Abstract
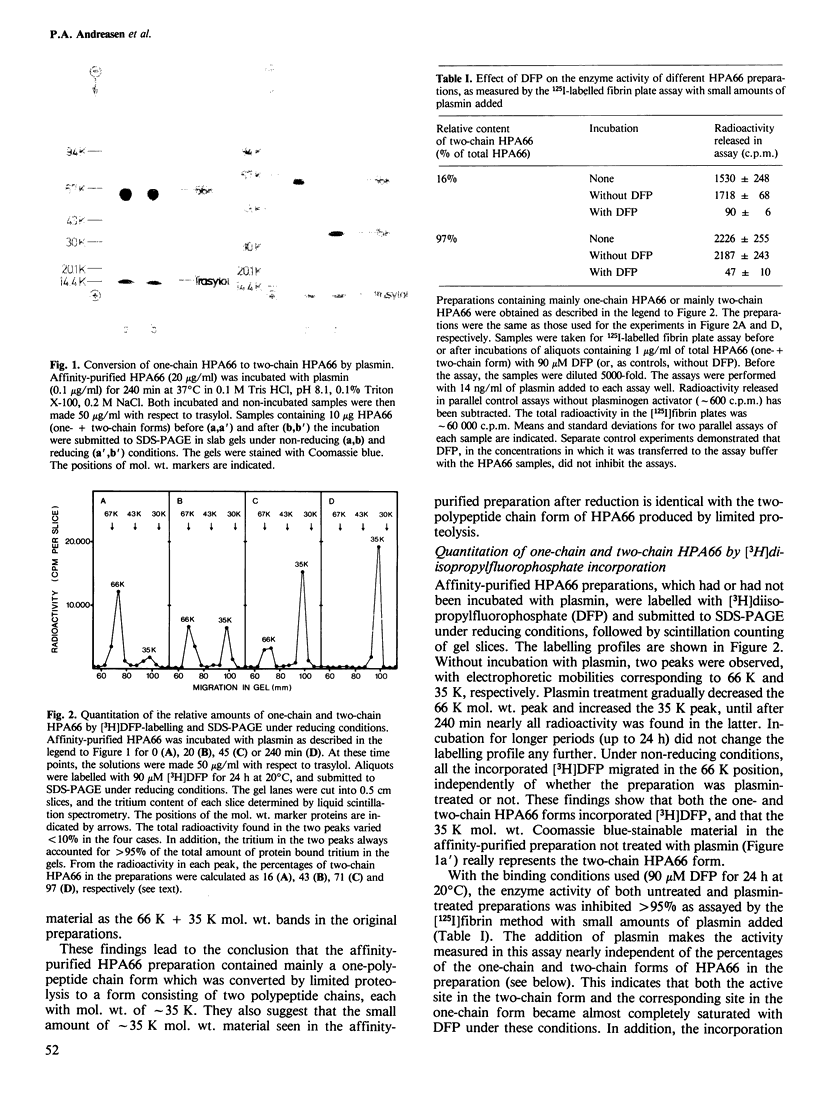
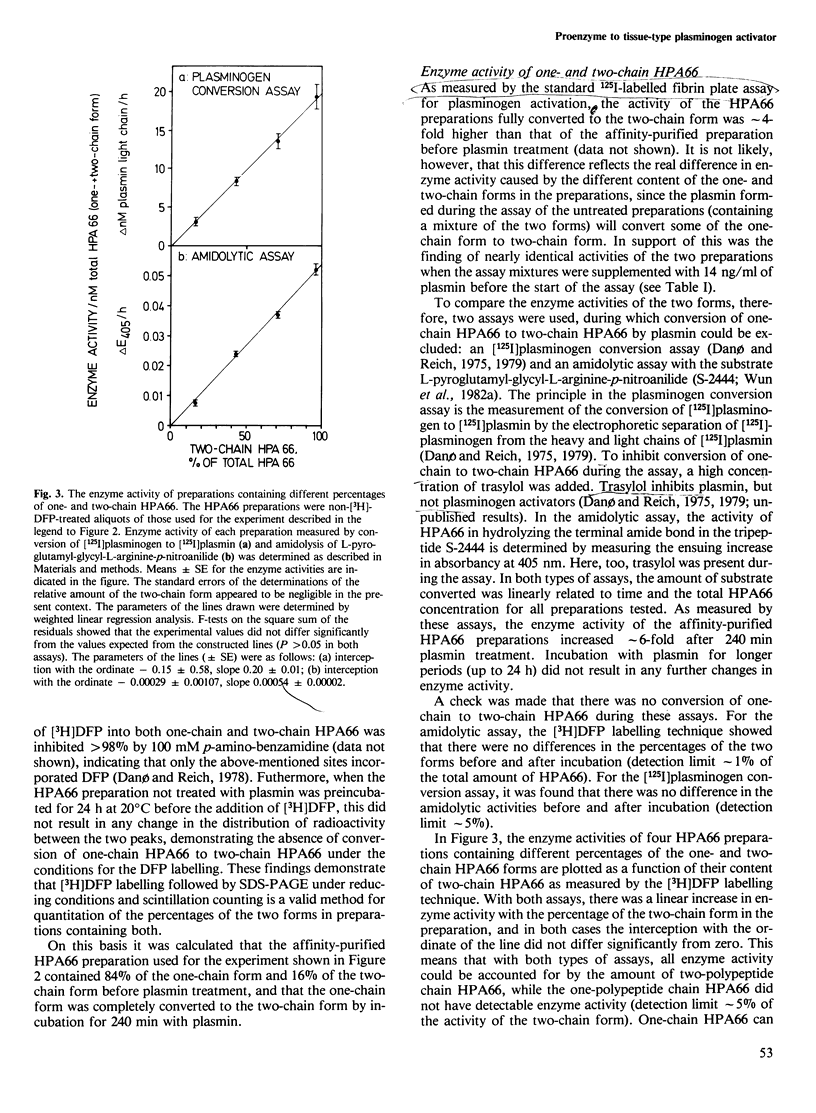
The human 66 000 mol. wt. plasminogen activator (HPA66; tissue-type plasminogen activator) has been purified from melanoma cells by a one-step affinity method with a monoclonal antibody. HPA66 purified in this way consists mainly of a one-polypeptide chain form with small amounts (15%) of a form containing two polypeptide chains held together by one or more disulphide bridges. The one-chain form was converted to the two-chain form by catalytic amounts of plasmin. During the conversion, the enzyme activity of HPA66, as measured by an [125I]plasminogen conversion assay and with a chromogenic substrate, increased linearly with the percentage of the two-chain form. A linear regression analysis showed that all enzyme activity could be accounted for by the two-chain form, while the one-chain form had no measurable enzyme activity (detection limit approximately 5% of the activity of the two-chain form). Together with previous findings of inactive proenzymes to murine and human approximately 50 000 mol. wt. (urokinase-type) plasminogen activators, these findings indicate that plasminogen activators are generally formed from inactive one-chain proenzymes which are converted to active two-chain enzymes by limited proteolysis, thus demonstrating a third step in a cascade reaction leading to extracellular proteolysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Von Kaulla K. N. Dissimilarity of human vascular plasminogen activator and human urokinase. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):354–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astedt B. No crossreaction between circulating plasminogen activator and urokinase. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):535–539. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers W. H., Strickland S., Reich E. Ovarian plasminogen activator: relationship to ovulation and hormonal regulation. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder B. R., Spragg J., Austen K. F. Purification and characterization of human vascular plasminogen activator derived from blood vessel perfusates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1998–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonsall R. W., Hunt S. Characteristics of interactions between surfactants and the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 12;249(1):266–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Silverstein S. C., Acs G. Immunological analysis of plasminogen activators from normal and transformed hamster cells. Evidence that the plasminogen activators produced by SV40 virus-transformed hamster embryo cells and normal hamster lung cells are antigenically identical. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):419–434. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Moller V., Ossowski L., Nielsen L. S. Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator from mouse cells transformed by an oncogenic virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 13;613(2):542–555. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Nielsen L. S., Møller V., Engelhart M. Inhibition of a plasminogen activator from oncogenic virus-transformed mouse cells by rabbit antibodies against the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 5;630(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Reich E. Plasminogen activator from cells transformed by an oncogenic virus: inhibitors of the activation reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 12;566(1):138–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Reich E. Serine enzymes released by cultured neoplastic cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):745–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Ny T., Rånby M., Hedén L. O., Palm G., Holmgren E., Josephson S. Isolation of cDNA sequences coding for a part of human tissue plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):349–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler W. A., Steffens G. J., Otting F., Kim S. M., Frankus E., Flohé L. The primary structure of high molecular mass urokinase from human urine. The complete amino acid sequence of the A chain. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Oct;363(10):1155–1165. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.2.