Abstract
Background
In 2014, UNAIDS announced the 90-90-90 treatment targets to curb the HIV epidemic by 2020: 90% of people living with HIV know their HIV status, 90% of people who know their HIV status access treatment and 90% of people on treatment have suppressed viral loads. Monitoring and evaluation are needed to track linkage and retention throughout the continuum of care. We propose a systematic review and meta-regression to identify the different methodological approaches used to define the steps in the HIV care cascade in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), where most people with HIV live, and to assess the proportion of participants retained at each step.
Methods
We will include cohort and cross-sectional studies published between 2004 and 2016 that report on the HIV care cascade among adults in SSA. The PubMed, Embase and CINAHL databases will be searched. Two reviewers will independently screen titles and abstracts, assess the full texts for eligibility and extract data. Disagreements will be resolved by consensus or consultation with a third reviewer. We will assess the number and proportion of individuals retained in the HIV care cascade from HIV diagnosis to linkage to care, engagement in pre-ART care, initiation of ART, retention on ART, and viral suppression. The data will be analysed using random effects meta-regression analysis. Publication bias will be assessed by funnel plots.
Discussion
This review will contribute to a better understanding of the HIV care cascade in SSA. It will help programs identify gaps and approaches to improve care and treatment for people living with HIV and reduce HIV transmission.
Systematic review registration
PROSPERO CRD42017055863
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13643-017-0562-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: HIV, HIV care cascade, Antiretroviral therapy, HIV diagnosed, Linkage to care, Viral suppression, HIV care continuum, Systematic review, Meta-analysis, Sub-Saharan Africa
Background
In 2014, UNAIDS proposed the 90-90-90 Fast-Track treatment targets to curb the HIV/AIDS epidemic. These targets stipulate that, by 2020, 90% of people living with HIV worldwide should know their diagnosis, 90% of these people should be on antiretroviral therapy (ART), and 90% of these persons (i.e., 73% of all people living with HIV) should be virally suppressed [1–3]. The HIV care cascade, also known as the HIV care continuum, outlines the sequential steps of HIV care from initial diagnosis to the goal of viral suppression [4, 5] (Fig. 1). To achieve universal access to HIV care and treatment with viral suppression, each HIV-positive individual must progress along this cascade. HIV testing services [6, 7], earlier diagnosis [8, 9], linkage and retention in care [10–12] and earlier ART initiation [13–16] are key components to achieve the 90-90-90 goals [17].
Fig. 1.
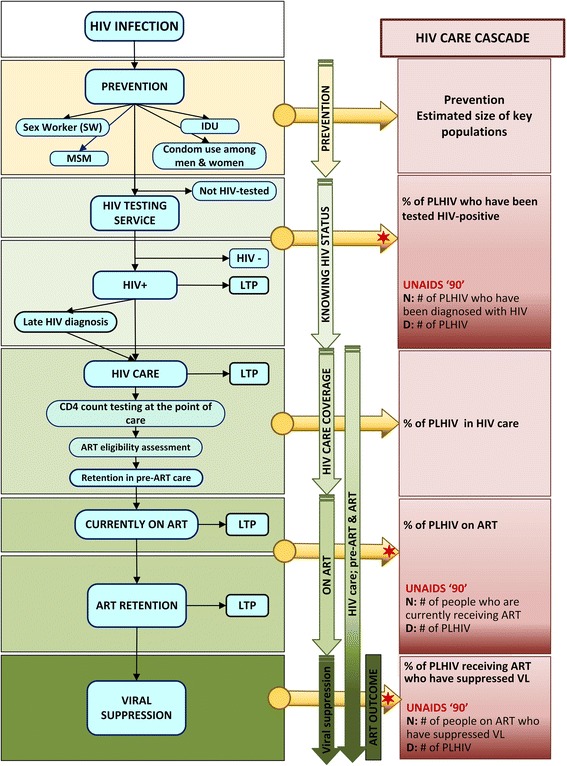
HIV care cascade and assessment of ART eligibility (adapted from WHO guidelines [34]). ART, antiretroviral therapy; IDU, injection drug use; LTP, loss to programme; MSM, men who have sex with men; PLHIV, people living with HIV; VL, viral load
The cascade can be used to evaluate HIV programme performance and serve as a monitoring tool to identify gaps and opportunities for specific interventions to improve outcomes [18]. In sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) and elsewhere, significant gaps remain [19–21], and retention along the HIV care cascade remains a major problem [22–27]. However, studies analysing the HIV care cascade use different methodologies and calculations to construct the cascade. For each element in the cascade, either measured or estimated, definitions vary and methods are often not well described [5]. The use of different measures, for example how retention in HIV care is defined or the threshold for viral suppression, to estimate the cascade stages may affect the results [28]. It is therefore difficult to compare published cascades across regions and calendar periods.
