Abstract
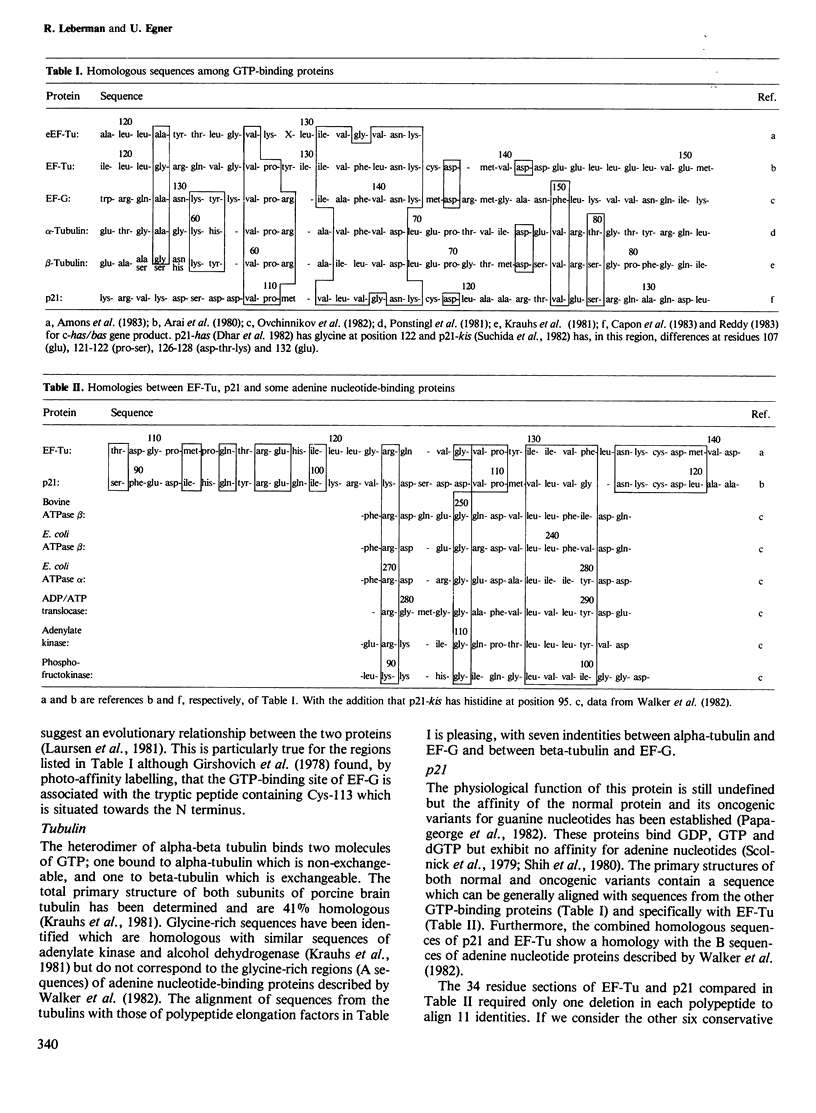
An examination of the available amino acid sequences of GTP-binding proteins has revealed that each contains a polypeptide essentially homologous for all of them. These sequences for elongation factor-Tu (EF-Tu) and the human bladder protein p21 exhibit a singular degree of homology (50%). Chemical and structural evidence indicates that this sequence in EF-Tu constitutes part of the nucleotide-binding site. The homologous sequences may therefore contribute to the GTP-binding sites of the other proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Clark B. F., Duffy L., Jones M. D., Kaziro Y., Laursen R. A., L'Italien J., Miller D. L., Nagarkatti S., Nakamura S. Primary structure of elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1326–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kawakita M., Nakamura S., Ishikawa K., Kaziro Y. Studies on the polypeptide elongation factors form E. coli. VI. Characterization of sulfhydryl groups in EF-Tu and EF-Ts. J Biochem. 1974 Sep;76(3):523–534. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Ellis R. W., Shih T. Y., Oroszlan S., Shapiro B., Maizel J., Lowy D., Scolnick E. Nucleotide sequence of the p21 transforming protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):934–936. doi: 10.1126/science.6287572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. Homology between human bladder carcinoma oncogene product and mitochondrial ATP-synthase. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):262–264. doi: 10.1038/301262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girshovich A. S., Bochkareva E. S., Pozdnyakov V. A., Ovchinnikov Y. A. The GTP-binding center of elongation factor G is located in its N-terminal domain. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 15;85(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. D., Petersen T. E., Nielsen K. M., Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Gausing K., Clark B. F. The complete amino-acid sequence of elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):507–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F., McPherson A., Wang A. H., Rich A. Biochemical and structural studies of the tetragonal crystalline modification of the Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6751–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Gast W. H., Schulz G. E., Leberman R. Low resolution structure of partially trypsin-degraded polypeptide elongation factor, EF-TU, from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 25;117(4):999–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauhs E., Little M., Kempf T., Hofer-Warbinek R., Ade W., Ponstingl H. Complete amino acid sequence of beta-tubulin from porcine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4156–4160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A., L'Italien J. J., Nagarkatti S., Miller D. L. The amino acid sequence of elongation factor Tu of Escherichia coli. The complete sequence. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8102–8109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Hachmann J., Weissbach H. The reactions of the sulfhydryl groups on the elongation factors Tu and Ts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa K., la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Rasmussen K. M., Miller D. L., Clark B. F. High resolution x-ray crystallographic analysis of a modified form of the elongation factor Tu: guanosine diphosphate complex. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 5;125(3):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90406-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Alakhov YuB, Bundulis YuP, Bundule M. A., Dovgas N. V., Kozlov V. P., Motuz L. P., Vinokurov L. M. The primary structure of elongation factor G from Escherichia coli. A complete amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 8;139(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80503-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papageorge A., Lowy D., Scolnick E. M. Comparative biochemical properties of p21 ras molecules coded for by viral and cellular ras genes. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):509–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.509-519.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Krauhs E., Little M., Kempf T. Complete amino acid sequence of alpha-tubulin from porcine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2757–2761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Science. 1983 Jun 3;220(4601):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.6844927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Papageorge A. G., Shih T. Y. Guanine nucleotide-binding activity as an assay for src protein of rat-derived murine sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida N., Ryder T., Ohtsubo E. Nucleotide sequence of the oncogene encoding the p21 transforming protein of Kirsten murine sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):937–939. doi: 10.1126/science.6287573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade M., Laursen R. A., Miller D. L. Amino acid sequence of elongation factor Tu. Sequence of a region containing the thiol group essential for GTP binding. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 15;53(1):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. H., Jr, Arscott L. D., Schulz G. E. Amino acid sequence homology between pig heart lipoamide dehydrogenase and human erythrocyte glutathione reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2199–2201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A., Leberman R. A sulphydryl group is not essential for the binding of GDP to elongation factor Tu. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A., Warren W. F., Leberman R. Structural requirements of the GDP binding site of elongation factor Tu. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):241–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



