Abstract
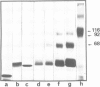
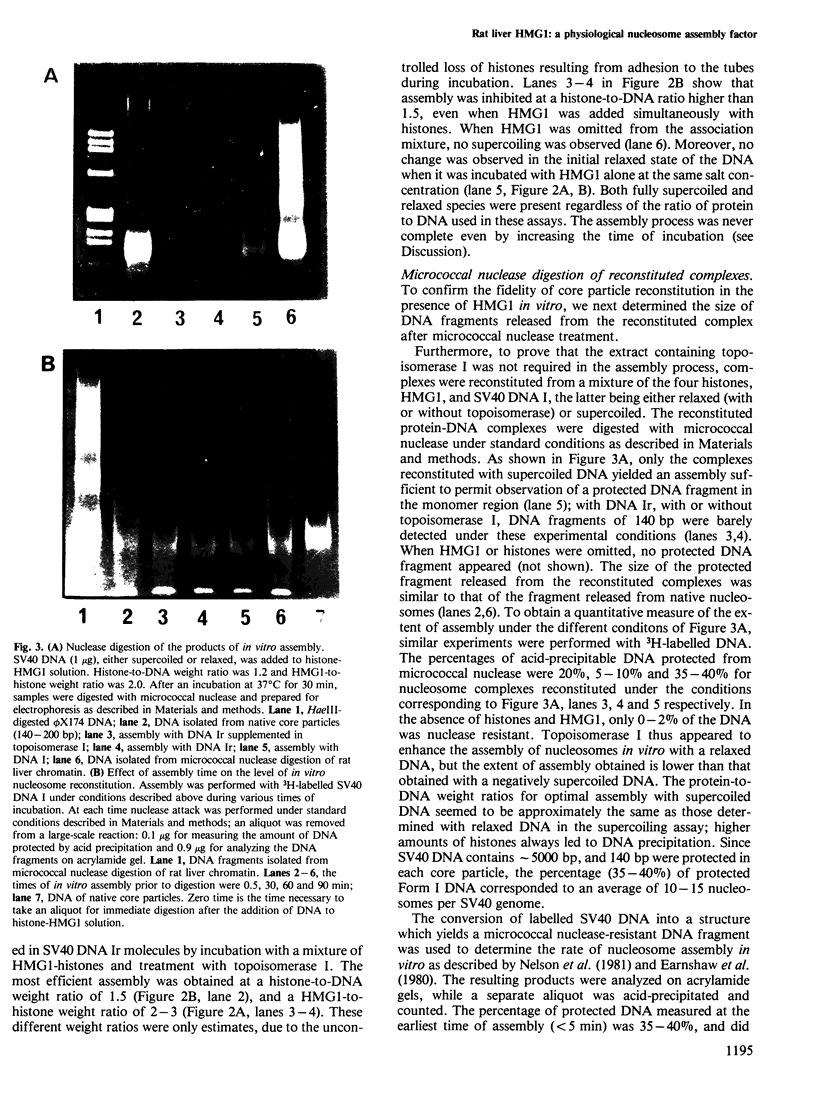
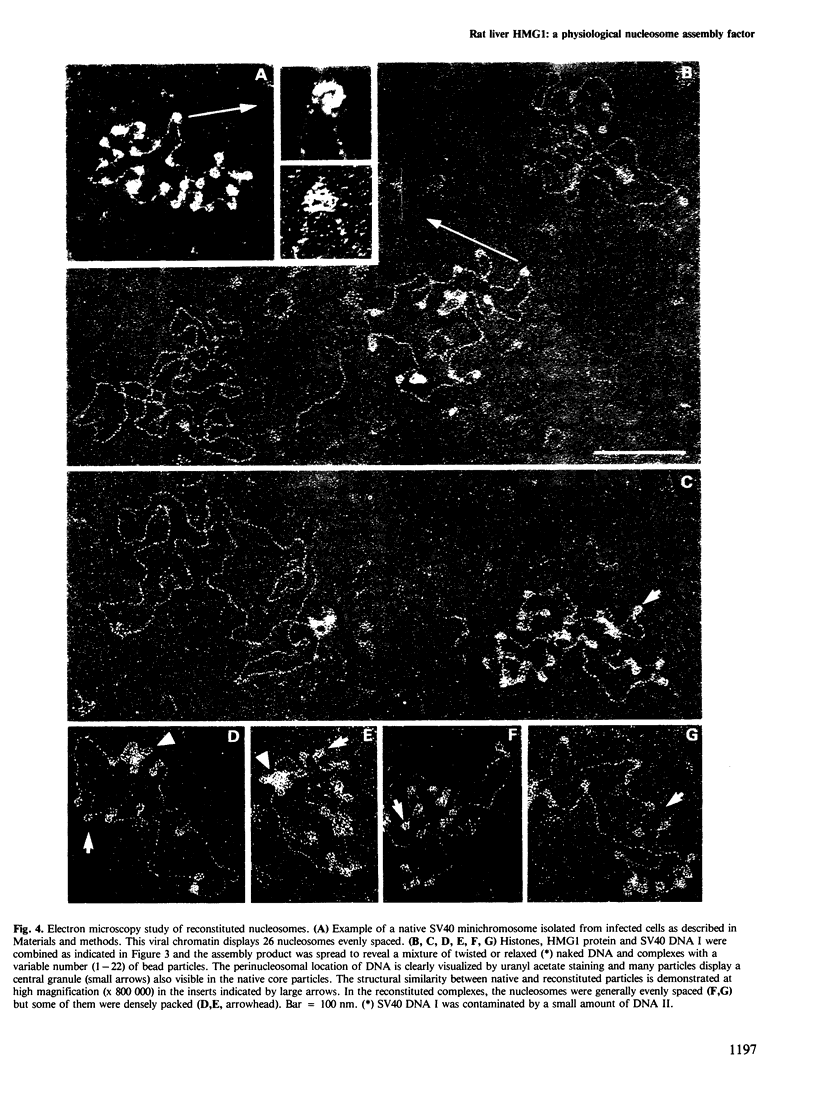
Incubation of rat liver single-stranded DNA-binding protein HMG1 with the four core histones at 0.15 M NaCl favors histone association primarily into tetramers and, to a lesser extent, into octamers. The assembly of pre-formed histone-HMG1 complexes with DNA yields nucleosome-like subunits which satisfy most of the criteria defining native core particles: (i) the circular DNA extracted from the complexes is supercoiled indicating that the initially relaxed DNA acquired superhelical turns during complex formation in the presence of topoisomerase I; (ii) the digestion of the complexes with micrococcal nuclease yields a DNA fragment of approximately 140 bp in length; (iii) electron microscopy of the reconstituted complexes shows a beaded structure with the DNA wrapped around the histone cores, leading to a reduction in the contour length of the genome compared with free DNA. Moreover, in the presence of HMG1, nucleosome assembly occurs rapidly at 0.15 M NaCl. Therefore, in addition to its DNA-binding properties, HMG1 mediates the assembly of nucleosomes in vitro under conditions of physiological ionic strength. The possible involvement of these properties in the DNA replication process is discussed.
Full text
PDF
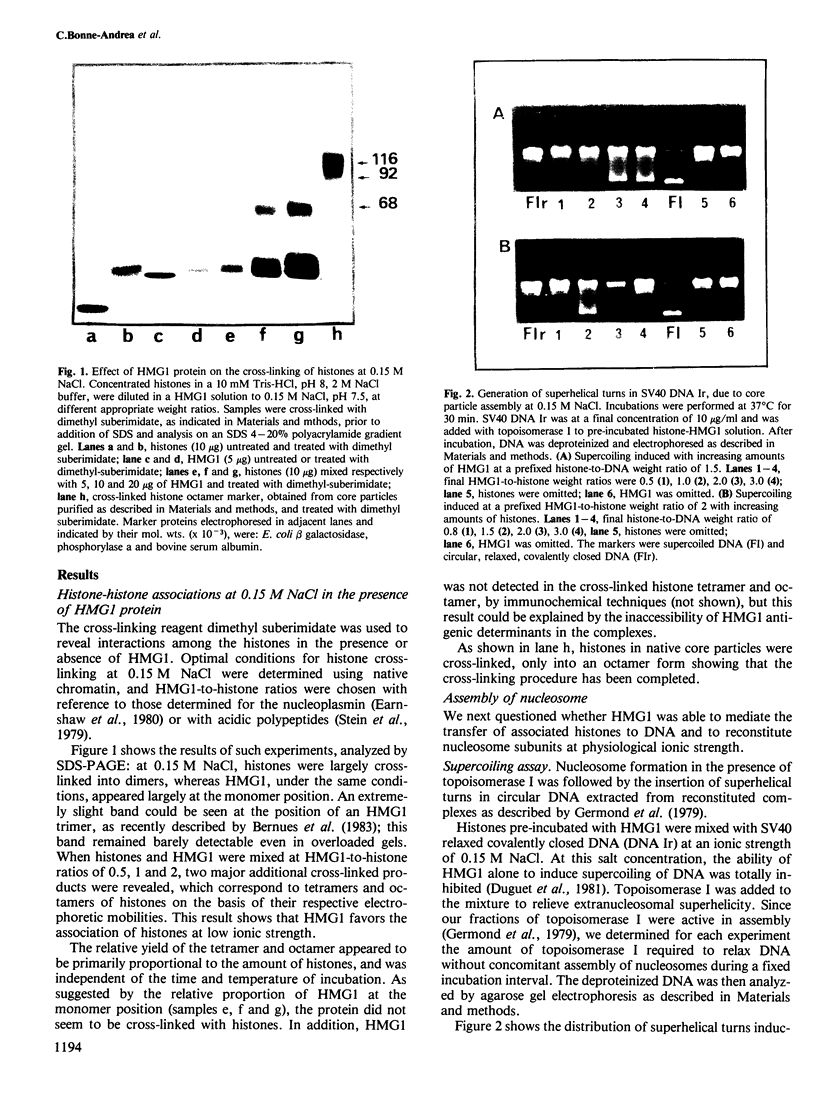



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernués J., Querol E., Martinez P., Barris A., Espel E., Lloberas J. Detection by chemical cross-linking of interaction between high mobility group protein 1 and histone oligomers in free solution. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11020–11024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne C., Duguet M., de Recondo A. M. Rat liver DNA binding proteins: physiological variations. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80517-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne C., Sautiere P., Duguet M., de Recondo A. M. Identification of a single-stranded DNA binding protein from rat liver with high mobility group protein 1. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2722–2725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Technique d'isolement des noyaux cellulaires basée sur leur densité. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1957;39(12):1521–1533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballo M., Puigdomènech P., Palau J. DNA and histone H1 interact with different domains of HMG 1 and 2 proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1759–1764. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Turner C. H., Mayes E., Crane-Robinson C. Conformation and domain structure of the non-histone chromosomal proteins, HMG 1 and 2. Isolation of two folded fragments from HMG 1 and 2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., McConaughy B. L. Purification and characterization of the DNA untwisting enzyme from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4638–4642. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Replication of eukaryotic chromosomes: a close-up of the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:627–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Ducommun M., Zollinger M., Kellenberger E. A new preparation method for dark-field electron microscopy of biomacromolecules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Bonne C., de Recondo A. M. Single-strand deoxyribonucleic acid binding protein from rat liver changes the helical structure of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3598–3603. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Soussi T., Rossignol J. M., Méchali M., De Recondo A. M. Stimulation of rat liver alpha- and beta-type DNA polymerases by an homologous DNA-unwinding protein. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., de Recondo A. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid unwinding protein isolated from regenerating rat liver. Physical and functional properties. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1660–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Honda B. M., Laskey R. A., Thomas J. O. Assembly of nucleosomes: the reaction involving X. laevis nucleoplasmin. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90474-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Rouvière-Yaniv J., Yaniv M., Brutlag D. Nicking-closing enzyme assembles nucleosome-like structures in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3779–3783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Sanders C., Johns E. W. A new group of chromatin-associated proteins with a high content of acidic and basic amino acids. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):14–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Rill R. L. Circular dichroism, thermal denaturation, and deoxyribonuclease I digestion studies of nucleosomes highly enriched in high mobility group proteins HMG 1 and HMG 2. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1042–1046. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Shires A., Tanphaichitr N., Chalkley R. Modifications to histones immediately after synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Finch J. T. Nucleosomes are assembled by an acidic protein which binds histones and transfers them to DNA. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):416–420. doi: 10.1038/275416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Wiegand R., Brutlag D. Ribonucleic acid and other polyanions facilitate chromatin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2594–2601. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palter K. B., Foe V. E., Alberts B. M. Evidence for the formation of nucleosome-like histone complexes on single-stranded DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):451–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeck G. R., Isackson P. J., Teller D. C. Domain structure in high molecular weight high mobility group nonhistone chromatin proteins. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):76–78. doi: 10.1038/300076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Jorcano J. L., Eder G., Lurz R. In vitro core particle and nucleosome assembly at physiological ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3284–3288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Allfrey V. G. Processing of newly synthesized histone molecules. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):117–128. doi: 10.1126/science.1166303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter K. V., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Interactions of a purified non-histone chromosomal protein with DNA and histone. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):263–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Isenberg I. Interactions between the subfractons of calf thymus H1 and nonhistone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4242–4247. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Whitlock J. P., Jr, Bina M. Acidic polypeptides can assemble both histones and chromatin in vitro at physiological ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5000–5004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Nedospasov S. A., Schmatchenko V. V., Bakayev V. V., Chumackov P. M., Georgiev G. P. Compact form of SV40 viral minichromosome is resistant to nuclease: possible implications for chromatin structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3303–3325. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Gooderham K., Hastings J. R., Mayes E., Johns E. W. The primary structures of non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG 1 and 2. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Han S., Wong M. L. Assembly of newly replicated chromatin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]