Abstract
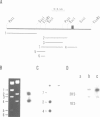
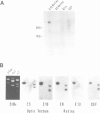
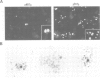
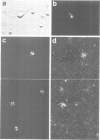
A transient transfection assay has been developed to analyse promoter activity in neuronal cells freshly dissociated from the chick central nervous system. The assay enabled us to identify cis-acting regulatory elements within the 5'-flanking region of the alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene. In differentiated retina, regulatory elements direct reporter gene expression to a small subset of neurons which has been identified as ganglion cells, i.e. to the population of neurons in which alpha 7 transcripts were localized by in situ hybridization. However, these promoter elements exhibit ubiquitous activity in undifferentiated neural cells and in mesodermal stem cells. Our study supports the idea that alpha 7 regulatory elements acquire their neuronal specificity in the course of embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballivet M., Nef P., Couturier S., Rungger D., Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Cooper E. Electrophysiology of a chick neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes after cDNA injection. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand D., Ballivet M., Rungger D. Activation and blocking of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor reconstituted in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1993–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Evans K., Goldman D., Martin G., Treco D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a possible neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):368–374. doi: 10.1038/319368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Duvoisin R. M., Connolly J. G., Wada E., Jensen A., Gardner P. D., Ballivet M., Deneris E. S., McKinnon D. Alpha 3, alpha 5, and beta 4: three members of the rat neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-related gene family form a gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4472–4482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. T., Jacob M. H., Couturier S., Ballivet M., Berg D. K. Expression and regulation of neuronal acetylcholine receptor mRNA in chick ciliary ganglia. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):495–502. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier S., Bertrand D., Matter J. M., Hernandez M. C., Bertrand S., Millar N., Valera S., Barkas T., Ballivet M. A neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit (alpha 7) is developmentally regulated and forms a homo-oligomeric channel blocked by alpha-BTX. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):847–856. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90344-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier S., Erkman L., Valera S., Rungger D., Bertrand S., Boulter J., Ballivet M., Bertrand D. Alpha 5, alpha 3, and non-alpha 3. Three clustered avian genes encoding neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-related subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17560–17567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Brownlee G. G. Disruption of a C/EBP binding site in the factor IX promoter is associated with haemophilia B. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):444–446. doi: 10.1038/345444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daubas P., Devillers-Thiéry A., Geoffroy B., Martinez S., Bessis A., Changeux J. P. Differential expression of the neuronal acetylcholine receptor alpha 2 subunit gene during chick brain development. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90032-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneris E. S., Boulter J., Swanson L. W., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Beta 3: a new member of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family is expressed in brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6268–6272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneris E. S., Connolly J., Boulter J., Wada E., Wada K., Swanson L. W., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Primary structure and expression of beta 2: a novel subunit of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin M. W. The inner plexiform layer of the vertebrate retina: a quantitative and comparative electron microscopic analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Dec;140(4):479–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.901400406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvoisin R. M., Deneris E. S., Patrick J., Heinemann S. The functional diversity of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is increased by a novel subunit: beta 4. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D., Keshet I., Shani M., Levine A., Razin A., Cedar H. Demethylation of CpG islands in embryonic cells. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):239–241. doi: 10.1038/351239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Deneris E., Luyten W., Kochhar A., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Members of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family are expressed in different regions of the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):965–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90705-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henley J. M., Lindstrom J. M., Oswald R. E. Acetylcholine receptor synthesis in retina and transport to optic tectum in goldfish. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1627–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.3715468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt C. E., Garlick N., Cornel E. Lipofection of cDNAs in the embryonic vertebrate central nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90095-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg K. E., Meyer G. E. Cloning of a putative neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit. J Neurochem. 1989 Mar;52(3):988–991. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb02553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapur R. P., Hoyle G. W., Mercer E. H., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Some neuronal cell populations express human dopamine beta-hydroxylase-lacZ transgenes transiently during embryonic development. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):717–727. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L. C., Burkhalter A., Dreyer W. J. Fluorescent latex microspheres as a retrograde neuronal marker for in vivo and in vitro studies of visual cortex. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):498–500. doi: 10.1038/310498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail J. H., Cowan W. M. The development of the chick optic tectum. I. Normal morphology and cytoarchitectonic development. Brain Res. 1971 May 21;28(3):391–419. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail J. H., Cowan W. M. The development of the chick optic tectum. II. Autoradiographic studies. Brain Res. 1971 May 21;28(3):421–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Tauck D. L. Voltage-dependent conductances of solitary ganglion cells dissociated from the rat retina. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:361–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masland R. H., Mills J. W. Autoradiographic identification of acetylcholine in the rabbit retina. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):159–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter J. M., Matter-Sadzinski L., Ballivet M. Expression of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes in the developing chick visual system. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoon S. C. Evidence for shifting connections during development of the chick retinotectal projection. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2570–2580. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Oneyser C., Alliod C., Couturier S., Ballivet M. Genes expressed in the brain define three distinct neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):595–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prada Carmen, Puga José, Pérez-Méndez Luisa, López Rosario, Ramírez Galo. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Neurogenesis in the Chick Retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;3(6):559–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E. R., Cohen J., Lindsay R., Noble M. Two types of astrocytes in cultures of developing rat white matter: differences in morphology, surface gangliosides, and growth characteristics. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1289–1300. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager G. H. Development of the retinotectal projection in the chicken. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1980;63:I-VIII, 1-90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B., Pike S. H., Nadel D. B., Lindstrom J. M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-like molecules in the retina, retinotectal pathway, and optic tectum of the frog. J Neurosci. 1989 Feb;9(2):565–573. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-02-00565.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. Biochemistry of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the vertebrate brain. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1988;30:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepfer R., Conroy W. G., Whiting P., Gore M., Lindstrom J. Brain alpha-bungarotoxin binding protein cDNAs and MAbs reveal subtypes of this branch of the ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamily. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90031-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepfer R., Whiting P., Esch F., Blacher R., Shimasaki S., Lindstrom J. cDNA clones coding for the structural subunit of a chicken brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatz C. J. Impulse activity and the patterning of connections during CNS development. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):745–756. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90333-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira A. W., Millar T. J., Ishimoto I., Epstein M. L., Johnson C. D., Dahl J. L., Morgan I. G. Localization of choline acetyltransferase-like immunoreactivity in the embryonic chick retina. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jun 22;260(4):526–538. doi: 10.1002/cne.902600406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Chen W., Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Oettinger M. A. Constitutive and coordinately regulated transcription of yeast genes: promoter elements, positive and negative regulatory sites, and DNA binding proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:489–503. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel Z., Nirenberg M. Localization of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis in retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada E., Wada K., Boulter J., Deneris E., Heinemann S., Patrick J., Swanson L. W. Distribution of alpha 2, alpha 3, alpha 4, and beta 2 neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit mRNAs in the central nervous system: a hybridization histochemical study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jun 8;284(2):314–335. doi: 10.1002/cne.902840212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Ballivet M., Boulter J., Connolly J., Wada E., Deneris E. S., Swanson L. W., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Functional expression of a new pharmacological subtype of brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):330–334. doi: 10.1126/science.2832952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. K., Schmidt J. Receptors for alpha-bungarotoxin in the developing visual system of the chick. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):524–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazulla S., Schmidt J. Two types of receptors for alpha-bungarotoxin in the synaptic layers of the pigeon retina. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 9;138(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]