ozeki H. Comparative and functional anatomy of group II catalytic introns--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):5–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita J. O., Rushlow K. E., Hallick R. B. Characterization of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast RNA polymerase specific for ribosomal RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11194–11199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. Sixteen discrete RNA components in the cytoplasmic ribosome of Euglena gracilis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 5;215(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. "Five easy pieces". Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):663–663. doi: 10.1126/science.1948046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemeister G., Buchholz C., Hachtel W. Genes for the plastid elongation factor Tu and ribosomal protein S7 and six tRNA genes on the 73 kb DNA from Astasia longa that resembles the chloroplast DNA of Euglena. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Feb;220(3):425–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00391749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Splicing takes a holliday. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):888–889. doi: 10.1126/science.1386941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson J. K., Drager R. G., Copertino D. W., Christopher D. A., Jenkins K. P., Yepiz-Plascencia G., Hallick R. B. Intercistronic group III introns in polycistronic ribosomal protein operons of chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):183–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00282464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchy M., Schmelzer C. Restoration of the self-splicing activity of a defective group II intron by a small trans-acting RNA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90204-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yepiz-Plascencia G. M., Radebaugh C. A., Hallick R. B. The Euglena gracilis chloroplast rpoB gene. Novel gene organization and transcription of the RNA polymerase subunit operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1869–1878. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]