Abstract
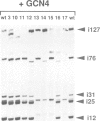
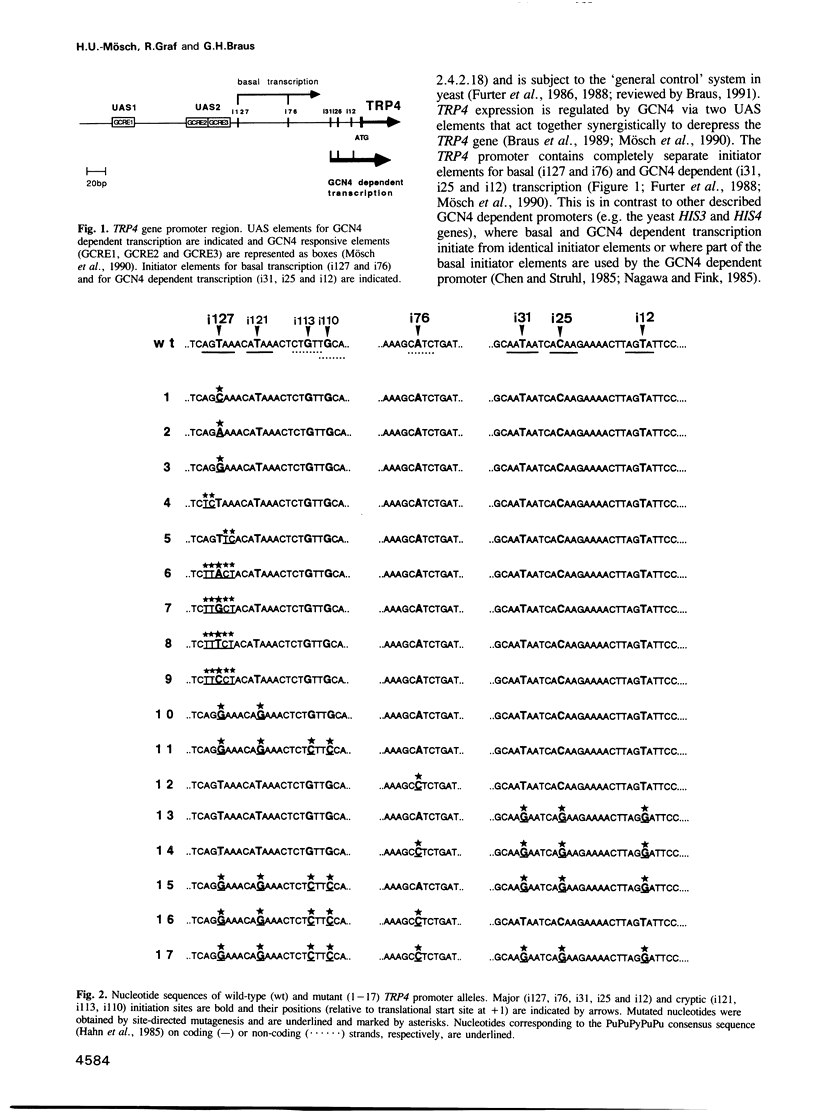
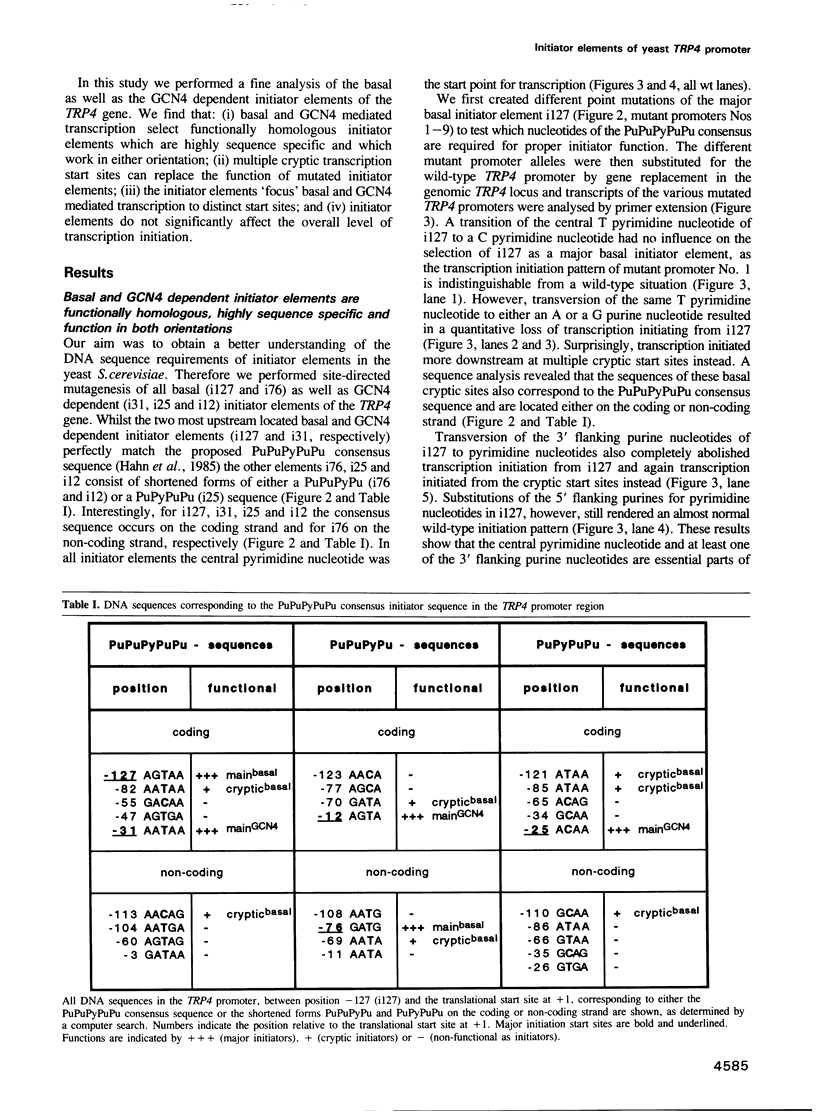
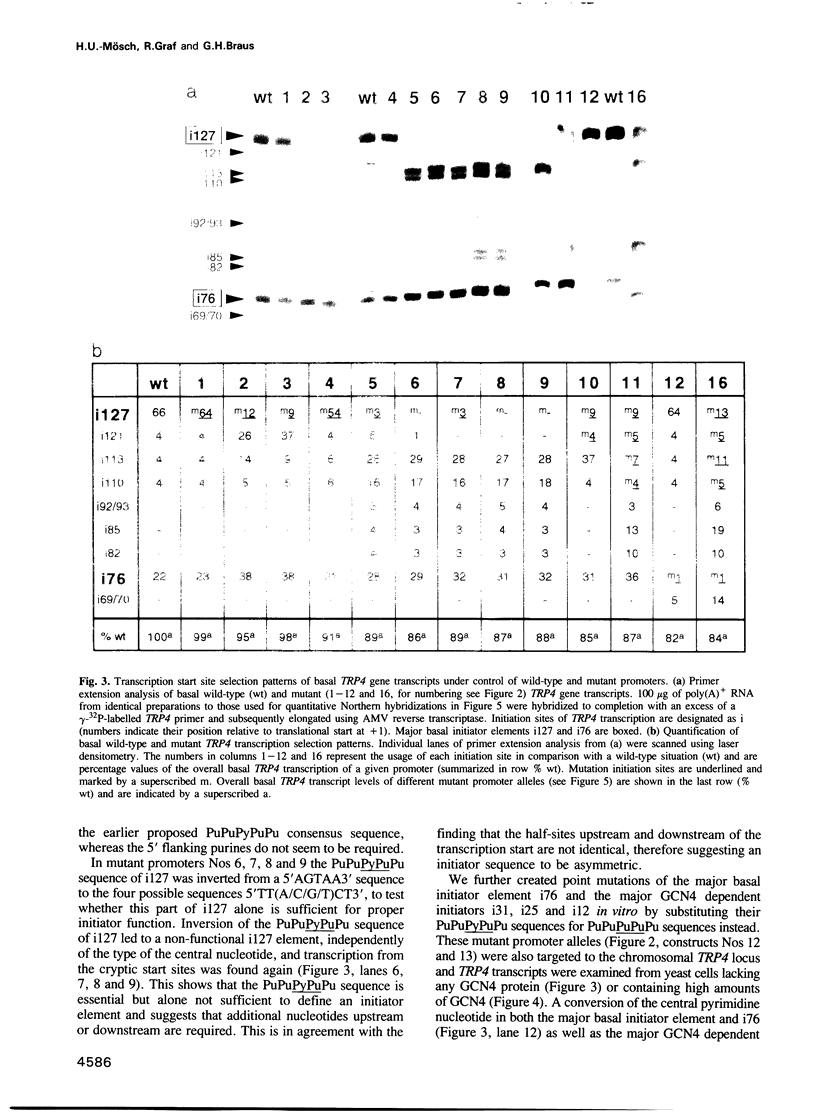
Transcription from the yeast TRP4 promoter initiates at two basal (i127 and i76) and three GCN4 dependent (i31, i25 and i12) initiator elements. All of these elements contain not more than one deviation from the earlier proposed initiator consensus sequence PuPuPyPuPu, a pyrimidine nucleotide flanked on either side by two purine nucleotides. A point mutation analysis of these elements in various combinations was performed and revealed that the central pyrimidine nucleotide and at least one of the 3' flanking purine nucleotides of the PuPuPyPuPu consensus sequence are essential but alone not sufficient to define a functional initiator element. Multiple cryptic transcription start sites, which function independently whether they are located on the coding or the non-coding strand, can replace the function of mutated initiator elements and therefore the overall level of transcription initiation is not affected. The sequence specificity is identical for basal and GCN4 dependent initiator elements demonstrating that they are functionally homologous. These findings imply that the role of initiator elements is to 'focus' the start point(s) of transcription to distinct sites located in the region between the site(s) of the assembly of the transcriptional complex and the start codon of translation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. T., Styles C., Fink G. R. Multiple global regulators control HIS4 transcription in yeast. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):874–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3303332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braus G. H. Aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a model system for the regulation of a eukaryotic biosynthetic pathway. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):349–370. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.349-370.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braus G., Mösch H. U., Vogel K., Hinnen A., Hütter R. Interpathway regulation of the TRP4 gene of yeast. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):939–945. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Function of a yeast TATA element-binding protein in a mammalian transcription system. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):37–42. doi: 10.1038/334037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast mRNA initiation sites are determined primarily by specific sequences, not by the distance from the TATA element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter-Graves E. M., Hall B. D. DNA sequence elements required for transcription initiation of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe ADH gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(3):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00264447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter R., Braus G., Paravicini G., Mösch H. U., Niederberger P., Hütter R. Regulation of the TRP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae at the transcriptional level and functional analysis of its promotor. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):168–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00338409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furter R., Paravicini G., Aebi M., Braus G., Prantl F., Niederberger P., Hütter R. The TRP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and structural analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6357–6373. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Regulatory proteins in yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:425–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. UASs and enhancers: common mechanism of transcriptional activation in yeast and mammals. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):303–305. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. A., Struhl K. Functional distinctions between yeast TATA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5298–5304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Helser T. L., Zitomer R. S. Sequences required for transcriptional initiation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC7 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3785–3791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy A. M., Zitomer R. S. A sequence that directs transcriptional initiation in yeast. Curr Genet. 1990 Aug;18(2):105–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00312597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. A hierarchy of trans-acting factors modulates translation of an activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2349–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Positive regulation in the general amino acid control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5374–5378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Mechanisms of gene regulation in the general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):248–273. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.248-273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Bacteriophage T4 late promoters: mapping 5' ends of T4 gene 23 mRNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maicas E., Friesen J. D. A sequence pattern that occurs at the transcription initiation region of yeast RNA polymerase II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3387–3393. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Smith M. Transcription initiation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Multiple, independent T-A-T-A sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):363–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G., Niederberger P., Hütter R. Tryptophan biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: control of the flux through the pathway. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):48–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.48-59.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mösch H. U., Graf R., Schmidheini T., Braus G. Three GCN4 responsive elements act synergistically as upstream and as TATA-like elements in the yeast TRP4 promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2951–2957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Brenner M., Yamamoto T., Besnard F., Roeder R. G., Freese E. A downstream initiation element required for efficient TATA box binding and in vitro function of TFIID. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):86–88. doi: 10.1038/348086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederberger P., Aebi M., Hütter R. Identification and characterization of four new GCD genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1986;10(9):657–664. doi: 10.1007/BF00410913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen J., Mellor J. Characterisation of sequences required for RNA initiation from the PGK promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3219–3225. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Koenig-Rauseo I., Hinnen A. One-step gene replacement in yeast by cotransformation. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Molecular mechanisms of transcriptional regulation in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:1051–1077. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireos G., Penn M. D., Greer H. 5' untranslated sequences are required for the translational control of a yeast regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]