Few studies have evaluated the methods used to define the HIV care cascade in low- and middle-income countries, or in SSA [18]. A previous systematic review from 2014 looking at the whole cascade from HIV testing to viral suppression failed to identify any eligible studies from low-income countries [29]. A more recent review evaluated the cascade based on national estimates but did not include smaller in-depth studies [30]. In SSA, surveys conducted between 2007 and 2011 found that 36% of people in the region had never been tested for HIV [31], and less than 50% of HIV-positive persons knew their HIV status [20]. Focusing on SSA, we aim to perform a systematic review and meta-regression analysis to assess the different methodological approaches used to define the steps in the HIV care cascade and to estimate the numbers or proportion of people retained in each cascade step.
Methods
This systematic review protocol was written following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) guidelines [32]. The PRISMA-P checklist can be found as Additional file 1.
Aims
The first aim of this systematic review is to describe the different concepts and methodologies used in the published literature to define the steps in the HIV care cascade in SSA. The second aim is to obtain comparable measures of the number or proportion of people retained in the different steps of the HIV care cascade, based on the findings from the first aim.
Eligibility criteria
Study designs and setting
We will include cohort and cross-sectional studies with data collected between January 2004 and March 2016 in any country in SSA (Table 1). Studies that examine two or more of the following cascade elements will be included: the number or proportion of persons diagnosed with HIV (first UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment target), linkage of HIV-positive persons to pre-ART care, retention in pre-ART care, initiating ART, remaining on ART (second UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment target), and virological suppression among persons on ART (third UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment target).
Table 1.
Selection criteria
| Criteria | Variables |
|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria | |
| HIV-positive people aged 15 years and older in sub-Saharan Africa | |
| Study period after 01 January 2004 (ART initiation after 01 January 2004) | |
| General population | |
| Reporting on a cascade with two or more elements (HIV diagnosed, linked to care, retained in care, on ART, virally suppressed) | |
| Observational studies: cohort or cross-sectional studies | |
| Published in English, French or Spanish | |
| Exclusion criteria | |
| Publication type | |
| Narrative reviews | |
| Commentaries, editorials or letters | |
| Conference abstracts | |
| Study design | |
| Randomized controlled trials | |
| Qualitative studies | |
| Case series | |
| Simulations or modelling studies | |
| Unclear study design | |
| Study population | |
| Populations outside sub-Saharan Africa | |
| Children | |
| Specific sub-populations (for example patients with tuberculosis, or pregnant women) | |
Population
We will include studies of the general population living with HIV. This will encompass male and female participants living with HIV-1 aged 15 years or older. We will exclude studies of patients with specific co-morbidities such as tuberculosis or opportunistic infections. Studies in patients with HIV-2 will also be excluded. If the HIV type is not specified, HIV-1 will be assumed. We will exclude studies of prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) as the PMTCT care cascade differs substantially from the general HIV care cascade [33, 34]. We will also exclude intervention studies that examine the effectiveness of measures to improve the HIV care continuum.
Outcomes
Primary outcomes
The primary outcome is the concept, methodology and definition used to identify a reported stage of the cascade. We will describe these narratively and classify studies into suitable groups.
Secondary outcomes
The secondary outcomes include the number or proportion of persons retained at each cascade step (see also Fig. 1 and Additional file 2 ):
HIV diagnosis (UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment target)
Linkage to pre-ART care
Retention in pre-ART care
- On ART (UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment target) with
- Start of ART
- Retention on ART
Suppression of viral load (UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment target)
Information sources
Electronic databases
We have conducted a comprehensive literature search with the help of two librarians with expertise in systematic reviews. We restricted the search to articles published in English, French and Spanish between January 2004 and March 2016, since the scale-up of ART in SSA started around 2004 [35, 36]. We performed the searches in PubMed, Embase and CINAHL.
