Abstract
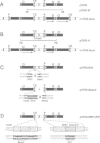
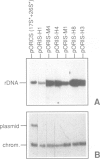
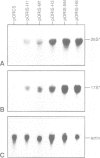
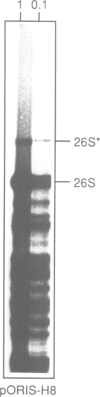
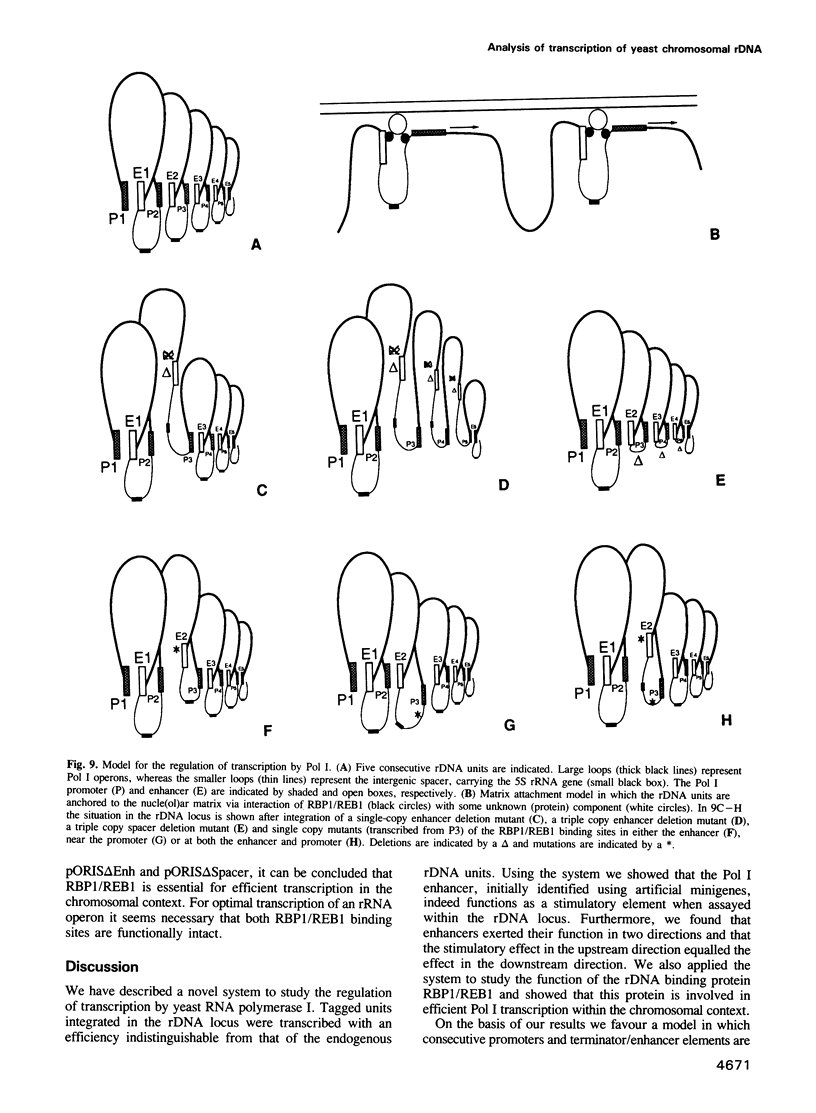
We have developed a novel system to study transcription by yeast RNA polymerase I (Pol I) of mutated rDNA units within the chromosomal context. For this, complete rDNA units carrying specific oligonucleotide tags in both the 17S and 26S rRNA genes were integrated into the chromosomal rDNA locus. Using this novel system, we analysed the action of the rDNA enhancer in stimulating transcription within the chromosomal context. We found that the enhancer acts as a stimulatory element in both directions, mainly on its two most proximal rRNA operons. Deletion of the sequences between the enhancer and the Pol I promoter in the tagged, integrated unit indicated that this part of the intergenic spacer contains no other transcriptional regulatory elements for Pol I. We also applied the system to study the function of the rDNA binding protein RBP1/REB1. For this purpose, we analysed tagged units in which either one or both of the binding sites for this protein have been inactivated. We found that mutations of both binding sites strongly diminish the transcription of the adjacent operon. The protein is hypothesized to play a crucial role in keeping the chromosomal rDNA units in an optimal spatial configuration by anchoring consecutive enhancers and promoters to the nucle(ol)ar matrix.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandl C. J., Struhl K. A nucleosome-positioning sequence is required for GCN4 to activate transcription in the absence of a TATA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4256–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Additional RNA polymerase I initiation site within the nontranscribed spacer region of the rat rRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2388–2396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Transcriptional role for the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2766–2773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Lue N. F., Buchman A. R., LaPointe J. W., Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A yeast protein that influences the chromatin structure of UASG and functions as a powerful auxiliary gene activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):503–514. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. The nucleoskeleton and the topology of transcription. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 20;185(3):487–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. A complex array of sequences enhances ribosomal transcription in Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):813–827. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90407-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. Spacer promoters are essential for efficient enhancement of X. laevis ribosomal transcription. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson P., Cook P. R., Jackson D. A. Active RNA polymerase I is fixed within the nucleus of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2207–2214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Chao W., Jacob S. T. An enhancer element in the far upstream spacer region of rat ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11616–11622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Jacob S. T. A cis-acting sequence within the rat ribosomal DNA enhancer region can modulate RNA polymerase II-directed transcription of the metallothionein I gene in vitro. DNA. 1989 Jun;8(5):311–320. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firek S., Read C., Smith D. R., Moss T. The Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene terminator contains sequences that both enhance and repress ribosomal transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3777–3784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Dixit A., Jacob S. T. A 37-base pair element in the far upstream spacer region can enhance transcription of rat rDNA in vitro and can bind to the core promoter-binding factor(s). J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Di Nocera P. P. Multiple repeated units in Drosophila melanogaster ribosomal DNA spacer stimulate rRNA precursor transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Fiorentini P., Di Nocera P. P. Spacer promoters are orientation-dependent activators of pre-rRNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4667–4677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Transcription occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):919–925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Termination of transcription of ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00229816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Unusual enhancer function in yeast rRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4986–4993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju Q. D., Morrow B. E., Warner J. R. REB1, a yeast DNA-binding protein with many targets, is essential for growth and bears some resemblance to the oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5226–5234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Oliemans J., Offenberg H., Dekker A. F., Piper P. W., Planta R. J., Klootwijk J. 3'-End formation of transcripts from the yeast rRNA operon. