Abstract
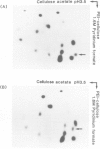
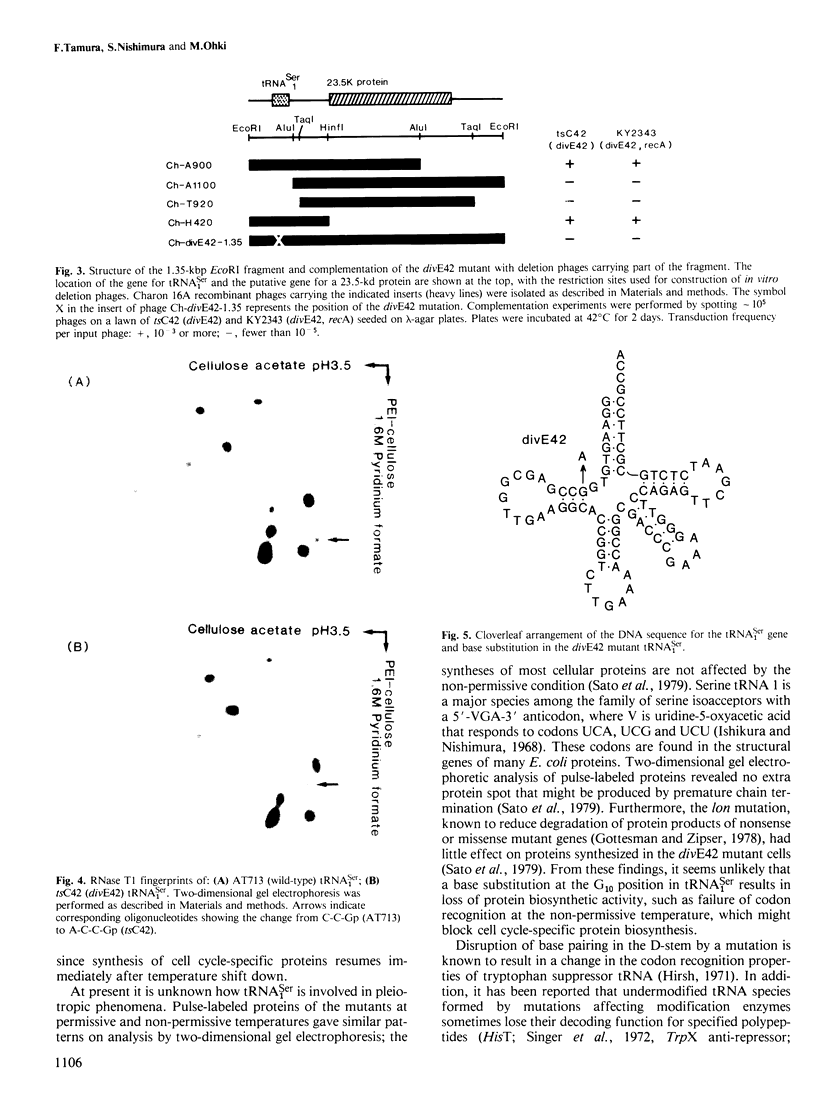
The temperature-sensitive divE mutant of Escherichia coli cannot synthesize certain membrane and cytoplasmic proteins at a non-permissive temperature. Growth of the mutant cells is arrested at a specific stage of the cell cycle when exposed to the non-permissive conditions, suggesting that the divE mutant possesses a defect in cell division control. From sequence determination of a cloned 1.35-kbp DNA fragment that complements the temperature-sensitive divE42 mutation, we characterized two genes in the segment ; one for tRNASer1 and the other for a 23 500 dalton protein. In parallel experiments we cloned the homologous 1.35-kbp DNA fragment from the divE42 mutant and determined its entire nucleotide sequence. Comparison of the two sequences showed that the mutation site is located not in the protein gene, but in the tRNA gene, where A10 is replaced by G10 in the D-stem. Lambda transducing phages carrying the subcloned tRNASer1 gene complemented the divE42 mutation, thereby confirming the conclusion obtained from sequence analyses of the fragments. This finding indicates that tRNASer1 is specifically involved in regulation of cell cycle-specific protein synthesis, coupled with an important step in the process of cell division, or that usage of serine tRNA is functionally specific for the biosynthesis of certain proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd A., Holland I. B. Protein d, an iron-transport protein induced by filtration of cultures of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Yarus M., Soll L. The effect of an Escherichia coli regulatory mutation on transfer RNA structure. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Zipser D. Deg phenotype of Escherichia coli lon mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):844–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.844-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E. Separation of 32P-labelled ribonucleic acid components. The use of polyethylenimine-cellulose (TLC) as a second dimension in separating oligoribonucleotides of '4.5 S' and 5 S from E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D. Tryptophan transfer RNA as the UGA suppressor. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):439–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Dahlberg J. E. Small ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. I. Characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5024–5032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Ozeki H. Gross map location of Escherichia coli transfer RNA genes. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):419–446. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Shimura Y., Sakano H., Ozeki H. Precursor molecules of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs accumulated in a temperature-sensitive mutant. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):69–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikura H., Nishimura S. Fractionation of serine transfer ribonucleic acids from Escherichia coli and their coding properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90336-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikura H., Yamada Y., Nishimura S. The nucleotide sequence of a serine tRNA from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jul 15;16(1):68–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80688-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki M., Sato S. Regulation of expression of lac operon by a novel function essential for cell growth. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):654–656. doi: 10.1038/253654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oki M., Mitsui H. Defective membrane synthesis in an E. coli mutant. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):64–66. doi: 10.1038/252064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieczenik G., Barrell B. G., Gefter M. L. Bacteriophage phi 80-induced low molecular weight RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):152–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Ohki M., Yura T., Ito K. Genetic studies of an Escherichia coli K-12 temperature-sensitive mutant defective in membrane protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):305–313. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.305-313.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C. E., Smith G. R., Cortese R., Ames B. N. [Mutant tRNA His ineffective in repression and lacking two pseudouridine modifications]. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):72–74. doi: 10.1038/newbio238072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamato I., Anraku Y., Ohki M. A pleiotropic defect of membrane synthesis in a thermosensitive mutant tsC42 of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8584–8589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wachter R., Fiers W. Preparative two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of 32 P-labeled RNA. Anal Biochem. 1972 Sep;49(1):184–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]