Abstract
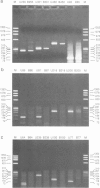
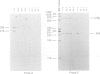
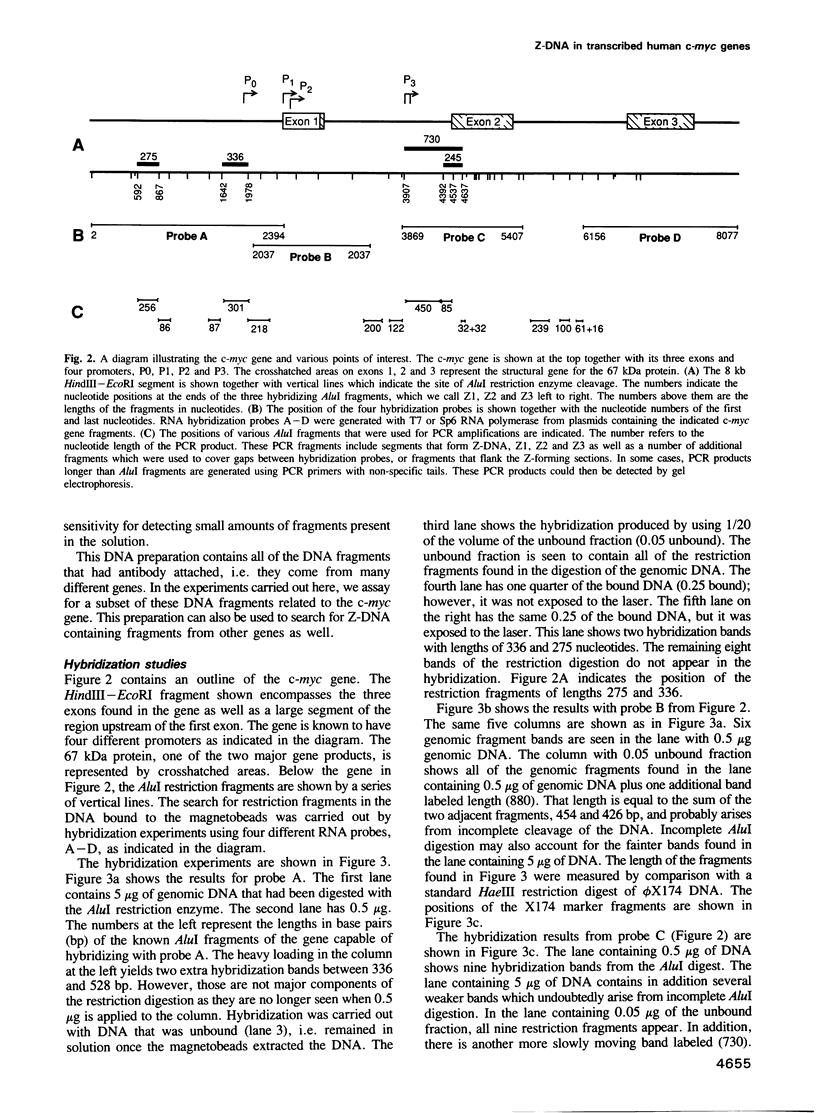
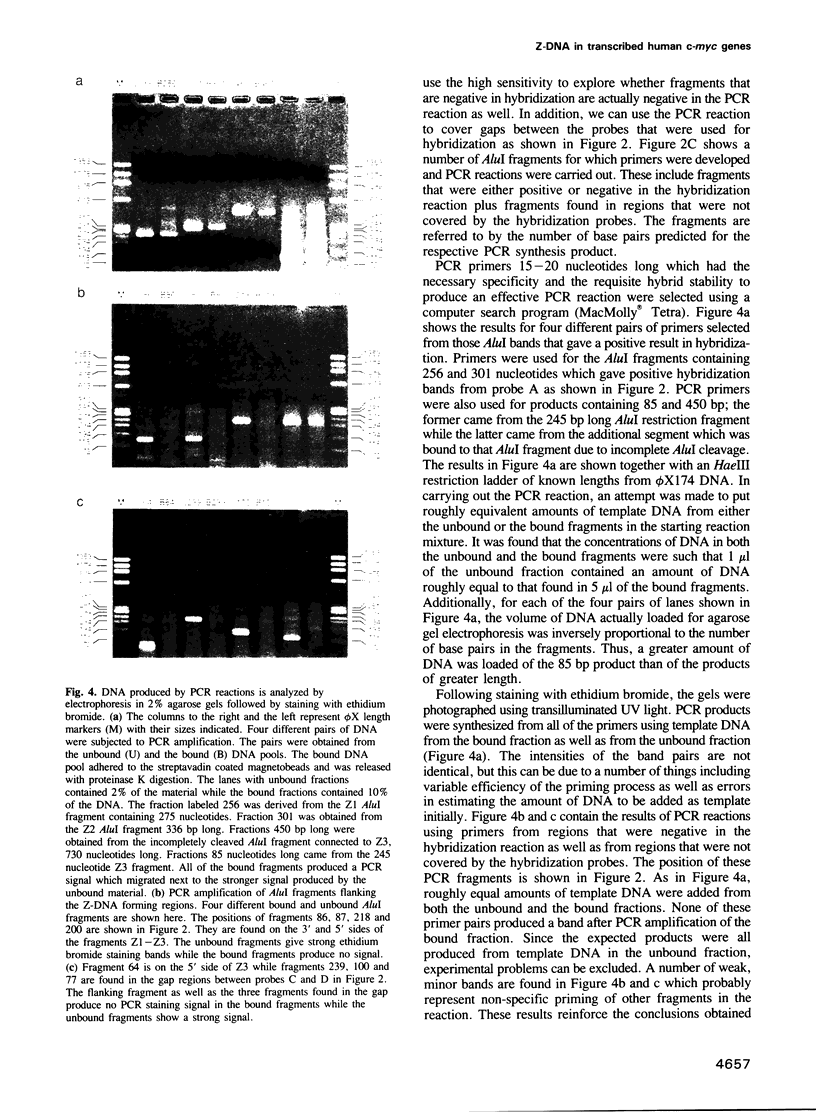
When human U937 cells are placed in agarose microbeads and treated with a detergent, the cytoplasmic membrane is lysed and the nuclear membrane is permeabilized. However, the nuclei remain intact and maintain both replication and transcription. Biotin labeled monoclonal antibodies against Z-DNA have been diffused into this system and used to measure the amount of Z-DNA present in the nuclei. It has previously been shown that the amount of Z-DNA present decreases due to relaxation by topoisomerase I and increases as the level of transcription increases. Here we measure the formation of Z-DNA in the c-myc gene by crosslinking the antibodies to DNA using laser radiation at 266 nm for 10 ns. The crosslinked DNA is isolated by restriction digestion, separation of antibody labeled fractions through the biotin residue, and subsequent proteolysis to remove the crosslinked antibody. Three AluI restriction fragments of the c-myc gene are shown to form Z-DNA when the cell is transcribing c-myc. The Z-DNA forming segments are near the promoter regions of the gene. However, when U937 cells start to differentiate and transcription of the c-myc gene is down-regulated, the Z-DNA content goes to undetectable levels within 30-60 min.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budowsky E. I., Abdurashidova G. G. Polynucleotide-protein cross-links induced by ultraviolet light and their use for structural investigation of nucleoproteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;37:1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60694-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd R. C., Cohen M. S., Newman S. L., Gray T. K. Vitamin D metabolites change the phenotype of monoblastic U937 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7538–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorbic T., Wittig B. Chromatin from transcribed genes contains HMG17 only downstream from the starting point of transcription. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2393–2399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge P., Nordheim A. Transcription-induced conformational change in a topologically closed DNA domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2941–2946. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Bornkamm G. W. Expression of normal and translocated c-myc alleles in Burkitt's lymphoma cells: evidence for different regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1965–1972. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D. Elongation and maturation of c-myc RNA is inhibited by differentiation inducing agents in HL60 cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1199–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Polack A., Kofler E., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B., Bornkamm G. W. Expression of P0- and P3-RNA from the normal and translocated c-myc allele in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1397–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Feigon J., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Wang A. H., Habener J. F., Rich A. An assessment of the Z-DNA forming potential of alternating dA-dT stretches in supercoiled plasmids. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3648–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazin C., Dupont de Dinechin S., Hampe A., Masson J. M., Martin P., Stehelin D., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the human c-myc locus: provocative open reading frame within the first exon. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):383–387. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlund M., Orn A., Pattengale P. K., Jansson M., Wigzell H., Nilsson K. Natural killer cells kill tumour cells at a given stage of differentiation. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):848–850. doi: 10.1038/292848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. J. Z-DNA: a prodrome for the 1990s. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):675–680. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. S., Ellison M. J., Quigley G. J., Rich A. A computer aided thermodynamic approach for predicting the formation of Z-DNA in naturally occurring sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2737–2744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. A general method for preparing chromatin containing intact DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Yuan J., Cook P. R. A gentle method for preparing cyto- and nucleo-skeletons and associated chromatin. J Cell Sci. 1988 Jul;90(Pt 3):365–378. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Ruiz A., Requena J. M., Lopez M. C., Alonso C. A potential Z-DNA-forming sequence is located between two transcription units alternatively expressed during development of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H., Quigley G. J., Ellison M. J., Rich A. The Z-Z junction: the boundary between two out-of-phase Z-DNA regions. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5257–5263. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa T. F., Stoddard D., Zhou G. W., Ho P. S. Quantitative analysis of DNA secondary structure from solvent-accessible surfaces: the B- to Z-DNA transition as a model. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 8;28(16):6642–6651. doi: 10.1021/bi00442a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali R., Bhalla A. K., Farrow S. M., Williams M. M., Lal S., Lydyard P. M., O'Riordan J. L. Early regulation of c-myc mRNA by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human myelomonocytic U937 cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;3(1):43–48. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0030043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovalsky O. I., Panyutin I. G., Budowsky E. I. Sequence-specificity of the alkali-sensitive lesions induced in DNA by high-intensity ultraviolet laser radiation. Photochem Photobiol. 