Abstract
Ascobolus immersus artificial gene repeats were shown previously to be subject premeiotically to both cytosine methylation and inactivation. We studied sexual progenies of strains harbouring two wild type copies of the endogenous met2 gene lying either in tandem array or at ectopic unlinked positions, by (i) investigating the methylation status, (ii) searching for mutations and (iii) analysing the inheritance of inactivation both in mitotic and sexual offspring. 100% of the 'tandem' progeny and 64% of the 'ectopic' progeny had methylated repeats and displayed gene inactivation. Similar methylation patterns involving all or most of the cytosine residues within the repeats were observed in both arrangements. The inactivated met2 copies were totally devoid of mutation, as deduced from: (i) extensive restriction site analysis and DNA sequencing; (ii) the finding that all the Met- derivatives tested reverted to prototrophy in selective conditions; and (iii) the finding that an inactivated copy of met2 stripped of its methylation through amplification in Escherichia coli regained activity when reintroduced in A.immersus. In the absence of selection, gene silencing and methylation were faithfully maintained through mitotic divisions and through five successive sexual cycles. Altogether, these data show the epimutational nature of this methylation induced premeiotically (MIP) process.
Full text
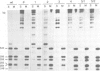
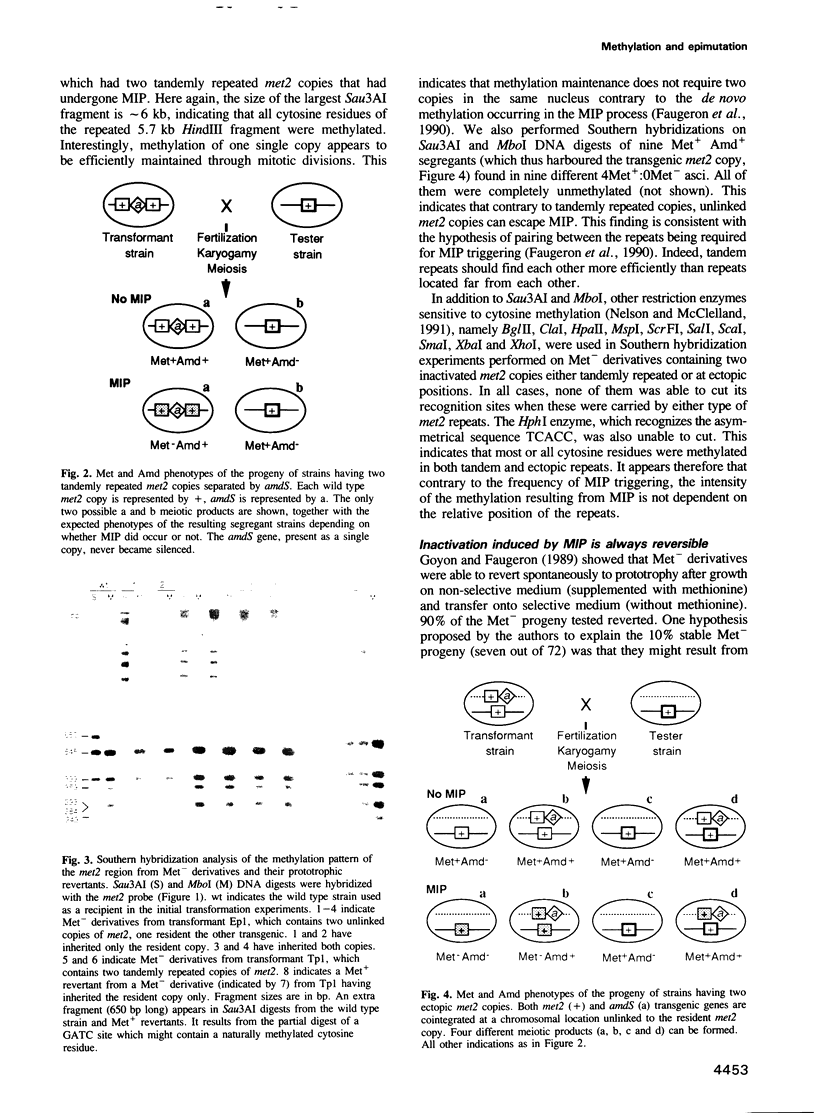
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to study eukaryotic DNA methylation: II. The symmetry of methylated sites supports semi-conservative copying of the methylation pattern. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambareri E. B., Jensen B. C., Schabtach E., Selker E. U. Repeat-induced G-C to A-T mutations in Neurospora. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1571–1575. doi: 10.1126/science.2544994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambareri E. B., Singer M. J., Selker E. U. Recurrence of repeat-induced point mutation (RIP) in Neurospora crassa. Genetics. 1991 Apr;127(4):699–710. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faugeron G., Goyon C., Grégoire A. Stable allele replacement and unstable non-homologous integration events during transformation of Ascobolus immersus. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faugeron G., Rhounim L., Rossignol J. L. How does the cell count the number of ectopic copies of a gene in the premeiotic inactivation process acting in Ascobolus immersus? Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):585–591. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V. About maize transposable elements and development. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90891-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fincham J. R. Generation of new functional mutant alleles by premeiotic disruption of the Neurospora crassa am gene. Curr Genet. 1990 Dec;18(5):441–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00309914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyon C., Faugeron G., Rossignol J. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the met2 gene from Ascobolus immersus. Gene. 1988 Mar 31;63(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90533-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyon C., Faugeron G. Targeted transformation of Ascobolus immersus and de novo methylation of the resulting duplicated DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2818–2827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Cedar H., Razin A. Substrate and sequence specificity of a eukaryotic DNA methylase. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):620–622. doi: 10.1038/295620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Mutations and epimutations in mammalian cells. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep-Oct;250(1-2):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90192-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Corrick C. M., King J. A. Isolation of genomic clones containing the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and their use in the analysis of structural and regulatory mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1430–1439. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. A., Holliday R. Azacytidine-induced reactivation of a DNA repair gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2944–2949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Taylor S. M. Cellular differentiation, cytidine analogs and DNA methylation. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. Altered gene expression in plants due to trans interactions between homologous genes. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Dec;8(12):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90220-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kricker M. C., Drake J. W., Radman M. Duplication-targeted DNA methylation and mutagenesis in the evolution of eukaryotic chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1075–1079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange C., Jugel A., Walter J., Noyer-Weidner M., Trautner T. A. 'Pseudo' domains in phage-encoded DNA methyltransferases. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):645–648. doi: 10.1038/352645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., McClelland M. Site-specific methylation: effect on DNA modification methyltransferases and restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2045–2071. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Cambareri E. B., Jensen B. C., Haack K. R. Rearrangement of duplicated DNA in specialized cells of Neurospora. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U. DNA methylation and chromatin structure: a view from below. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90193-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Garrett P. W. DNA sequence duplications trigger gene inactivation in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6870–6874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Jensen B. C., Richardson G. A. A portable signal causing faithful DNA methylation de novo in Neurospora crassa. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):48–53. doi: 10.1126/science.2958937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U. Premeiotic instability of repeated sequences in Neurospora crassa. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:579–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. S., Kan J. L., Baker D. J., Kaplan B. E., Dembek P. Recognition of unusual DNA structures by human DNA (cytosine-5)methyltransferase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 5;217(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90609-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke K., Rauhut E., Noyer-Weidner M., Lauster R., Pawlek B., Behrens B., Trautner T. A. Sequential order of target-recognizing domains in multispecific DNA-methyltransferases. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2601–2609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Crowther P. J., Doherty J., Jefferson S., DeCruz E., Noyer-Weidner M., Smith S. S., Michael M. Z., Graham M. W. Quantitative evaluation of Escherichia coli host strains for tolerance to cytosine methylation in plasmid and phage recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3469–3478. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]