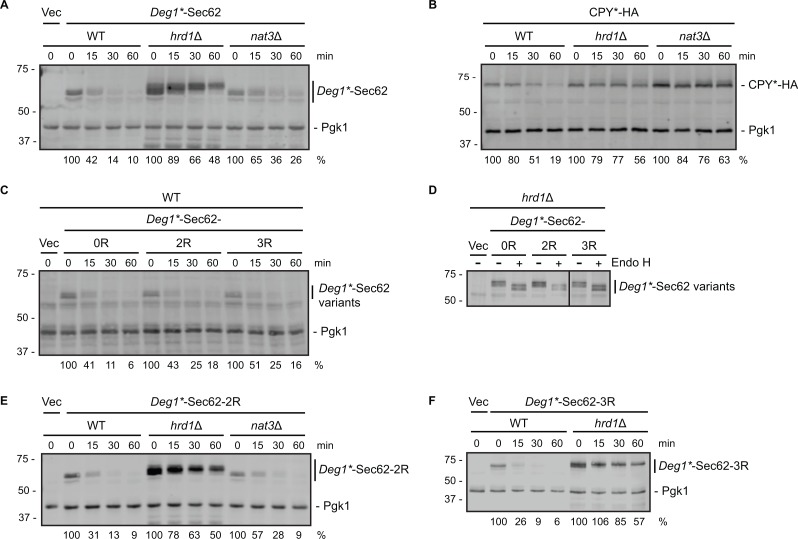
Figure 2. Neither N-terminal acetylation nor internal acetylation is required for Hrd1-dependent degradation of Deg1*-Sec62.
(A) Cycloheximide chase analysis of yeast cells of the indicated genotypes expressing Deg1*-Sec62 or harboring an empty vector. (B) Cycloheximide chase analysis of yeast cells of the indicated genotypes expressing HA-tagged CPY*. (C) Cycloheximide chase analysis of wild-type yeast cells expressing variants of Deg1*-Sec62 or harboring an empty vector. (D) Lysates from hrd1Δ cells expressing the indicated variants of Deg1*-Sec62 or harboring an empty vector were incubated in the absence or presence of Endo H. The black line indicates that intervening lanes have been omitted. (E) Cycloheximide chase analysis of yeast cells of the indicated genotypes expressing Deg1*-Sec62-2R or harboring an empty vector. (F) Cycloheximide chase analysis of yeast cells of the indicated genotypes expressing Deg1*-Sec62-3R or harboring an empty vector. Pgk1 serves as a loading control for (A, B C, E, F). For each cycloheximide chase, the percentage of protein remaining at each time point (normalized to Pgk1) is indicated below the image. Experiments depicted in (A, C, E, F) were repeated at least three times, and a representative image is presented for each. The control experiment in (B) (to verify previously published behavior of the tested strains with respect to CPY* degradation; Hiller et al., 1996; Zattas et al., 2013) and assessment of Endo H sensitivity in (D) (to confirm protein N-linked glycosylation status) were each performed one time. Vec, Vector. WT, wild-type. 0R, no mutation of acetylation sites. 2R, Lys3 and Lys7 mutated to Arg to prevent internal acetylation. 3R, Asn2, Lys3, and Lys7 mutated to Arg to prevent N-terminal and internal acetylation.