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2703–2710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. A novel promoter in the mouse rDNA spacer is active in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3487–3492. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkens T., Riggs D. L., Heck J. D., Planta R. J., Nomura M. The yeast RNA polymerase I promoter: ribosomal DNA sequences involved in transcription initiation and complex formation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5363–5370. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkens T., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Oliemans J., Planta R. J. A yeast ribosomal DNA-binding protein that binds to the rDNA enhancer and also close to the site of Pol I transcription initiation is not important for enhancer functioning. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):351–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00340714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Xenopus ribosomal gene enhancers function when inserted inside the gene they enhance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8999–9009. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestel R., Yip M., Holland J. P., Wang E., Kang J., Holland M. J. Sequences within the spacer region of yeast rRNA cistrons that stimulate 35S rRNA synthesis in vivo mediate RNA polymerase I-dependent promoter and terminator activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1243–1254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Proteins that bind to the yeast rDNA enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9061–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R. Purification and characterization of the yeast rDNA binding protein REB1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20778–20783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Boon K., van der Sande C. A., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. Functional analysis of transcribed spacers of yeast ribosomal DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3989–3996. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Knol J., Maas P., Dekker A. F., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. Linker scanning of the yeast RNA polymerase I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9661–9678. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Venema J., van der Linden G., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. A system for the analysis of yeast ribosomal DNA mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):551–559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Mougey E. B., Sollner-Webb B. The Xenopus ribosomal DNA 60- and 81-base-pair repeats are position-dependent enhancers that function at the establishment of the preinitiation complex: analysis in vivo and in an enhancer-responsive in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5093–5104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D. Yeast ribosomal DNA genes are located on chromosome XII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):410–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Pape L. K., Henderson S. L., Ryan K., Paalman M. H., Lopata M. A., Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B. Enhancers for RNA polymerase I in mouse ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4816–4825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. Sequence elements essential for function of the Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4282–4288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Planta R. J. Ribosome biogenesis in yeast. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:89–129. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs D. L., Nomura M. Specific transcription of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 35 S rDNA by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7596–7603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Henderson S. L., Dougherty K. M., Wejksnora P. J., Sollner-Webb B. An RNA polymerase I promoter located in the CHO and mouse ribosomal DNA spacers: functional analysis and factor and sequence requirements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1513–1525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Nicholson P. R., Stillman D. J. Identification of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA-binding protein involved in transcriptional regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1743–1753. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Synthesis of ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):256–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.256-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sande C. A., Kulkens T., Kramer A. B., de Wijs I. J., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Termination of transcription by yeast RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9127–9146. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]