LETTER
We have read with great interest the report by Marshall et al. regarding the efficacy of the combination of ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) and aztreonam (ATM) against metallo-β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (1).
These results confirm our experience with two patients treated with CAZ-AVI and ATM. Considering that the ATM-AVI combination is still in early development, clinical observations supporting effective treatment options using currently approved drugs should be shared to document successful therapeutic strategies until a randomized trial resolves potential discrepancies between the in vitro and in vivo activities of these agents (2).
The first patient was a 69-year-old male who developed while in intensive care a catheter-related infection with suppurated thrombophlebitis complicated with persistent bacteremia due to a Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate producing Oxa48 and NDM-1 carbapenemases, identified by PCR (Xpert Carba-R; Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). It was susceptible only to amikacin (disk diffusion assay, EUCAST guidelines) and colistin (broth microdilution MIC, 0.25 mg/liter). Transthoracic echocardiography ruled out infective endocarditis. The following antimicrobial treatment lines were used in the hope that synergy would occur: colistin, imipenem (MIC, 32 mg/liter), fosfomycin (MIC, >256 mg/liter), levofloxacin (MIC, >32 mg/liter), and amikacin.
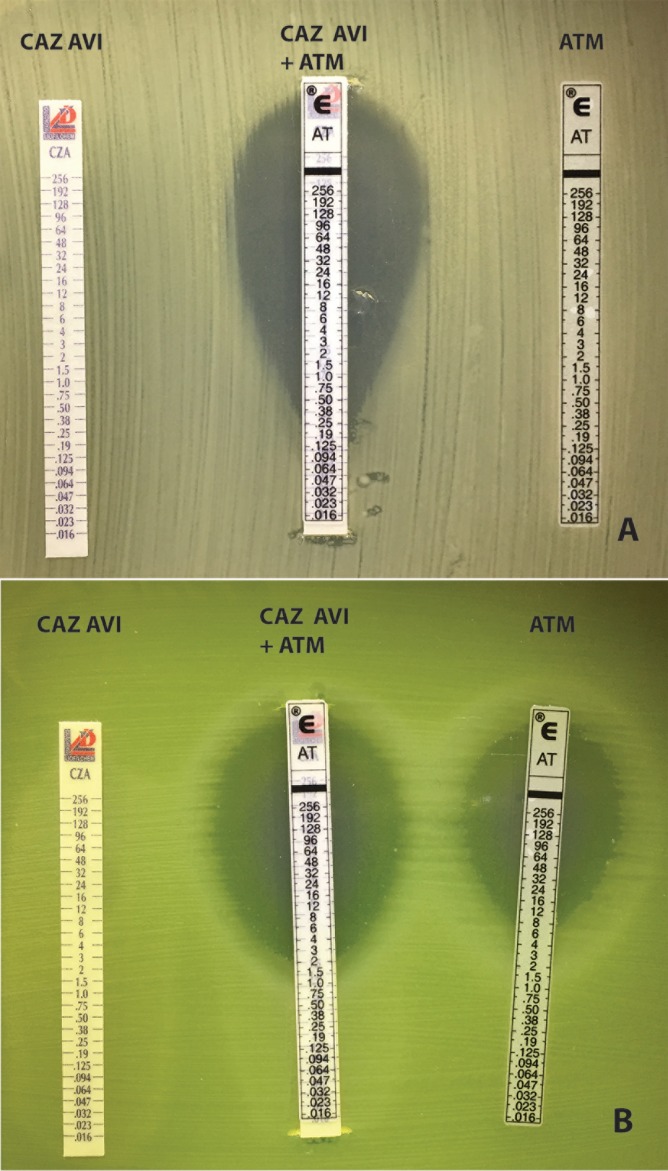
ATM and CAZ-AVI MICs were >256 mg/liter. However, the CAZ-AVI/ATM combination was shown to be synergistic, with an MIC of 0.125 mg/liter, determined by first applying an ATM strip (Etest, bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France) and then a CAZ-AVI strip (Liofilchem, I2A, Montpellier, France) on a Mueller-Hinton plate and reading the inhibition on the ATM strip scale (Fig. 1, top panel).
