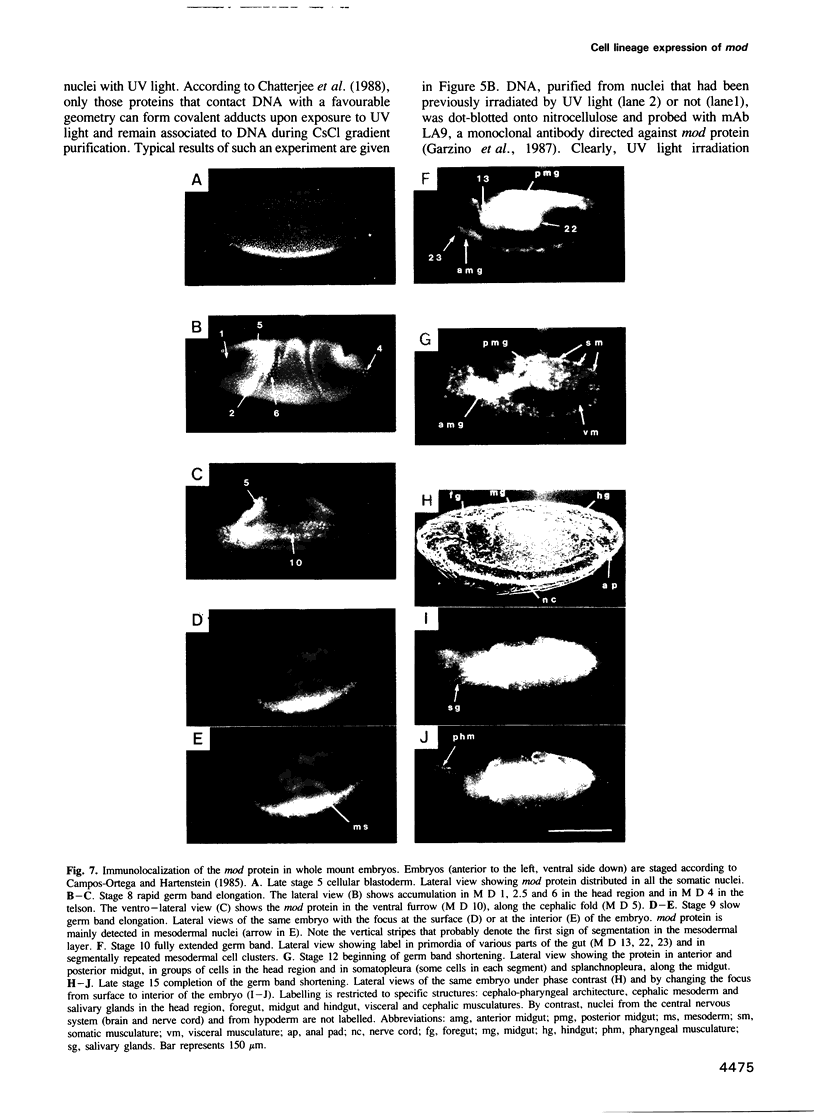
Abstract
Variegation in Drosophila is a manifest illustration of the important role played by chromatin structure in gene expression. We have isolated mutants of modulo (mod) and shown that this gene is a dominant suppressor of variegation. Null mutants are recessive lethal with a melanotic tumour phenotype. The mod protein directly binds DNA, which indicates that it may serve to anchor multimeric complexes promoting chromatin compaction and silencing. Using a specific monoclonal antibody we examined by immunocytochemistry the accumulation pattern of mod protein during embryogenesis. The protein is first detected before the blastoderm cellularization in all somatic nuclei, precisely when pericentromeric heterochromatin becomes visible. After the first cell division, mod protein is expressed in lineages of specific embryonic primordia. Based on its dominant phenotype, expression pattern and DNA-binding activity of its product, we propose that mod regulates chromatin structure and activity in specific cell lineages.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonifer C., Hecht A., Saueressig H., Winter D. M., Sippel A. E. Dynamic chromatin: the regulatory domain organization of eukaryotic gene loci. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Oct;47(2):99–108. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Bruner M., Flint S. J., Harter M. L. DNA-binding properties of an adenovirus 289R E1A protein. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):835–841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C. Position effect variegation in Drosophila: towards a genetics of chromatin assembly. Bioessays. 1989 Jul;11(1):14–17. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E., Alberts B. M. Reversible chromosome condensation induced in Drosophila embryos by anoxia: visualization of interphase nuclear organization. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1623–1636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E. Mitotic domains reveal early commitment of cells in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1989 Sep;107(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M., Glover D. M., Saumweber H. Nuclear antigens follow different pathways into daughter nuclei during mitosis in early Drosophila embryos. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jun;82:155–172. doi: 10.1242/jcs.82.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M. The maternally expressed Drosophila gene encoding the chromatin-binding protein BJ1 is a homolog of the vertebrate gene Regulator of Chromatin Condensation, RCC1. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1225–1236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzino V., Berenger H., Pradel J. Expression of laminin and of a laminin-related antigen during early development of Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1989 May;106(1):17–27. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzino V., Moretti C., Pradel J. Nuclear antigens differentially expressed during early development of Drosophila melanogaster. Biol Cell. 1987;61(1-2):5–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1987.tb00563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Lis J. T. In vivo interactions of RNA polymerase II with genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2009–2018. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Histone function in transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:643–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Nucleosomes: regulators of transcription. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):395–400. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90299-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyurkovics H., Gausz J., Kummer J., Karch F. A new homeotic mutation in the Drosophila bithorax complex removes a boundary separating two domains of regulation. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2579–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G. Genomic imprinting: review and relevance to human diseases. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):857–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Ruddell A., Sinclair D., Grigliatti T. Chromosomal structure is altered by mutations that suppress or enhance position effect variegation. Chromosoma. 1990 Oct;99(6):391–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01726690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Position-effect variegation after 60 years. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):422–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90304-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Seirafi A., Hinton J. C., Sidebotham J. M., Waddell L., Pavitt G. D., Owen-Hughes T., Spassky A., Buc H., Higgins C. F. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90458-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irminger-Finger I., Laymon R. A., Goldstein L. S. Analysis of the primary sequence and microtubule-binding region of the Drosophila 205K MAP. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2563–2572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James T. C., Eissenberg J. C., Craig C., Dietrich V., Hobson A., Elgin S. C. Distribution patterns of HP1, a heterochromatin-associated nonhistone chromosomal protein of Drosophila. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;50(1):170–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James T. C., Elgin S. C. Identification of a nonhistone chromosomal protein associated with heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster and its gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3862–3872. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Schedl P. A position-effect assay for boundaries of higher order chromosomal domains. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90318-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejci E., Garzino V., Mary C., Bennani N., Pradel J. Modulo, a new maternally expressed Drosophila gene encodes a DNA-binding protein with distinct acidic and basic regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8101–8115. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D. Proposed genetic basis of Huntington's disease. Trends Genet. 1990 Aug;6(8):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90206-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke J., Kotarski M. A., Tartof K. D. Dosage-dependent modifiers of position effect variegation in Drosophila and a mass action model that explains their effect. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):181–198. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Sedat J. Localization of antigenic determinants in whole Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscatelli F., Lena D., Mettei M. G., Fontes M. A male with two contiguous inactivation centers on a single X chromosome: study of X inactivation and XIST expression. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 May;1(2):115–119. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paro R., Hogness D. S. The Polycomb protein shares a homologous domain with a heterochromatin-associated protein of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):263–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paro R. Imprinting a determined state into the chromatin of Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90303-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A., Doshen J., Tanaka E., Goldstein L. S. Genetic analysis of a Drosophila microtubule-associated protein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):377–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V. Transvection and long-distance gene regulation. Bioessays. 1990 Sep;12(9):409–414. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploton D., Thiry M., Menager M., Lepoint A., Adnet J. J., Goessens G. Behaviour of nucleolus during mitosis. A comparative ultrastructural study of various cancerous cell lines using the Ag-NOR staining procedure. Chromosoma. 1987;95(2):95–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00332182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter G., Giarre M., Farah J., Gausz J., Spierer A., Spierer P. Dependence of position-effect variegation in Drosophila on dose of a gene encoding an unusual zinc-finger protein. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):219–223. doi: 10.1038/344219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Pfeifer G. P. X-chromosome inactivation and cell memory. Trends Genet. 1992 May;8(5):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90219-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C. Parental imprinting of genes. Sci Am. 1990 Oct;263(4):52–60. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1090-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva C. M., Tully D. B., Petch L. A., Jewell C. M., Cidlowski J. A. Application of a protein-blotting procedure to the study of human glucocorticoid receptor interactions with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1744–1748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P. B., Miller J. R., Pearce J., Kothary R., Burton R. D., Paro R., James T. C., Gaunt S. J. A sequence motif found in a Drosophila heterochromatin protein is conserved in animals and plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):789–794. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Karpen G. H. Sixty years of mystery. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):779–784. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D., Bishop C., Jones M., Hobbs C. A., Locke J. Towards an understanding of position effect variegation. Dev Genet. 1989;10(3):162–176. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D., Bremer M. Mechanisms for the construction and developmental control of heterochromatin formation and imprinted chromosome domains. Dev Suppl. 1990:35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. L., Johnson T. K., Denell R. E. Lethal(1) aberrant immune response mutations leading to melanotic tumor formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genet. 1991;12(3):173–187. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Activating chromatin. Curr Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):366–368. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. T., Goldberg M. L. The Drosophila zeste gene and transvection. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wustmann G., Szidonya J., Taubert H., Reuter G. The genetics of position-effect variegation modifying loci in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):520–527. doi: 10.1007/BF02464926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink B., Engström Y., Gehring W. J., Paro R. Direct interaction of the Polycomb protein with Antennapedia regulatory sequences in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):153–162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink B., Paro R. In vivo binding pattern of a trans-regulator of homoeotic genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):468–471. doi: 10.1038/337468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]