Abstract
In order to investigate the importance of 3-methyladenine in cellular sensitivity to chemical methylating agents we have constructed retroviral vectors for the integration and expression of the Escherichia coli tag gene in mammalian cells. The tag gene encodes 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase-1 which specifically removes 3-alkyladenines from DNA. The constructs were introduced into Chinese hamster V79 cells by liposome mediated transfection or into murine haemopoietic stem cells by cocultivation with a lipofected, virus-packaging cell line. In both cases, stable transfectants were selected for resistance to the antibiotic, G418, conferred by expression of the neo gene carried by the vector. Measurements of 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase activity in cell extracts showed an up to 10-fold increase in cell lines with stably integrated tag gene sequences. These cell lines were significantly more resistant to the cytotoxic effects of methylmethanesulfonate and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea than their parent cell lines, indicating that 3-methyladenine repair is a limiting factor in cellular resistance to these methylating agents. Furthermore, the mutation frequency induced by methylmethanesulfonate was reduced to 50% of normal by expression of 3-methyladenine I activity in the Chinese hamster cells, indicating that m3A is not only a cytotoxic but also a premutagenic lesion in mammalian cells. It is concluded that an alkylation repair gene function of a type only thought to be present in bacteria can yield a hyperresistant phenotype when transferred to mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF
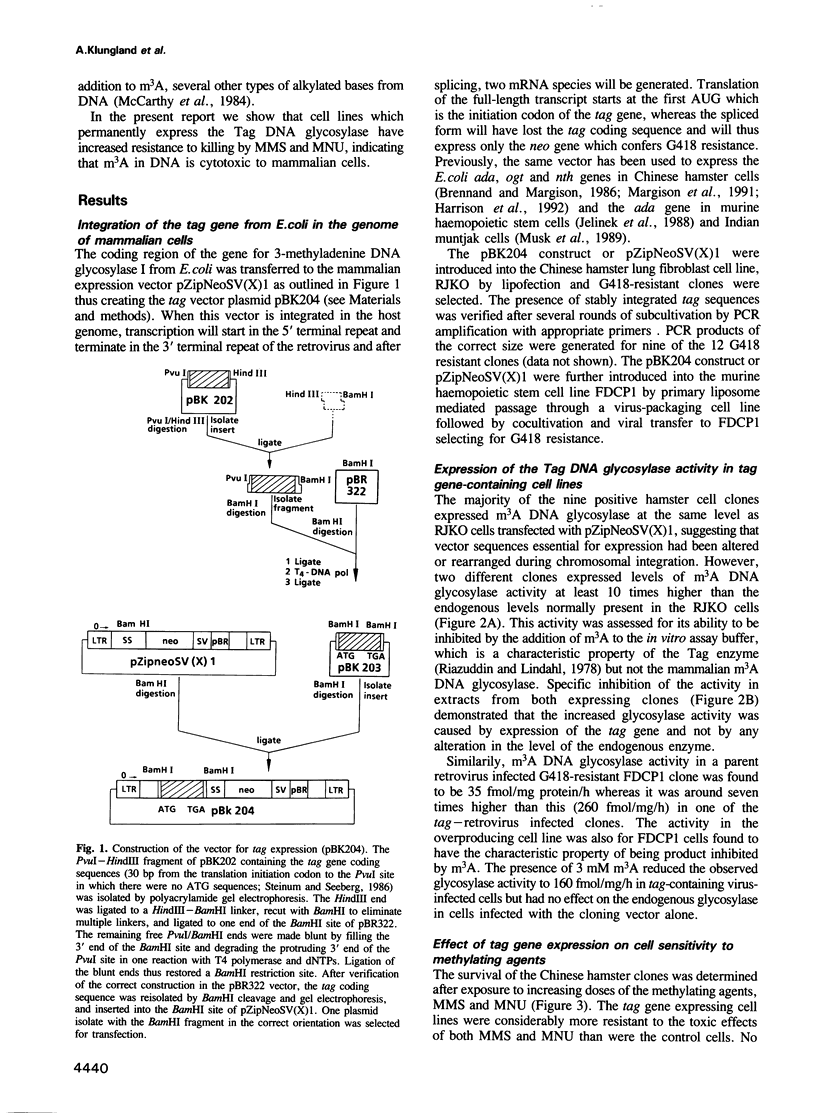
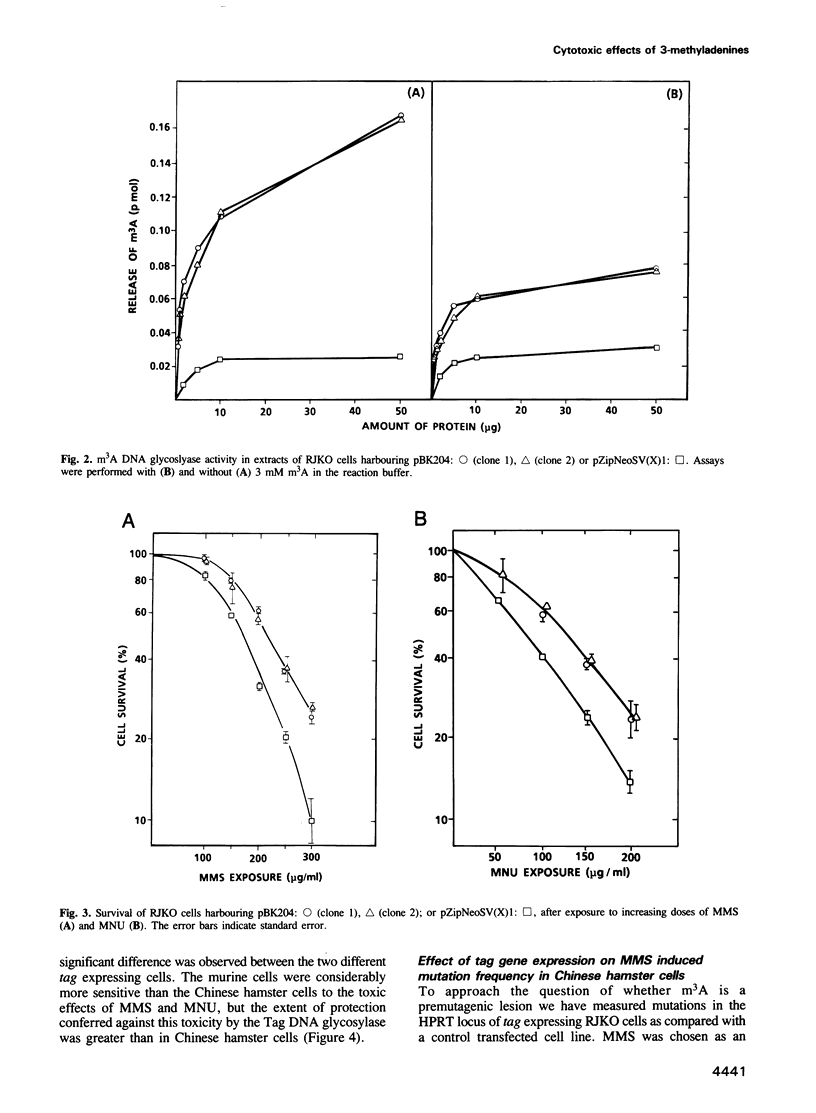
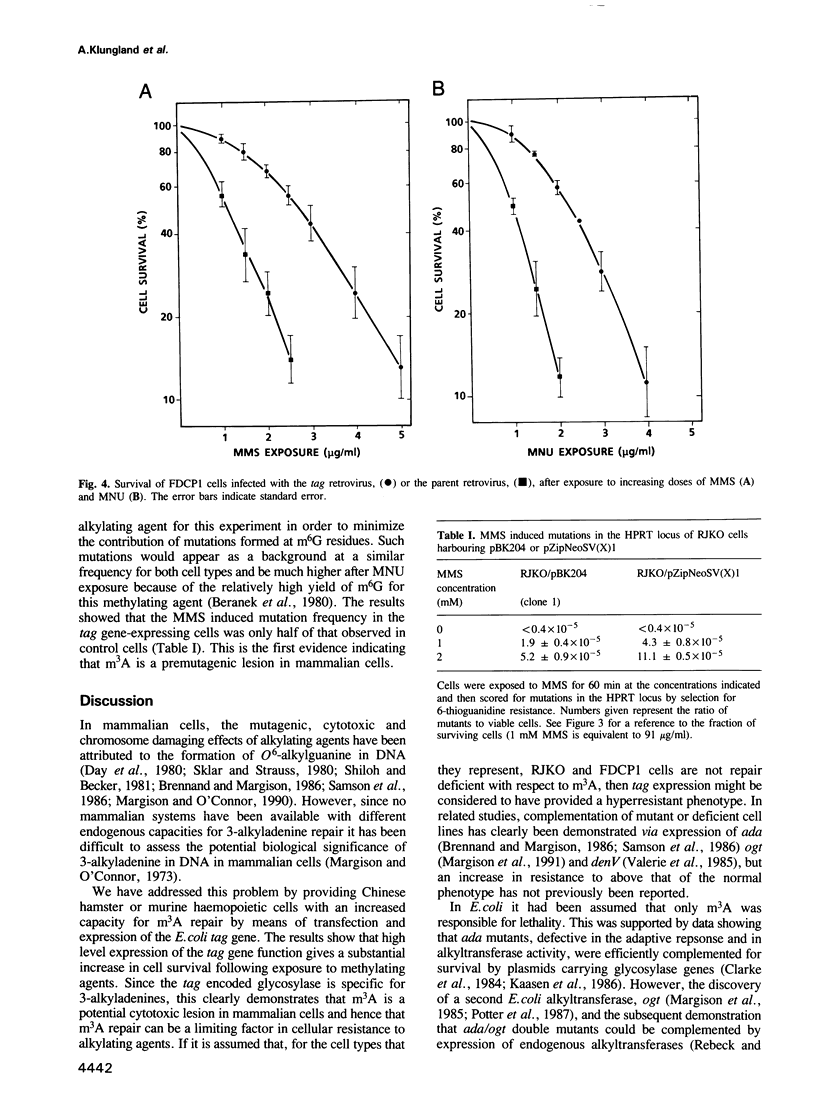


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beranek D. T., Weis C. C., Swenson D. H. A comprehensive quantitative analysis of methylated and ethylated DNA using high pressure liquid chromatography. Carcinogenesis. 1980 Jul;1(7):595–606. doi: 10.1093/carcin/1.7.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelland S., Seeberg E. Purification and characterization of 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase I from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2787–2801. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Margison G. P. Reduction of the toxicity and mutagenicity of alkylating agents in mammalian cells harboring the Escherichia coli alkyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6292–6296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti D., Ibeanu G. C., Tano K., Mitra S. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a human cDNA encoding the DNA repair protein N-methylpurine-DNA glycosylase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15710–15715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke N. D., Kvaal M., Seeberg E. Cloning of Escherichia coli genes encoding 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylases I and II. