Abstract
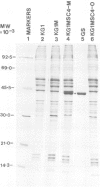
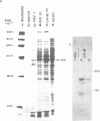
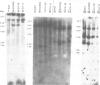
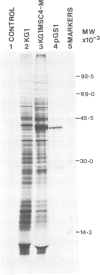
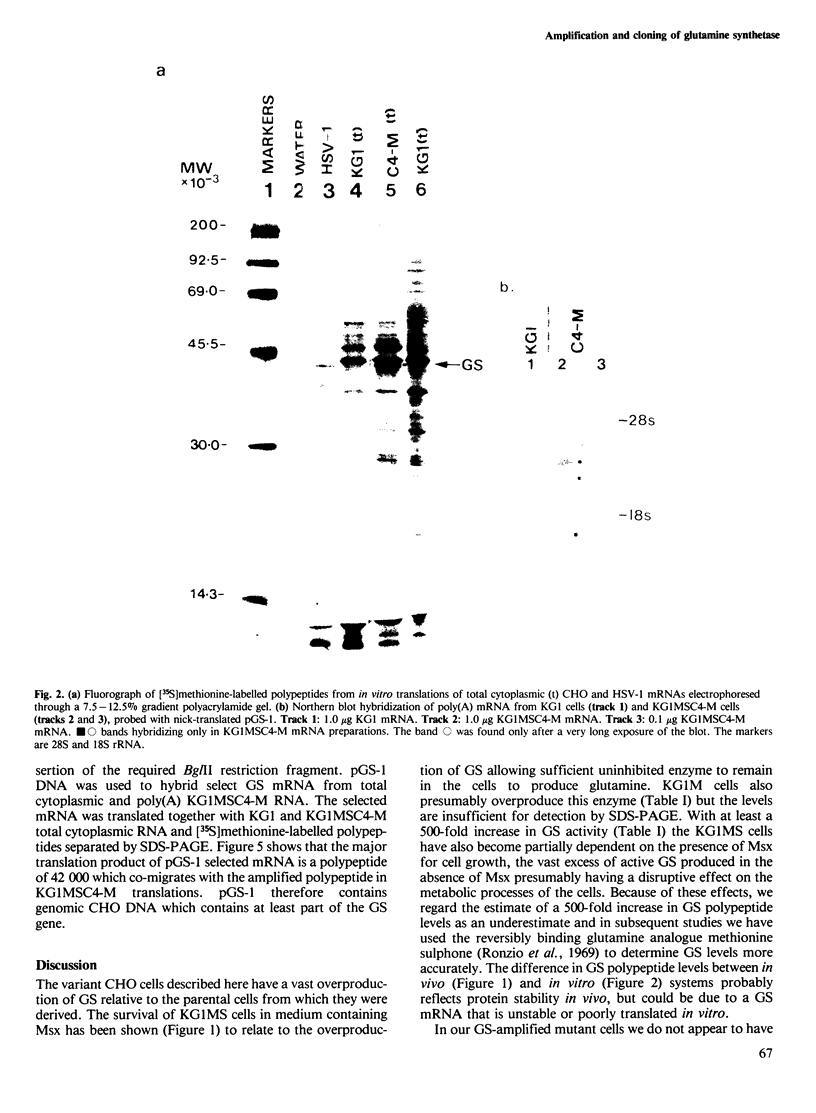
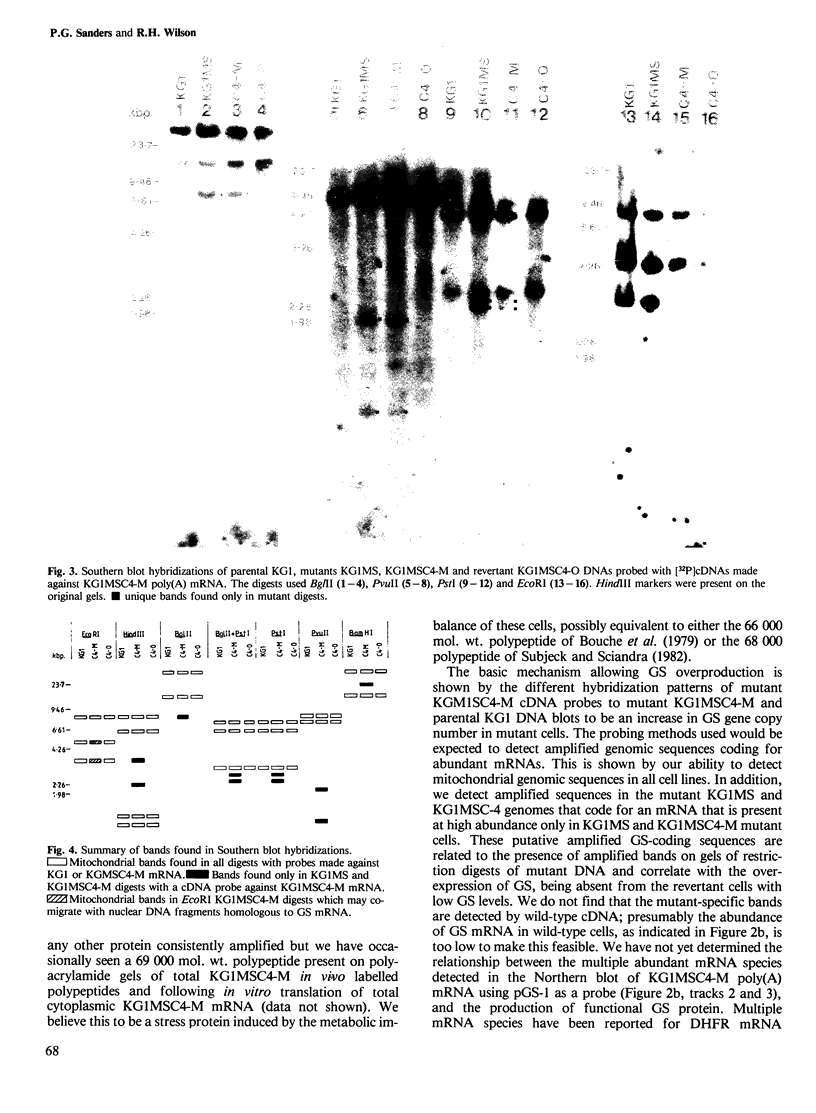
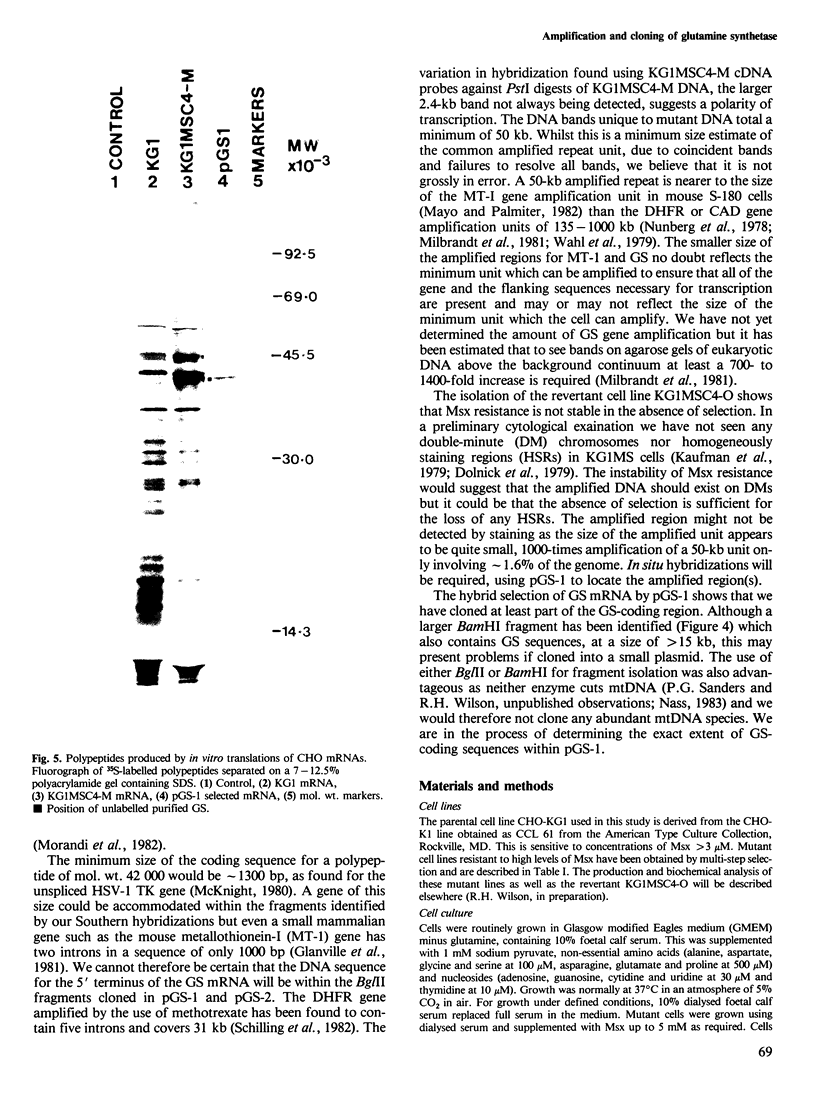
A Chinese hamster ovary cell line, KG1MS which is resistant to 5 mM methionine sulphoximine overproduces glutamine synthetase. Overproduction of this 42 000 mol. wt. polypeptide is not seen in either parental KG1 or revertant KG1MSC4-0 cell lines which are resistant to 3 microM and 8 microM methionine sulphoximine, respectively. Restriction endonuclease analysis of DNA from KG1MS cells produces a pattern of amplified DNA fragments not seen in parental KG1 or revertant KG1MSC4-0 digests. Hybridization of cDNA probes complementary to KG1MS poly(A) mRNA against Southern blots of KG1MS restriction digests identifies a specific subset within these amplified sequences which is not detected by cDNA probes made from parental KG1 poly(A) mRNA. One 8.2-kb BglII fragment of KG1MS DNA identified by cDNA hybridization has been cloned to produce recombinant pGS-1. mRNA hybrid selected by pGS-1 translates to a 42 000 mol. wt. polypeptide which co-migrates in polyacrylamide gels with the over-produced protein in KG1MS cells and purified glutamine synthetase. pGS-1 also hybridizes to several mRNA species abundant in KG1MSC4-M, but not KG1, poly(A) mRNA extracts. The high level of resistance to methionine sulphoximine shown by KG1MS cells is due to amplification of a DNA sequence of at least 50 kb which contains the coding region for the enzyme glutamine synthetase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. Plasmid detection and sizing in single colony lysates. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):393–394. doi: 10.1126/science.318764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D., Clayton D. A. The number of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid genomes in mouse L and human HeLa cells. Quantitative isolation of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7991–7995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock C. J., Tyler-Smith C. Gene amplification in methotrexate-resistant mouse cells. II. Rearrangement and amplification of non-dihydrofolate reductase gene sequences accompany chromosomal changes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):219–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouche G., Amalric F., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Zalta J. P. Effects of heat shock on gene expression and subcellular protein distribution in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1739–1747. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolnick B. J., Berenson R. J., Bertino J. R., Kaufman R. J., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Correlation of dihydrofolate reductase elevation with gene amplification in a homogeneously staining chromosomal region in L5178Y cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):394–402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in unstably methotrexate-resistant cells are associated with double minute chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka R. G., Tokins G. M., Crook R. B. Clonal differences in glutamine synthetase activity of hepatoma cells. Effects of glutamine and dexamethasone. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jul;54(1):175–179. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Crombie I. K., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Control of protein synthesis in herpesvirus-infected cells: analysis of the polypeptides induced by wild type and sixteen temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV strain 17. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):347–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Palmiter R. D. Glucocorticoid regulation of the mouse metallothionein I gene is selectively lost following amplification of the gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3061–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., White W. C., Rothman S. M., Hamlin J. L. Methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells have amplified a 135-kilobase-pair region that includes the dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6043–6047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morandi C., Masters J. N., Mottes M., Attardi G. Multiple forms of human dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNA. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of their DNA coding sequence. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):583–607. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscona A. A., Piddington R. Stimulation by hydrocortisone of premature changes in the developmental pattern of glutamine synthetase in embryonic retina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):409–411. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nass M. M. Restriction map of Chinese hamster mitochondrial DNA containing replication coordinates: comparison with Syrian hamster mitochondrial genome. Gene. 1983 Mar;21(3):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes are localized to a homogeneously staining region of a single chromosome in a methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5553–5556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pishak M. R., Phillips A. T. Glucocorticoid stimulation of glutamine synthetase production in cultured rat glioma cells. J Neurochem. 1980 Apr;34(4):866–872. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. The cell-free synthesis of herpesvirus-induced polypeptides. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glutamine synthetase by methionine sulfoximine. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Newman C., Williamson D. H. A simple cytochemical technique for demonstration of DNA in cells infected with mycoplasmas and viruses. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):461–462. doi: 10.1038/253461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Koenen M., Otto K., Müller-Hill B. pUR222, a vector for cloning and rapid chemical sequencing of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4087–4098. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeier D. C., Milman G. Chinese hamster liver glutamine synthetase. Purification, physical and biochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2272–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]