FIG 1.
Susceptibility testing showing with ellipsometry the effect of the synergistic combination of CAZ-AVI and ATM. The combination (middle strip) was tested by first applying an ATM strip to the Mueller-Hinton (MH) agar, removing it after 5 min, and then applying a CAZ-AVI strip on the exact same location and placing back the ATM strip to read the susceptibility to ATM in the presence of AVI (and CAZ). (Top panel) K. pneumoniae NDM-1/OXA-48 from patient 1. (Bottom panel) Pseudomonas aeruginosa NDM-1/AmpC from patient 2.
After 26 days of constant bacteremia (32 positive blood cultures), and 7 h after drawing a positive blood culture, the antimicrobial regimen was switched to a combination of CAZ-AVI (2 g-0.5 g three times a day [t.i.d.]) and ATM (2 g t.i.d.) for 10 days administered in that order. Blood cultures drawn 3 h after the infusion of the combination were negative and remained negative until the patient died of heart failure 32 days later, free of infection after 108 days of intensive care.
The second patient was a 55-year-old male weighing 40 kg, with myasthenia, thymoma, and chronic restrictive respiratory failure. He presented with pneumonia featuring large abscesses documented microbiologically by bronchoalveolar lavage caused by an NDM1-producing, AmpC-hyperproducing strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa susceptible only to amikacin and colistin (MIC, 0.25 mg/liter).
CAZ-AVI and ATM MICs were, respectively, >256 mg/liter and 12 mg/liter. Synergy showed that the MIC of ATM in the presence of CAZ and AVI decreased to 2 mg/liter (Fig. 1, bottom panel). Given his low weight, the patient was switched to a combination of CAZ-AVI (2.5 g every 12 h) and ATM (2 g twice a day [b.i.d.]) for 6 weeks. He recovered quickly and was considered cured at 6 months after completion of antibiotics.
Overall, we believe that these cases illustrate the efficacy of the ATM-AVI combination to treat infections by metallo-β-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacilli producing additional Ambler's class A, C, or D β-lactamases. The rationale that avibactam inactivates the class A, C, or D β-lactamases to restore susceptibility to ATM is confirmed by its high efficacy in patients with severe infection and no conventional therapeutic options. It validates the solid in vitro data documenting the potential of the ATM-AVI combination drug (3).
REFERENCES
- 1.Marshall S, Hujer AM, Rojas LJ, Papp-Wallace KM, Humphries RM, Spellberg B, Hujer KM, Marshall EK, Rudin SD, Perez F, Wilson BM, Wasserman RB, Chikowski L, Paterson DL, Vila AJ, van Duin D, Kreiswirth BN, Chambers HF, Fowler VG, Jacobs MR, Pulse ME, Weiss WJ, Bonomo RA. 2017. Can ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam overcome β-lactam resistance conferred by metallo-β-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae? Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e02243-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02243-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Monogue ML, Abbo LM, Rosa R, Camargo JF, Martinez O, Bonomo RA, Nicolau DP. 17 April 2017. In vitro discordance with in vivo activity: humanized exposures of ceftazidime-avibactam, aztreonam, and tigecycline alone and in combination against New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a murine lung infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother AAC.00486-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00486-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mischnik A, Baumert P, Hamprecht A, Rohde A, Peter S, Feihl S, Knobloch J, Gölz H, Kola A, Obermann B, Querbach C, Willmann M, Gebhardt F, Tacconelli E, Gastmeier P, Seifert H, Kern WV; DZIF-ATHOS Study Group. 2017. Susceptibility to cephalosporin combinations and aztreonam/avibactam among third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae recovered on hospital admission. Int J Antimicrob Agents 49:239–242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]