Abstract
The human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV-18) promoter contains a TPA responsive element (TRE) which confers TPA responsiveness on a heterologous promoter. In the context of the HPV-18 promoter, however, this AP-1 site is inactive. We have identified a negative regulatory domain in the HPV-18 promoter which represses the constitutive and TPA-induced AP-1 activity. This negative regulatory sequence has been mapped to 44 nucleotides (OL13). We identified this element as a transcriptional silencer based on its ability to interfere with transcriptional initiation. This HPV-18 silencer domain was narrowed down further to 23 nucleotides, the OL13B element, which bears similarity to three other silencer sequences, present in the mouse N-ras gene upstream regulatory region, the mouse albumin gene enhancer and the adeno-associated virus P5 promoter. The transcriptional repressor protein YY1, which negatively regulates the P5 promoter, binds to the HPV-18 silencer with high affinity. Mutation of the YY1 binding site leads to an enhanced activity of the HPV-18 promoter, strongly suggesting that YY1 plays an important role in controlling HPV-18 early gene expression.
Full text
PDF



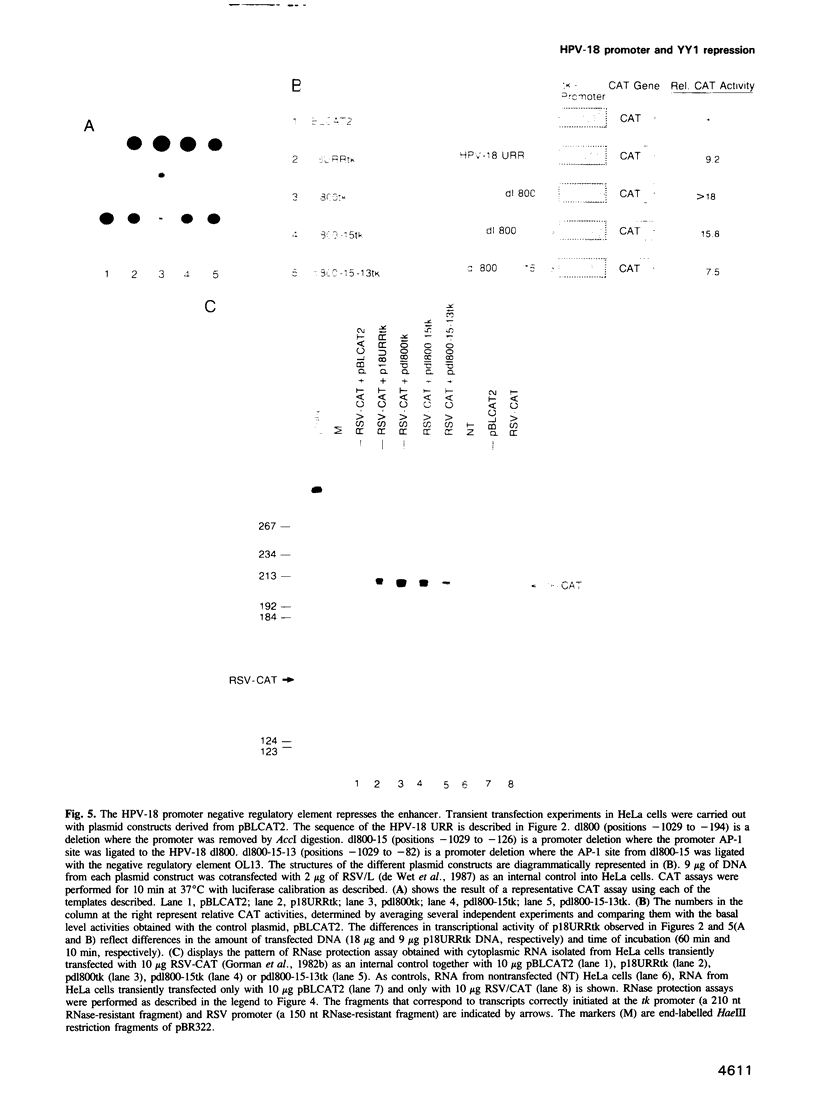






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard B. A., Bailly C., Lenoir M. C., Darmon M., Thierry F., Yaniv M. The human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18) E2 gene product is a repressor of the HPV18 regulatory region in human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4317–4324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4317-4324.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Bohmann D., Tsuchie H., Tjian R., Vogt P. K. v-jun encodes a nuclear protein with enhancer binding properties of AP-1. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):705–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Danos O. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the human papillomavirus type 18 genome. Phylogeny of papillomaviruses and repeated structure of the E6 and E7 gene products. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Morgenstern J. P., Crawford L., Banks L. Continued expression of HPV-16 E7 protein is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype of cells co-transformed by HPV-16 plus EJ-ras. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):513–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Becker K. G., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Driggers P. H., Levi B. Z., Appella E., Ozato K. Cloning of a negative transcription factor that binds to the upstream conserved region of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carranca A., Thierry F., Yaniv M. Interplay of viral and cellular proteins along the long control region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4321–4330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4321-4330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Bioassay for trans-activation using purified human immunodeficiency virus tat-encoded protein: trans-activation requires mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):821–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Grossman S., Bedell M. A., Laimins L. A. Inducible and constitutive enhancer domains in the noncoding region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Laimins L. A. Activation of human papillomavirus type 18 gene expression by herpes simplex virus type 1 viral transactivators and a phorbol ester. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):555–563. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.555-563.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Delta, a transcription factor that binds to downstream elements in several polymerase II promoters, is a functionally versatile zinc finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9799–9803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Boczko E. M., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. The mouse albumin enhancer contains a negative regulatory element that interacts with a novel DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3896–3905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Laimins L. A. A keratinocyte-specific transcription factor, KRF-1, interacts with AP-1 to activate expression of human papillomavirus type 18 in squamous epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9102–9106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo E. A., Shi Y., Shenk T. E., Levine A. J. Negative regulation of the BZLF1 promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3647–3655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3647-3655.