Abstract
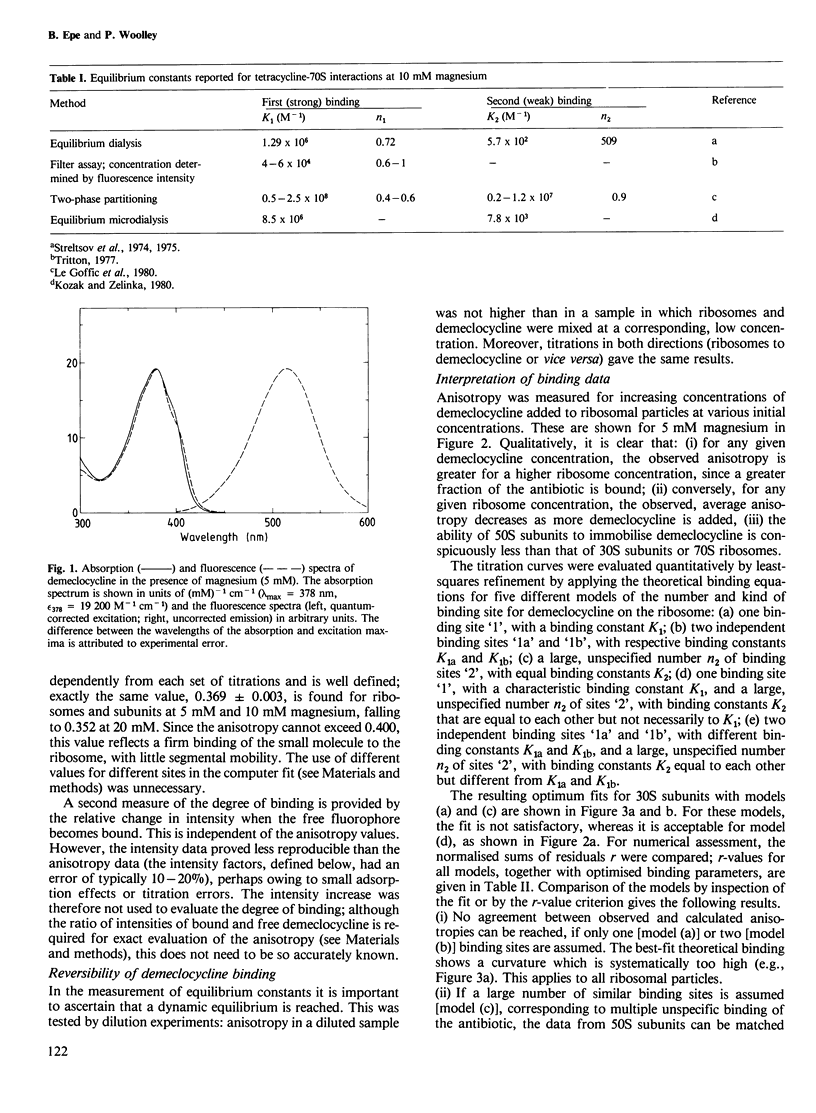
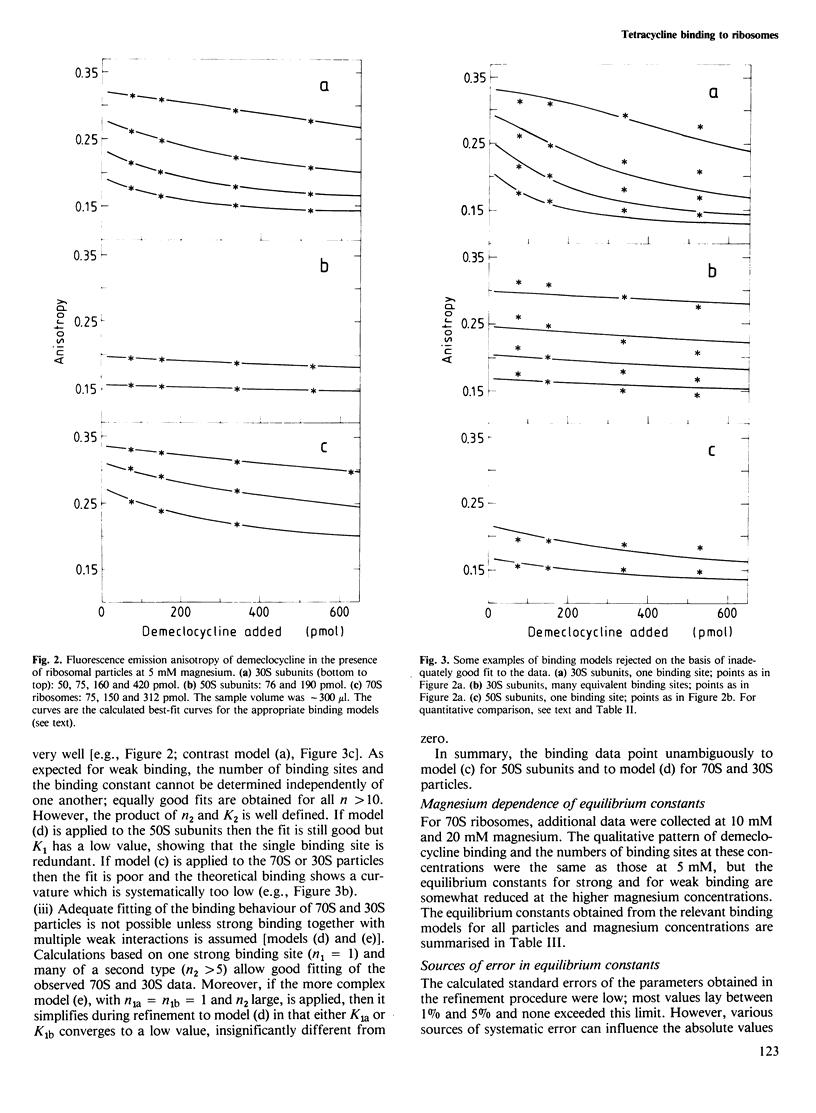
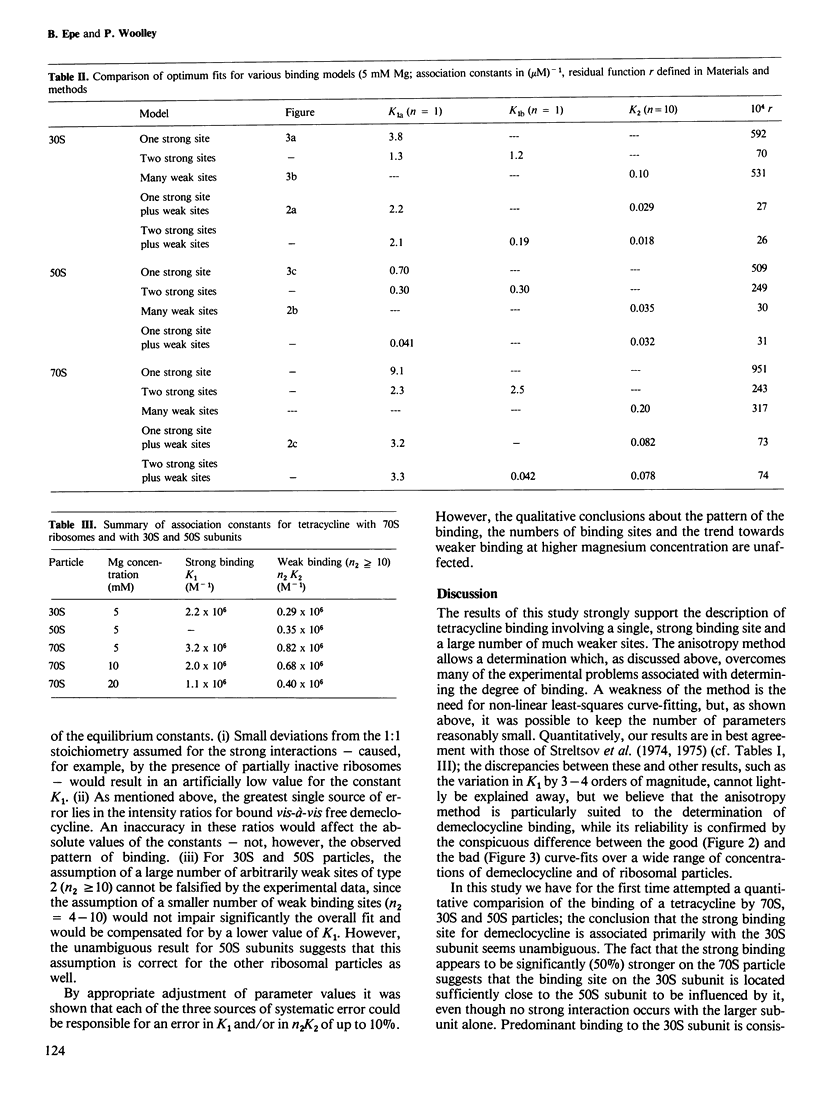
The binding of demeclocycline (6-demethylchlortetracycline) to ribosomes and ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli was investigated by using the fluorescence anisotropy of the antibiotic to determine the extent of binding. Binding data obtained from 70S and 30S particles differed fundamentally from those obtained from 50S subunits: the first two showed a strong, specific interaction while the third did not. In addition, all three particles possessed weak, unspecific binding sites. Computer-aided least-squares analysis of the data yielded the following numbers of sites and equilibrium constants: for 30S, n1 = 1, K1 = 2.2 X 10(6) M-1, n2 K2 = 0.029 X 10(6) M-1; for 50S, n1 = 0, n2 K2 = 0.035 X 10(6) M-1; for 70S, n1 = 1, K1 = 3.2 X 10(6) M-1, n2 K2 = 0.082 X 10(6) M-1. These data resolve current disagreement in the literature and are a prerequisite for quantitative studies of the mechanism of inhibition by tetracycline of protein biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodley J. W., Zieve F. J. On the specificity of the two ribosomal binding sites: studies with tetracycline. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):463–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90587-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Ireland D. S. Structural requirements for tetracycline activity. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1978;15:161–202. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNAMACHER R. H., MANDEL H. G. BINDING OF TETRACYCLINE TO THE 30S RIBOSOMES AND TO POLYURIDYLIC ACID. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 18;20:98–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90954-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connamacher R. H., Mandel H. G. Studies on the intracellular localization of tetracycline in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. E. Tetracycline inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. I. Binding of tetracycline to components of the system. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1917–1923. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1917-1923.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. E. Tetracycline inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. II. Effect of the binding of tetracycline to the components of the system. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.197-203.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijk J., Littlechild J. Purification of ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli under nondenaturing conditions. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:481–502. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUSSGANGER R. Vergleichende mikrobiologische Untersuchungen von Pyrrolidino-methyl-tetracyclin (Reverin) mit Tetracyclinhydrochlorid. Munch Med Wochenschr. 1958 Apr 25;100(17):665–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. A., Cooperman B. S., Strycharz W. A., Williams B. A., Tritton T. R. Photoincorporation of tetracycline into Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 25;118(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. A., Hasan T., Hall C. C., Strycharz W. A., Cooperman B. S. Photoincorporation of tetracycline into Escherichia coli ribosomes. Identification of the major proteins photolabeled by native tetracycline and tetracycline photoproducts and implications for the inhibitory action of tetracycline on protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):359–368. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapke B., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. IV. Classification of ribosomes by subunit interaction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holschuh K., Riesner D., Gassen H. G. Steps of mRNA translocation in protein biosynthesis. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):675–677. doi: 10.1038/293675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goffic F., Moreau N., Langrené S., Pasquier A. Binding of antibiotics to the bacterial ribosome studied by aqueous two-phase partitioning. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 15;107(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R. Dinucleotide codon-anticodon interaction as a minimum requirement for ribosomal aa-tRNA binding: stabilisation by viomycin of aa-tRNA in the A site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5813–5824. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Thach R. E. Inhibition of formylmethionyl-transfer RNA binding to ribosomes by tetracycline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1479–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhäuser K. G., Woolley P., Epe B., Dijk J. Structure of ribosomal protein L6 from Escherichia coli. A fluorescence study. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):587–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strel'tsov S. A., Kukhanova M. K., Gurskii G. V., Kraevskii A. A., Beliavskaia I. V. Sviazyvanie oksitetratsiklina s ribosomami E. coli. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1975 Nov-Dec;9(6):910–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streltsov S. A., Kukhanova M. K., Krayevsky A. A., Beljavskaja I. V., Victorova L. S., Gursky G. V., Treboganov A. D., Gottikh B. P. Binding of oxytetracycline to E coli ribosomes. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Sep;1(7):391–396. doi: 10.1007/BF00385671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritton T. R. Ribosome-tetracycline interactions. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4133–4138. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. P., Cantor C. R. Role of magnesium in the binding of tetracycline to Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G., Smith I. Chromosomal mutations causing resistance to tetracycline in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00267249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