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltoft K., Nielsen L. S., Zeuthen J., Danø K. Monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits a human Mr 52,000 plasminogen-activating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3720–3723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Grahn D. T., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. Activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor)--analogy with pancreatic zymogen-enzyme systems. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2645–2648. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo O., Rijken D. C., Collen D. Thrombolysis by human tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase in rabbits with experimental pulmonary embolus. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):590–591. doi: 10.1038/291590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson C., Nyberg-Arrhenius V., Wallén P. Dissolution of thrombi by tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase and streptokinase in an artificial circulating system. Thromb Res. 1981 Mar 15;21(6):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Biological control of factor VII. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Biegel D., Reich E. Mammary plasminogen activator: correlation with involution, hormonal modulation and comparison between normal and neoplastic tissue. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Hoylaerts M., Collen D. Fibrinolytic properties of one-chain and two-chain human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2920–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Relationship between tissue plasminogen activator and the activators in blood and vascular wall. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):815–830. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roblin R., Young P. L. Dexamethasone regulation of plasminogen activator in embryonic and tumor-derived human cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Aug;40(8 Pt 1):2706–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M., Bergsdorf N., Nilsson T. Enzymatic properties of the one- and two-chain form of tissue plasminogen activator. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 15;27(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M. Studies on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by tissue plasminogen activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 24;704(3):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller J., Nick H., Rickli E. E., Gillessen D., Lergier W., Studer R. O. Human low-molecular-weight urinary urokinase. Partial characterization and preliminary sequence data of the two polypeptide chains. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(2):251–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver L., Nielsen L. S., Stephens R., Danø K. Plasminogen activator released as inactive proenzyme from murine cells transformed by sarcoma virus. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May 17;124(2):409–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Gordon S., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):834–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetterlein D., Young P. L., Bell T. E., Roblin R. Immunological characterization of multiple weight forms of human cell plasminogen activators. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):575–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Bergsdorf N., Rånby M. Purification and identification of two structural variants of porcine tissue plasminogen activator by affinity adsorption on fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 24;719(2):318–328. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. L., Becker M. L., Hoal E. G., Dowdle E. B. Molecular species of plasminogen activators secreted by normal and neoplastic human cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):933–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Ossowski L., Reich E. A proenzyme form of human urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7262–7268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Schleuning W. D., Reich E. Isolation and characterization of urokinase from human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3276–3283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