Search strategy
The Medical Subject Headings (MeSH terms) for HIV and AIDS and key terms ‘cascade’, ‘continuum’, ‘linkage to care’, ‘retention in care’ and ‘ART initiation’ were cross-referenced with terms associated with 62 African countries (Additional file 3 shows the detailed search strategy). We will update the search prior to publication to include any additional eligible papers published after March 2016.
Study records
Data management
All records from our PubMed, Embase and CINAHL searches will be combined, uploaded into the reference management software Mendeley (version 1.15.3) and de-duplicated. We will use Microsoft Excel (version 2016 for Windows, Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) to record outcomes of the selection process.
Selection of eligible studies
Two reviewers will independently screen studies in two stages: title/abstract screening, followed by full text screening. A checklist with the eligibility criteria will be developed and pilot-tested on a random sample of 20 studies. Titles and abstracts will then be reviewed against the eligibility criteria by AG and FV. We will obtain full texts of all potentially eligible articles. Two reviewers will independently apply inclusion criteria (Additional file 4) to the full texts. At both screening steps, we will resolve disagreements by consensus, if necessary through discussion with a third reviewer (CM or ME). We will record all discrepancies on Excel spreadsheets, with reasons for inclusion or exclusion. The PRISMA study flow diagram will reflect this process and detail the reasons for exclusion of studies.
Data collection
We will develop a data extraction sheet to guide data collection. This sheet will direct collection of the definition and methods for each step of the cascade, the results of estimations or calculations and sources of data. The sheet will be pilot-tested by two reviewers (AG, CM) on a random sample of 10 articles and revised as needed. Two reviewers will independently read each article and extract the relevant data. Both sets of data will be entered into Epidata version 3.1 (EpiData Association, Denmark). Any discrepancies in the extracted data will be resolved by consensus, in discussion with a third reviewer (CM or ME) if necessary. We will contact study authors to resolve any information that is not clear.
Data items
The data items for extraction will be informed by items reported in the PRISMA statement [37–39]. We will extract the following from included studies:
Study characteristics (authors, year of publication, study period, study population, study design, aim of study, geographic location, duration of follow-up, key finding);
Study setting (location and type of facilities);
Characteristics of study populations (sample size, age, sex, marital status, weight, educational level, employment status, enrolment period, inclusion and exclusion criteria);
Definitions and methods used to construct cascade;
The number or proportion of persons diagnosed with HIV (90-90-90 treatment target), linkage to pre-ART care, retention in pre-ART care, on ART (90-90-90 treatment target), virological suppression (90-90-90 treatment target);
Clinical and laboratory data (CD4 cell counts, viral load, ART regimen, medical circumcision (only men), TB status, other co-infections and comorbidities).
Data synthesis
The main characteristics of included studies will first be narratively synthesized. Summary statistics will be used to describe study characteristics, including means (standard deviations) or medians (interquartile ranges), and frequencies (percentages). For each step of the cascade, we will calculate proportions with exact binomial 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) and present these in forest plots. We will calculate the between-study variance (tau-squared) and p values from tests of between-study heterogeneity. We expect substantial between-study heterogeneity, and the focus of the subsequent analyses will therefore be on the identification and exploration of sources of heterogeneity. We will explore associations between proportions at each step and country, setting (e.g. urban, periurban, rural; health care level, public or private setting) and study characteristics (e.g. study size, sampling frame) using random intercept logistic meta-regression (Binomial-Normal) models. These models avoid the biases that arise when Normal-Normal models (which model the within study variability via normal approximations) are applied to logit or arcsine-square root transformed proportions [40, 41]. Where appropriate, we will use the same models to calculate combined estimates of proportions. All analyses will be done in R version 3.2.3 (R Foundation, Vienna, Austria).
Dealing with missing data
If data are missing in key variables, we will contact the study authors for clarification. A description of missing data will be provided for each study, and we will discuss the possible implications of missing data.
Risk of bias in included studies
Two pairs of reviewers (AG and CM) will assess included studies using ROBINS-I, a tool for assessing risk of bias in nonrandomized studies of interventions for observational studies [42]. The tool will be adapted to the context of this systematic review, and to cross-sectional studies. ROBINS-I contains 34 questions from seven different bias domains. For each study, relevant domains of risk of bias will be graded as low, moderate, serious, critical or no information for risk of bias [43]. Publication bias will be assessed by visually inspecting funnel plot asymmetry and by including study size in the logistic model. The quality assessment will be cross-checked, and any disagreement will be resolved within the review team.
Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis will contribute to a better understanding of the different methodological approaches used in sub-Saharan African countries to define the steps in the HIV care cascade and to estimate the numbers or percentages of people retained at each step of the cascade. We will identify gaps in the cascade and areas for further research. Our results will be useful for the design of strategies for improving the care and treatment of people living with HIV and for reducing HIV transmission. This review will thus be highly relevant to inform health systems interventions and HIV prevention and treatment strategies in sub-Saharan Africa, and low- and middle-income countries in general.
Additional files
PRISMA-P 2015 Checklist. [17 items]. (DOCX 33 kb)
Complete cascade including all steps. A) HIV care cascade as defined by the WHO, B) Assessment of ART eligibility within the HIV care cascade. ART, antiretroviral therapy; D, denominator; LTP*, loss to programme (pre-ART); LTP**, loss to programme (post-ART); N, nominator; PLD, population level denominator; PBD, programme-based denominator. (JPG 5616 kb)
Search strategy (PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL). (PDF 79 kb)
Study eligibility form. (PDF 114 kb)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our librarians Beatrice Minder and Doris Kopp for their assistance with developing the search strategy and Christopher Ritter for editorial assistance. We would like to give special thanks to the MeSH Consortium Team—James Hargreaves (MeSH Consortium Director) as well as the IeDEA Collaboration (International Epidemiologic Database to evaluate AIDS).
Funding
No funding has been received for this protocol; it was funded by intramural funds. FV received support from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The funders had no role in study conception or design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the review.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AIDS
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- ART
Antiretroviral therapy
- CI
Confidence interval
- GRADE
Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation
- HBV
Hepatitis B virus
- HCV
Hepatitis C virus
- HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus
- LMIC
Low- and middle-income countries
- LTFU
Loss to follow-up
- MeSH
Medical subject headings
- PMTCT
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission
- PRISMA-P
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols
- PROSPERO
International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews
- ROBINS-I
Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies - of Interventions
- SSA
Sub-Saharan Africa
- TB
Tuberculosis
- UNAIDS
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
- WHO
World Health Organization
Authors’ contributions
AG and CM were responsible for preparing and registering the protocol. AG, BM and DK contributed to the search strategy. AG, FV, BR, ME and CM provided content expertise and assisted with preparation of the protocol. All authors provided critical revision of the protocol, and read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13643-017-0562-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Aysel Gueler, Email: aysel.gueler@ispm.unibe.ch.
Fiona Vanobberghen, Email: Fiona.Vanobberghen@lshtm.ac.uk.
Brian Rice, Email: Brian.Rice@lshtm.ac.uk.
Matthias Egger, Email: matthias.egger@ispm.unibe.ch.
Catrina Mugglin, Email: catrina.mugglin@ispm.unibe.ch.
References
- 1.Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 90-90-90—an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2014. www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/90-90-90_en_0.pdf. Accessed 14 Aug 2017.
- 2.Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). 90-90-90—On the right track towards the global target. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2016. http://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/90_90_90_Progress_ReportFINAL.pdf. Accessed 14 Aug 2017.