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(3):368–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00329931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. S., 3rd, Ziolkowski C. H., Scudiero D. A., Meyer S. A., Lubiniecki A. S., Girardi A. J., Galloway S. M., Bynum G. D. Defective repair of alkylated DNA by human tumour and SV40-transformed human cell strains. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):724–727. doi: 10.1038/288724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evensen G., Seeberg E. Adaptation to alkylation resistance involves the induction of a DNA glycosylase. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):773–775. doi: 10.1038/296773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Roufa D. J., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. 8-Azaguanine resistance in mammalian cells. I. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Genetics. 1972 Oct;72(2):239–252. doi: 10.1093/genetics/72.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek J., Kleibl K., Dexter T. M., Margison G. P. Transfection of murine multi-potent haemopoietic stem cells with an E. coli DNA alkyltransferase gene confers resistance to the toxic effects of alkylating agents. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jan;9(1):81–87. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaasen I., Evensen G., Seeberg E. Amplified expression of the tag+ and alkA+ genes in Escherichia coli: identification of gene products and effects on alkylation resistance. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.642-647.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Hjelmgren T., Lindahl T. Induction of a DNA glycosylase for N-methylated purines is part of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):770–773. doi: 10.1038/296770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Lindahl T., Ofsteng I., Evensen G. B., Seeberg E. Escherichia coli mutants deficient in 3-methyladenine-DNA glycosylase. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):101–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laval J. Two enzymes are required from strand incision in repair of alkylated DNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):829–832. doi: 10.1038/269829a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. New class of enzymes acting on damaged DNA. Nature. 1976 Jan 1;259(5538):64–66. doi: 10.1038/259064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveless A. Possible relevance of O-6 alkylation of deoxyguanosine to the mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of nitrosamines and nitrosamides. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):206–207. doi: 10.1038/223206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margison G. P., Cooper D. P., Brennand J. Cloning of the E. coli O6-methylguanine and methylphosphotriester methyltransferase gene using a functional DNA repair assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1939–1952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margison G. P., O'Connor P. J. Biological implications of the instability of the N-glycosidic bone of 3-methyldeoxyadenosine in DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 21;331(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margison G. P., Pegg A. E. Enzymatic release of 7-methylguanine from methylated DNA by rodent liver extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):861–865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy T. V., Karran P., Lindahl T. Inducible repair of O-alkylated DNA pyrimidines in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):545–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J. R., Ludlum D. B., Renard A., Verly W. G. Repair of O6-ethylguanine in DNA by a chromatin fraction from rat liver: transfer of the ethyl group to an acceptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6766–6770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musk S. R., Hatton D. H., Bouffler S. D., Margison G. P., Johnson R. T. Molecular mechanisms of alkylation sensitivity in Indian muntjac cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Jul;10(7):1299–1306. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.7.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold R. F., Warren W., Medcalf A. S., Amos J. Mutagenicity of carcinogenic methylating agents is associated with a specific DNA modification. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):596–599. doi: 10.1038/283596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor T. R., Laval F. Isolation and structure of a cDNA expressing a mammalian 3-methyladenine-DNA glycosylase. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3337–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., Hsie A. W. Chemical mutagenesis of mammalian cells can be quantified. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):815–817. doi: 10.1038/269815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson M., Lindahl T. Repair of alkylated DNA in Escherichia coli. Methyl group transfer from O6-methylguanine to a protein cysteine residue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10569–10571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter P. M., Wilkinson M. C., Fitton J., Carr F. J., Brennand J., Cooper D. P., Margison G. P. Characterisation and nucleotide sequence of ogt, the O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9177–9193. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck G. W., Samson L. Increased spontaneous mutation and alkylation sensitivity of Escherichia coli strains lacking the ogt O6-methylguanine DNA repair methyltransferase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2068–2076. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2068-2076.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riazuddin S., Lindahl T. Properties of 3-methyladenine-DNA glycosylase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2110–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Derfler B., Waldstein E. A. Suppression of human DNA alkylation-repair defects by Escherichia coli DNA-repair genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5607–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiloh Y., Becker Y. Kinetics of O6-methylguanine repair in human normal and ataxia telangiectasia cell lines and correlation of repair capacity with cellular sensitivity to methylating agents. Cancer Res. 1981 Dec;41(12 Pt 1):5114–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. All oxygens in nucleic acids react with carcinogenic ethylating agents. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):333–339. doi: 10.1038/264333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Brent T. P. Human lymphoblasts contain DNA glycosylase activity excising N-3 and N-7 methyl and ethyl purines but not O6-alkylguanines or 1-alkyladenines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):856–860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar R., Strauss B. Removal of O6-methylguanine from DNA of normal and xeroderma pigmentosum-derived lymphoblastoid lines. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):417–420. doi: 10.1038/289417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooncer E., Heyworth C. M., Dunn A., Dexter T. M. Self-renewal and differentiation of interleukin-3-dependent multipotent stem cells are modulated by stromal cells and serum factors. Differentiation. 1986;31(2):111–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinum A. L., Seeberg E. Nucleotide sequence of the tag gene from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3763–3772. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Nakamura T., Sekiguchi M. Roles of two types of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferases in DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1991 Jan;254(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90038-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Yang C. H., Goldthwait D. A. Two DNA glycosylases in Escherichia coli which release primarily 3-methyladenine. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1162–1169. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerie K., de Riel J. K., Henderson E. E. Genetic complementation of UV-induced DNA repair in Chinese hamster ovary cells by the denV gene of phage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7656–7660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



