Abstract
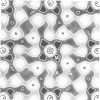
This paper presents the projected structure of the T-layer of Bacillus brevis, obtained from electron microscopic studies of the unstained protein layer in the frozen-hydrated state. Computer image processing is used to correct for the effects of the contrast transfer function, and to increase the signal-to-noise ratio by lattice averaging. The results obtained show a good agreement with those previously obtained using negatively stained specimens. It is shown that the contrast of T-layer embedded in ice can be approximated to pure phase contrast.
Full text
PDF
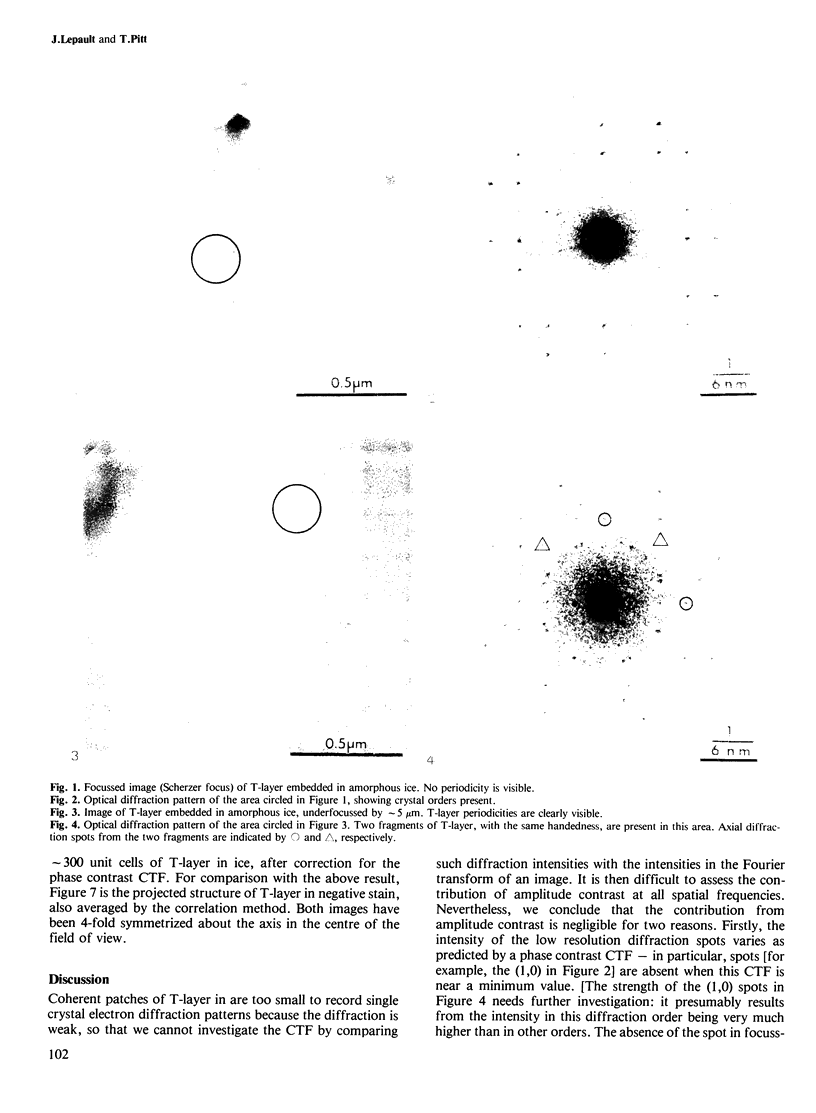
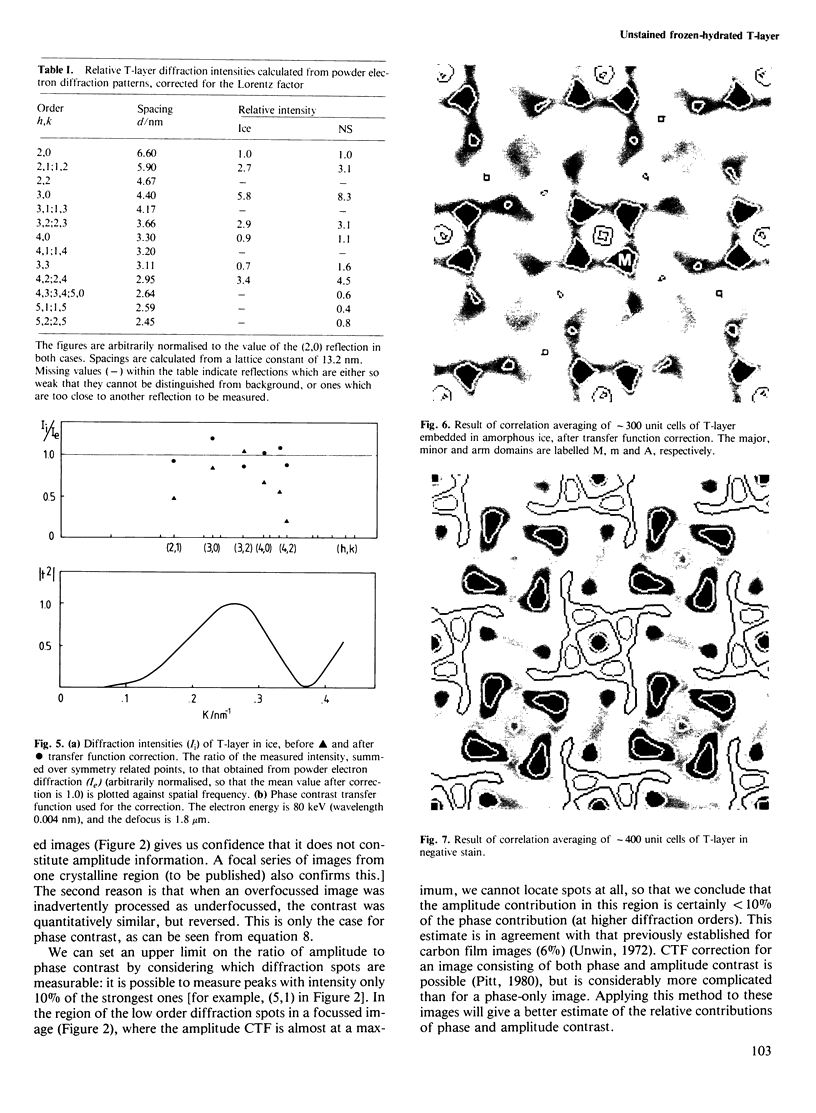


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi U., Smith P. R., Dubochet J., Henry C., Kellenberger E. A study of the structure of the T-layer of Bacillus brevis. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(6):498–522. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akey C. W., Edelstein S. J. Equivalence of the projected structure of thin catalase crystals preserved for electron microscopy by negative stain, glucose or embedding in the presence of tannic acid. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):575–612. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich I., Fox F., Knapek E., Lefranc G., Nachtrieb K., Weyl R., Zerbst H. Improvements in electron microscopy by application of superconductivity. Ultramicroscopy. 1977 Apr;2(2-3):241–249. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(76)91487-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Aebi U., Kellenberger E. Freeze drying and shadowing a two-dimensional periodic specimen. J Ultrastruct Res. 1977 Apr;59(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(77)80030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepault J., Booy F. P., Dubochet J. Electron microscopy of frozen biological suspensions. J Microsc. 1983 Jan;129(Pt 1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matricardi V. R., Moretz R. C., Parsons D. F. Electron diffraction of wet proteins: catalase. Science. 1972 Jul 21;177(4045):268–270. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4045.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Kistler J. Surface reliefs computed from micrographs of heavy metal-shadowed specimens. J Ultrastruct Res. 1977 Oct;61(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(77)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Glaeser R. M. Electron diffraction of frozen, hydrated protein crystals. Science. 1974 Dec 13;186(4168):1036–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4168.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Glaeser R. M. Electron microscopy of frozen hydrated biological specimens. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jun;55(3):448–456. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N. Beef liver catalase structure: interpretation of electron micrographs. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Henderson R. Molecular structure determination by electron microscopy of unstained crystalline specimens. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):425–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]