- 3.WHO. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach. Second edition. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/208825/1/9789241549684_eng.pdf. Accessed 9 June 2016. [PubMed]
- 4.Kay ES, Batey DS, Mugavero MJ. The HIV treatment cascade and care continuum: updates, goals, and recommendations for the future. AIDS Res Ther. 2016;13:35. doi: 10.1186/s12981-016-0120-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.IAPAC Guidelines for optimizing the HIV care continuum for adults and adolescents. Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care. 2015;14(Suppl 1):S3–s34. doi: 10.1177/2325957415613442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bradley H, Hall HI, Wolitski RJ, Van Handel MM, Stone AE, LaFlam M, Skarbinski J, Higa DH, Prejean J, Frazier EL, Patel R, Huang P, An Q, Song R, Tang T, et al. Vital signs: HIV diagnosis, care, and treatment among persons living with HIV--United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:1113–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Gardner EM, McLees MP, Steiner JF, Del Rio C, Burman WJ. The spectrum of engagement in HIV care and its relevance to test-and-treat strategies for prevention of HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(6):793–800. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nakagawa F, Lodwick RK, Smith CJ, Smith R, Cambiano V, Lundgren JD, Delpech V, Phillips AN. Projected life expectancy of people with HIV according to timing of diagnosis. AIDS. 2012;26(3):335–343. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32834dcec9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Phanuphak P, Lo Y-R. Implementing early diagnosis and treatment: programmatic considerations. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2015;10(1):69–75. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kranzer K, Govindasamy D, Ford N, Johnston V, Lawn SD. Quantifying and addressing losses along the continuum of care for people living with HIV infection in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. J Int AIDS Soc. 2012;15:17383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Rosen S, Fox MP. Retention in HIV care between testing and treatment in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2011;8:e1001056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Govindasamy D, Ford N, Kranzer K. Risk factors, barriers and facilitators for linkage to antiretroviral therapy care: a systematic review. AIDS. 2012;26(16):2059–2067. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283578b9b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cohen MS, Chen YQ, McCauley M, Gamble T, Hosseinipour MC, Kumarasamy N, Hakim JG, Kumwenda J, Grinsztejn B, Pilotto JHS, et al. Prevention of HIV-1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. New Engl J Med. 2011;365(6):493–505. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1105243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Egger M, May M, Chene G, Phillips AN, Ledergerber B, Dabis F, Costagliola D, Monforte AD, de Wolf F, Reiss P, et al. Prognosis of HIV-1-infected patients starting highly active antiretroviral therapy: a collaborative analysis of prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360(9327):119–129. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lahuerta M, Lima J, Elul B, Okamura M, Alvim MF, Nuwagaba-Biribonwoha H, Horowitz D, Fernandes R, Assan A, Abrams EJ, et al. Patients enrolled in HIV care in Mozambique: baseline characteristics and follow-up outcomes. Jaids-J Acq Imm Def. 2011;58(3):E75–E86. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31822ac0a9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Forrest J. HIV care continuum in Rwanda [MOSA3607 Non-Commercial Satellite] In: 21st International AIDS Conference (AIDS 2016) Knowing your epidemic and knowing your response - maximising routinely collected data to measure and monitor HIV epidemics in sub-Saharan Africa. Canada: Precision Global Health. http://programme.aids2016.org/PAGMaterial/PPT/4934_12196/Sabin,%20AIDS%202016%20Rwanda%20HIV%20care%20Continuum%2090-90-90%20targets%20FINAL.pptx. Accessed 14 Aug 2017.
- 17.WHO. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. http://www.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/85321/1/9789241505727_eng.pdf. Accessed 14 Aug 2017. [PubMed]
- 18.McNairy ML, Lamb MR, Abrams EJ, Elul B, Sahabo R, Hawken MP, Mussa A, Zwede A, Justman J, El-Sadr WM, et al. Use of a comprehensive HIV care cascade for evaluating HIV program performance: findings from 4 sub-Saharan African countries. Jaids-J Acq Imm Def. 2015;70(2):E44–E51. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Levi J, Raymond A, Pozniak A, Vernazza P, Kohler P, Hill A. Can the UNAIDS 90-90-90 target be achieved? A systematic analysis of national HIV treatment cascades. BMJ Global Health. 2016;1(2):e000010. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2015-000010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). The UNAIDS gap report. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2014. http://files.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/unaidspublication/2014/UNAIDS_Gap_report_en.pdf. Accessed 14 Aug 2017.
- 21.Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). How AIDS changed everything. MDG 6: 15 years, 15 lessons of hope from the AIDS response. Geneva: UNAIDS. 2015.
