Abstract
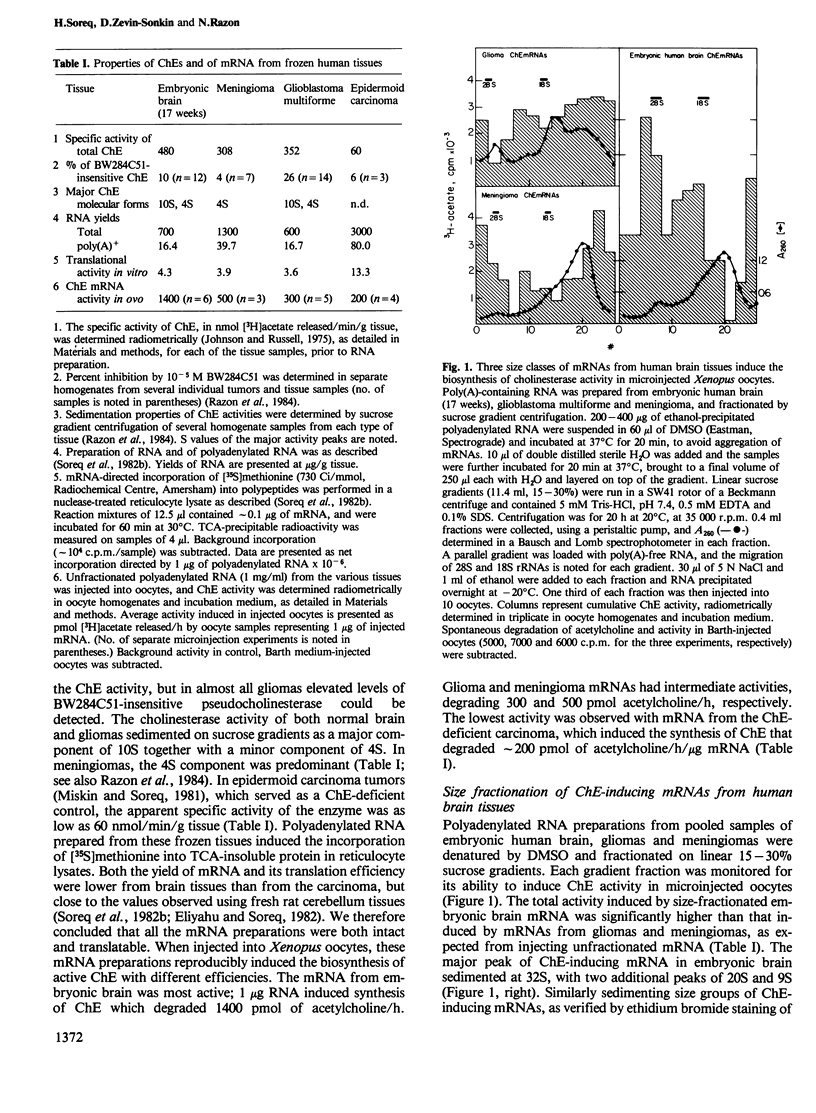
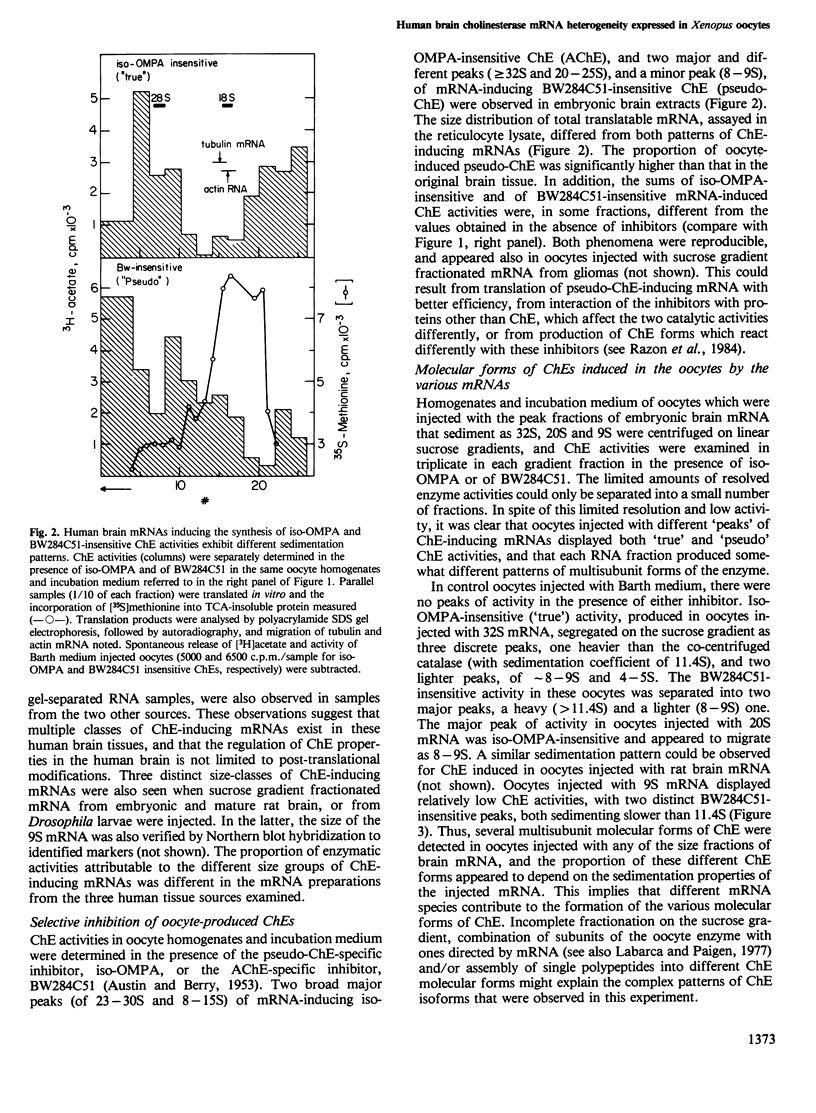
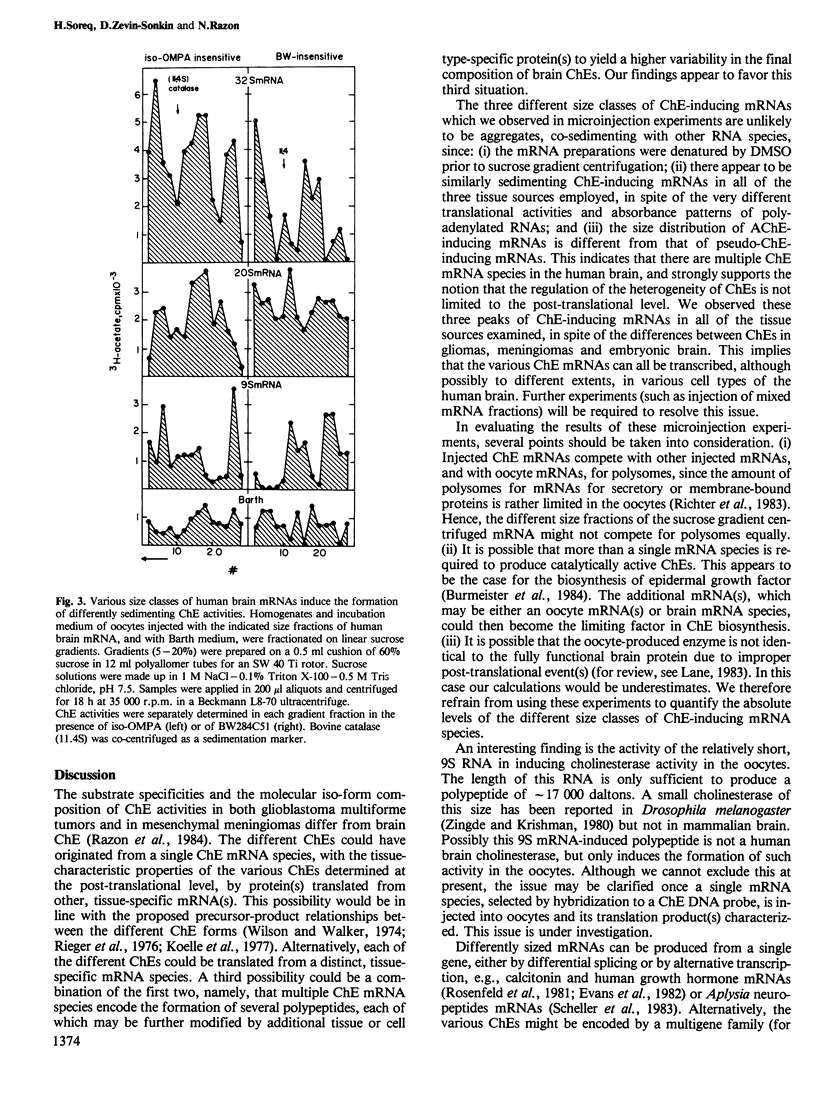
To resolve the origin(s) of the molecular heterogeneity of human nervous system cholinesterases (ChEs), we used Xenopus oocytes, which produce biologically active ChE when microinjected with unfractionated brain mRNA. The RNA was prepared from primary gliomas, meningiomas and embryonic brain, each of which expresses ChE activity with distinct substrate specificities and molecular forms. Sucrose gradient fractionation of DMSO-denatured mRNA from these sources revealed three size classes of ChE-inducing mRNAs, sedimenting at approximately 32S, 20S and 9S. The amounts of these different classes of ChE-inducing mRNAs varied between the three tissue sources examined. To distinguish between ChEs produced in oocytes and having different substrate specificities, their activity was determined in the presence of selective inhibitors. Both 'true' (acetylcholine hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.7) and 'pseudo' (acylcholine acylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.8) multimeric cholinesterase activities were found in the mRNA-injected oocytes. Moreover, human brain mRNAs inducing 'true' and 'pseudo' ChE activities had different size distribution, indicating that different mRNAs might be translated into various types of ChEs. These findings imply that the heterogeneity of ChEs in the human nervous system is not limited to the post-translational level, but extends to the level of mRNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTIN L., BERRY W. K. Two selective inhibitors of cholinesterase. Biochem J. 1953 Jul;54(4):695–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. A., Brimijoin S. Divergent regulation of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in tissues of the rat. J Neurochem. 1982 May;38(5):1393–1403. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Soreq H. Degranulation of rat cerebellum induces selective variations in gene expression. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):313–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Amara S. G., Rosenfeld M. G. RNA processing regulation of neuroendorcrine gene expression. DNA. 1982;1(4):323–328. doi: 10.1089/dna.1982.1.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr Pseudocholinesterase staining in the primary visual pathway of the macaque monkey. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):439–442. doi: 10.1038/299439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W. Multiple forms of acetylcholinesterase and their distribution in endplate and non-endplate regions of rat diaphragm muscle. J Neurobiol. 1973;4(4):343–361. doi: 10.1002/neu.480040404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedrzejczyk J., Silman I., Lyles J. M., Barnard E. A. Molecular forms of the cholinesterases inside and outside muscle endplates. Biosci Rep. 1981 Jan;1(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF01115148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle W. A., Smyrl E. G., Ruch G. A., Siddons V. E., Koelle G. B. Effect of protection of butyrylcholinesterase on regeneration of ganglionic acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1977 Feb;28(2):307–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. MRNA-directed synthesis of catalytically active mouse beta-glucuronidase in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4462–4465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D. The fate of genes, messengers, and proteins introduced into Xenopus oocytes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:89–116. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60580-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P. G. Comparative localization of acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase during morphogenesis of the chicken brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6413–6417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Razon N., Bartal A. D., Yarden Y., Schlessinger J., Soreq H. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):753–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meedel T. H., Whittaker J. R. Development of translationally active mRNA for larval muscle acetylcholinesterase during ascidian embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Soreq H. Microinjected Xenopus oocytes synthesize active human plasminogen activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3355–3363. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Evers D. C., Smith L. D. The recruitment of membrane-bound mRNAs for translation in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2614–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger F., Faivre-Bauman A., Benda P., Vigny M. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase: their de novo synthesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 1976 Nov;27(5):1059–1063. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb00308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Amara S. G., Roos B. A., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Altered expression of the calcitonin gene associated with RNA polymorphism. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):63–65. doi: 10.1038/290063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Synthesis, transport and fate of acetylcholinesterase in cultured chick embryos muscle cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Synthesis, transport, and fate of acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholine receptors in cultured muscle. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;91:259–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Jackson J. F., McAllister L. B., Rothman B. S., Mayeri E., Axel R. A single gene encodes multiple neuropeptides mediating a stereotyped behavior. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):7–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silman I., di Giamberardino L., Lyles L., Couraud J. Y., Barnard E. A. Parallel regulation of acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase in normal, denervated and dystrophic chicken skeletal muscle. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):160–162. doi: 10.1038/280160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Miskin R. Secreted proteins in the medium of microinjected Xenopus oocytes are degraded by oocyte proteases. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Parvari R., Silman I. Biosynthesis and secretion of catalytically active acetylcholinesterase in Xenopus oocytes microinjected with mRNA from rat brain and from Torpedo electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Gisiger V., Massoulié J. "Nonspecific" cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in rat tissues: molecular forms, structural and catalytic properties, and significance of the two enzyme systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. W., Walker C. R. Regulation of newly synthesized acetylcholinesterase in muscle cultures treated with diisopropylfluorophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