1990 Sep;52(3):509–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1990.tb01793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Möller A., Nordheim A., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Antibodies specific for left-handed Z-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. G., Ivhed I., Gidlund M., Pettersson U., Vennström B., Nilsson K. Phorbol ester-induced terminal differentiation is inhibited in human U-937 monoblastic cells expressing a v-myc oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2638–2642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D., Galindo J., Richman D. D. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of monoblastoid cells: cellular differentiation determines the pattern of virus replication. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3558–3564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3558-3564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Transcriptional block caused by a negative supercoiling induced structural change in an alternating CG sequence. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechaczyk M., Yang J. Q., Blanchard J. M., Jeanteur P., Marcu K. B. Posttranscriptional mechanisms are responsible for accumulation of truncated c-myc RNAs in murine plasma cell tumors. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmouni A. R., Wells R. D. Stabilization of Z DNA in vivo by localized supercoiling. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):358–363. doi: 10.1126/science.2678475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Chou P. J., Ho P. S. Mapping Z-DNA in the human genome. Computer-aided mapping reveals a nonrandom distribution of potential Z-DNA-forming sequences in human genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11846–11855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Control of c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovsky VYu, Dimitrov S. I., Russanova V. R., Angelov D., Pashev I. G. Laser-induced crosslinking of histones to DNA in chromatin and core particles: implications in studying histone-DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10069–10081. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Antibodies to DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):1–36. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Dorbic T., Rich A. The level of Z-DNA in metabolically active, permeabilized mammalian cell nuclei is regulated by torsional strain. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):755–764. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Dorbic T., Rich A. Transcription is associated with Z-DNA formation in metabolically active permeabilized mammalian cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2259–2263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wölfl S., Schräder M., Wittig B. Lack of correlation between DNA methylation and transcriptional inactivation: the chicken lysozyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):271–275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]