- 22.Duda SN, Farr AM, Lindegren ML, Blevins M, Wester CW, Wools-Kaloustian K, Ekouevi DK, Egger M, Hemingway-Foday J, Cooper DA, et al. Characteristics and comprehensiveness of adult HIV care and treatment programmes in Asia-Pacific, sub-Saharan Africa and the Americas: results of a site assessment conducted by the international epidemiologic databases to evaluate AIDS (IeDEA) collaboration. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Govindasamy D, Kranzer K, Ford N. Strengthening the HIV cascade to ensure an effective future ART response in sub-Saharan Africa. T Roy Soc Trop Med H. 2014;108(1):1–3. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trt105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sharma M, Ying R, Tarr G, Barnabas R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of community and facility-based HIV testing to address linkage to care gaps in sub-Saharan Africa. Nature. 2015;528(7580):S77–S85. doi: 10.1038/nature16044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nsanzimana S, Kanters S, Remera E, Forrest JI, Binagwaho A, Condo J, Mills EJ. HIV care continuum in Rwanda: a cross-sectional analysis of the national programme. Lancet Hiv. 2015;2(5):E208–E215. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(15)00024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Maman D, Chilima B, Masiku C, Ayouba A, Masson S, Szumilin E, Peeters M, Ford N, Heinzelmann A, Riche B, et al. Closer to 90-90-90. The cascade of care after 10 years of ART scale-up in rural Malawi: a population study. J Int AIDS Soc. 2016;19(1):20673. doi: 10.7448/IAS.19.1.20673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maman D, Zeh C, Mukui I, Kirubi B, Masson S, Opolo V, Szumilin E, Riche B, Etard JF. Cascade of HIV care and population viral suppression in a high-burden region of Kenya. AIDS. 2015;29(12):1557–1565. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nosyk B, Montaner JS, Colley G, Lima VD, Chan K, Heath K, Yip B, Samji H, Gilbert M, Barrios R, et al. The cascade of HIV care in British Columbia, Canada, 1996-2011: a population-based retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70254-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Medland NA, McMahon JH, Chow EP, Elliott JH, Hoy JF, Fairley CK. The HIV care cascade: a systematic review of data sources, methodology and comparability. J Int AIDS Soc. 2015;18:20634. doi: 10.7448/IAS.18.1.20634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Granich R, Gupta S, Hall I, Aberle-Grasse J, Hader S, Mermin J. Status and methodology of publicly available national HIV care continua and 90-90-90 targets: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2017;14(4):e1002253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). Global Report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2013. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2013. http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiology/2013/gr2013/UNAIDS_Global_Report_2013_en.pdf. Accessed 14 Aug 2017.
- 32.Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA, PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;349:g7647. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.McNairy ML, Teasdale CA, El-Sadr WM, Mave V, Abrams EJ. Mother and child both matter: reconceptualizing the prevention of mother-to-child transmission care continuum. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2015;10(6):403–410. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.WHO. Consolidated strategic information guidelines for HIV in the health sector may 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/164716/1/9789241508759_eng.pdf. Accessed 14 Aug 2017. [PubMed]
- 35.Johnson LF. Access to antiretroviral treatment in South Africa, 2004–2011. S Afr J Hiv Med. 2012;13(1):22–7.
- 36.Egger M, Boulle A, Schechter M, Miotti P. Antiretroviral therapy in resource-poor settings: scaling up inequalities? Int J Epidemiol. 2005;34(3):509–512. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyi110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Moher D, Tetzlaff J, Tricco AC, Sampson M, Altman DG. Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2007;4(3):447–455. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Turner L, Galipeau J, Garritty C, Manheimer E, Wieland LS, Yazdi F, Moher D. An evaluation of epidemiological and reporting characteristics of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) systematic reviews (SRs). PLoS One. 2013;8:e53536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 40.Hamza TH, van Houwelingen HC, Stijnen T. The binomial distribution of meta-analysis was preferred to model within-study variability. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stijnen T, Hamza TH, Ozdemir P. Random effects meta-analysis of event outcome in the framework of the generalized linear mixed model with applications in sparse data. Stat Med. 2010;29(29):3046–3067. doi: 10.1002/sim.4040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Henry D, Altman DG, Ansari MT, Boutron I, Carpenter JR, Chan A-W, Churchill R, Deeks JJ, Hróbjartsson A, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 43.Sterne JAC, Higgins JPT, R.G. E, Reeves BC: Risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions (ROBINS-I): detailed guidance, updated 12 October 2016. Available from http://www.riskofbias.info. Bmj-Brit Med J. 2016;355.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
PRISMA-P 2015 Checklist. [17 items]. (DOCX 33 kb)
Complete cascade including all steps. A) HIV care cascade as defined by the WHO, B) Assessment of ART eligibility within the HIV care cascade. ART, antiretroviral therapy; D, denominator; LTP*, loss to programme (pre-ART); LTP**, loss to programme (post-ART); N, nominator; PLD, population level denominator; PBD, programme-based denominator. (JPG 5616 kb)
Search strategy (PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL). (PDF 79 kb)
Study eligibility form. (PDF 114 kb)
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.


