Abstract
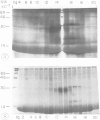
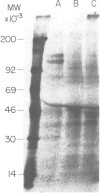
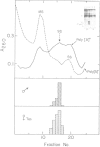
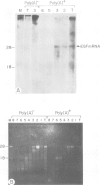
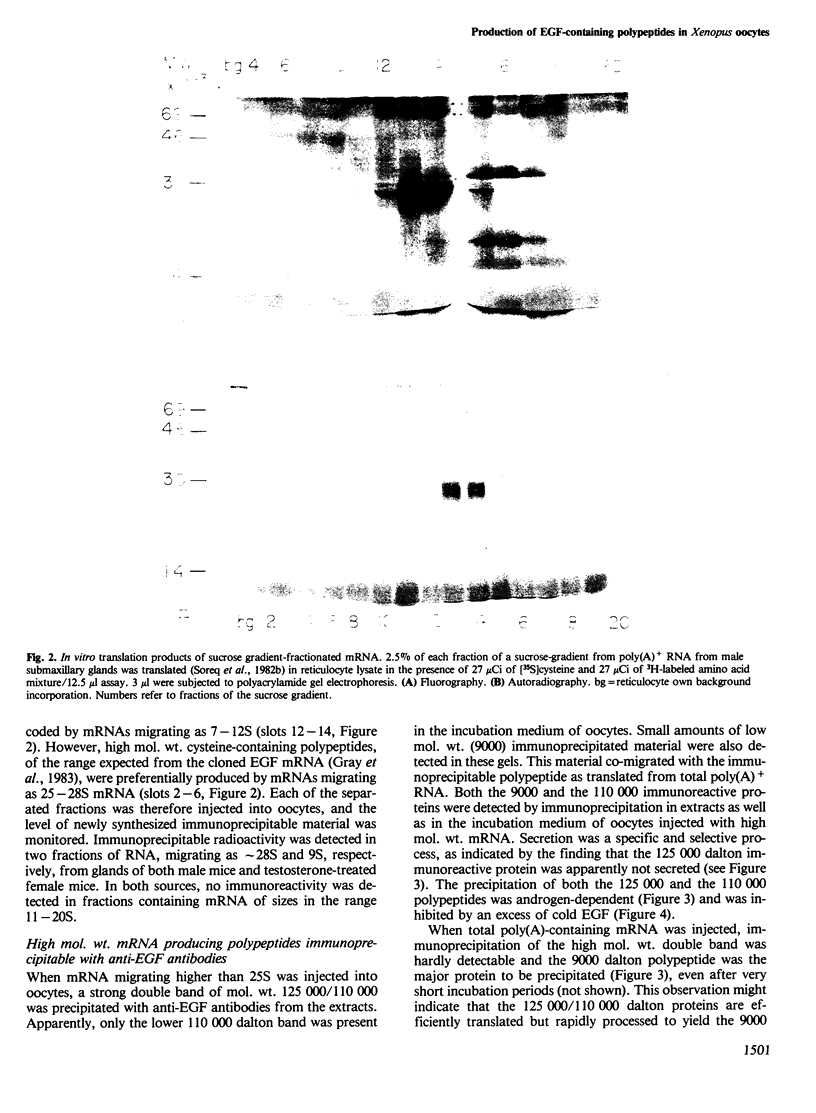
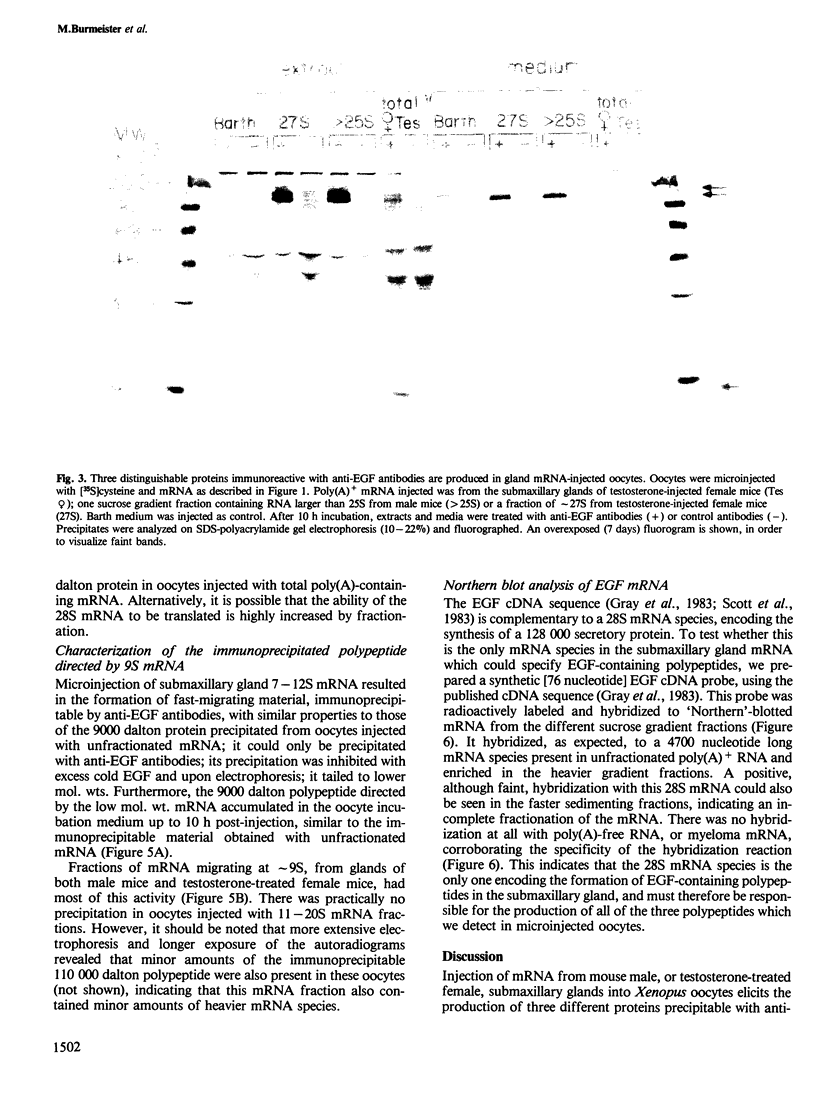
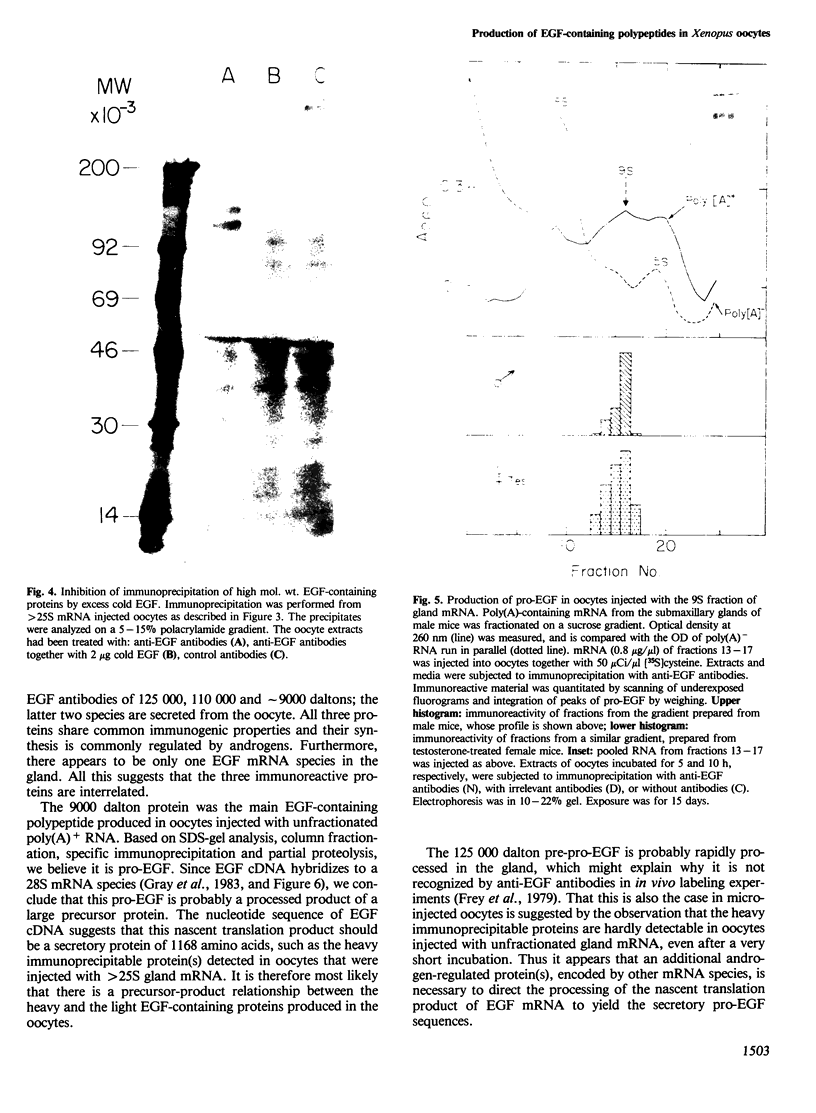
The biosynthesis of epidermal growth factor (EGF), a 6045 dalton mitogen produced in the mouse submaxillary gland under androgen regulation, was studied using Xenopus oocytes. Microinjection of total, unfractionated gland mRNA together with [35S]cysteine resulted in the production of a secretory polypeptide of approximately 9000 daltons, specifically immunoprecipitable with anti-EGF antibodies. A minor amount of a similarly immunoreactive 9000 dalton secretory polypeptide was produced from the sucrose gradient 9S fraction of gland mRNA. Other, more intensely labeled polypeptides, a cytoplasmic 125 000 dalton and a secretory 110 000 dalton protein were immunoprecipitated from oocytes injected with the greater than 25S mRNA fraction. The biosynthesis of both can hardly be detected in oocytes injected with unfractionated mRNA. All three polypeptides are produced under androgen regulation and share common immunoreactive properties. Northern blot analysis using a 76 nucleotide synthetic EGF cDNA probe revealed hybridization with a single 28S mRNA species. This, and the apparent interrelation between the three polypeptides, suggest that a gland-specific processing protein, encoded by a 9S mRNA, is required to produce the 9000 dalton pro-EGF from the nascent translation product of EGF mRNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bravo R., Salazar I., Allende J. E. Amino acid uptake in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Nov;103(1):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton L. E., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor in mouse saliva. Rapid isolation procedures for and characterization of 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7807–7812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byyny R. L., Orth D. N., Cohen S., Doyne E. S. Epidermal growth factor: effects of androgens and adrenergic agents. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):776–782. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byyny R. L., Orth D. N., Cohen S. Radioimmunoassay of epidermal growth factor. Endocrinology. 1972 May;90(5):1261–1266. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-5-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Morser J. Export of proteins from oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):517–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P., Forand R., Maciag T., Shooter E. M. The biosynthetic precursor of epidermal growth factor and the mechanism of its processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6294–6298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren R., Burstein Y., Soreq H. Synthetic leader peptide modulates secretion of proteins from microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7205–7209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D. The fate of genes, messengers, and proteins introduced into Xenopus oocytes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:89–116. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60580-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Soreq H. Microinjected Xenopus oocytes synthesize active human plasminogen activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3355–3363. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opdenakker G., Weening H., Collen D., Billiau A., de Somer P. Messenger RNA for human tissue plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(2):269–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. P., Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Initiation of 3T3 fibroblast cell division by epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Dec;86 (Suppl 2)(3 Pt 2):593–598. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Further characterization of the mRNA coding for immunoglobulin light-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Schreiber A. B., Levi A., Lax I., Libermann T., Yarden Y. Regulation of cell proliferation by epidermal growth factor. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(2):93–111. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Miskin R. Secreted proteins in the medium of microinjected Xenopus oocytes are degraded by oocyte proteases. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Parvari R., Silman I. Biosynthesis and secretion of catalytically active acetylcholinesterase in Xenopus oocytes microinjected with mRNA from rat brain and from Torpedo electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]