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciucci R., Pellicer A. Dissection of the mouse N-ras gene upstream regulatory sequences and identification of the promoter and a negative regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1334–1343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Atchison M. L. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9804–9808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pater M. M., Pater A. Human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 sequences in carcinoma cell lines of the cervix. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Thierry F., Howley P. M. Mutational analysis of cis elements involved in E2 modulation of human papillomavirus type 16 P97 and type 18 P105 promoters. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2849–2859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2849-2859.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer H. D., Freyaldenhoven M. P., Napierski I., Spitkovsky D. D., Bauknecht T., Dathan N. Delineation of human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer binding proteins: the intracellular distribution of a novel octamer binding protein p92 is cell cycle regulated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2363–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösl F., Achtstätter T., Bauknecht T., Hutter K. J., Futterman G., zur Hausen H. Extinction of the HPV18 upstream regulatory region in cervical carcinoma cells after fusion with non-tumorigenic human keratinocytes under non-selective conditions. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1337–1345. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07653.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift F. V., Bhat K., Younghusband H. B., Hamada H. Characterization of a cell type-specific enhancer found in the human papilloma virus type 18 genome. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1339–1344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Dostatni N., Arnos F., Yaniv M. Cooperative activation of transcription by bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 can occur over a large distance. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4431–4437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Yaniv M. The BPV1-E2 trans-acting protein can be either an activator or a repressor of the HPV18 regulatory region. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3391–3397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M. Heterogeneity of the human papillomavirus group. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4898–4903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4898-4903.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Bauknecht T., Bartsch D., zur Hausen H. Influence of chromosomal integration on glucocorticoid-regulated transcription of growth-stimulating papillomavirus genes E6 and E7 in cervical carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Oltersdorf T., Schwarz E., Gissmann L. Correlation of modified human papilloma virus early gene expression with altered growth properties in C4-1 cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3780–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Rittmüller C., zur Hausen H., Dürst M. Inhibition of tumorigenicity of cervical cancer cells in nude mice by HPV E6-E7 anti-sense RNA. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jul 9;51(5):831–834. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Viruses in human cancers. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1167–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.1659743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









