Abstract
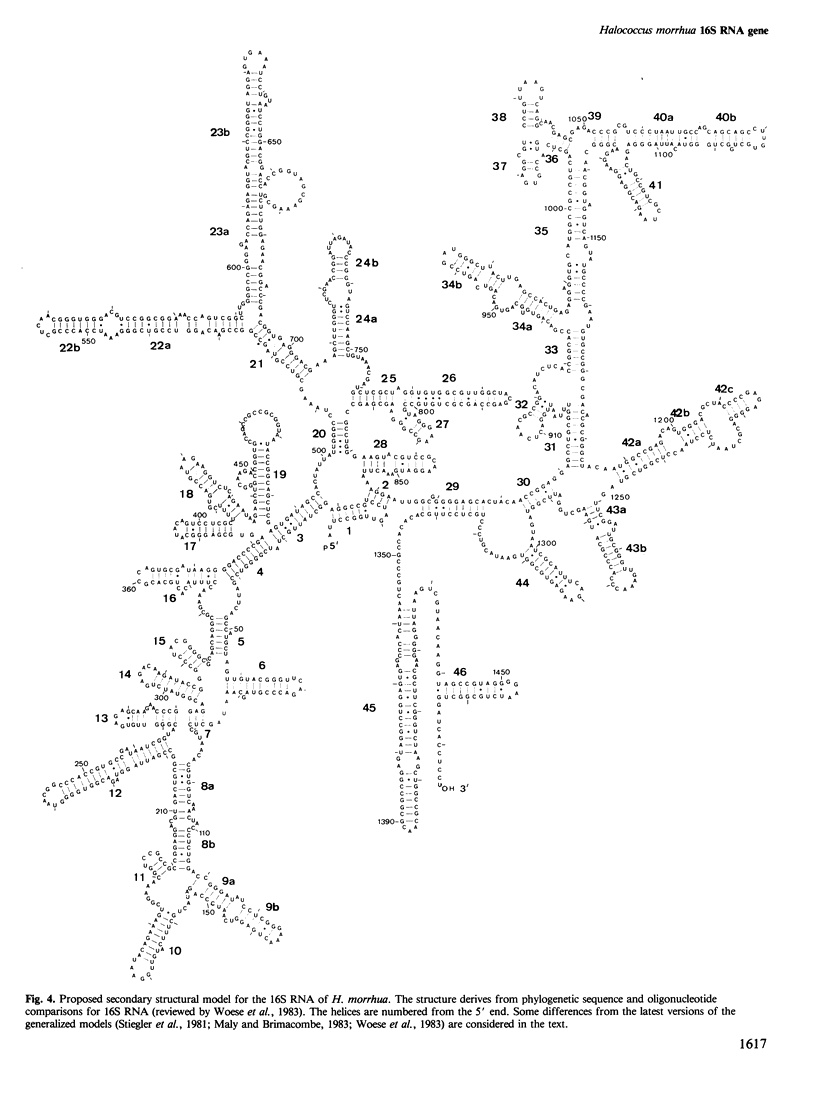
The sequence of the 16S rRNA gene from the archaebacterium Halococcus morrhua was determined by the dideoxynucleotide sequencing method. It is 1475 nucleotides long. This is the second archaebacterial sequence to be determined and it provides sequence comparison evidence for the secondary structural elements confined to the RNAs of this kingdom and, also, support for controversial or additional base pairing in the eubacterial RNAs. Six structural features are localized that have varied during the evolution of the archaebacteria, eubacteria and eukaryotes. Moreover, although the secondary structures of both sequenced archaebacterial RNAs strongly resemble those of eubacteria, they contain sufficient eukaryotic-like structural characteristics to reinforce the view that they belong to a separate line of evolutionary descent.
Full text
PDF
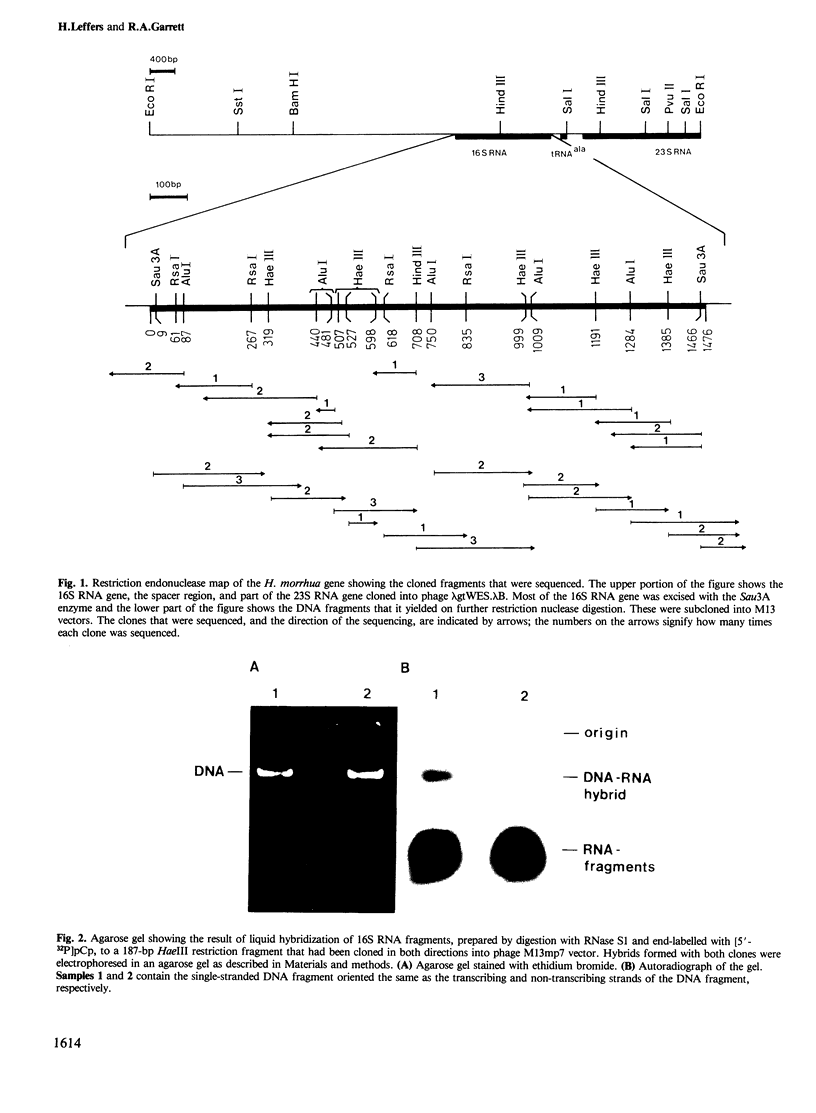
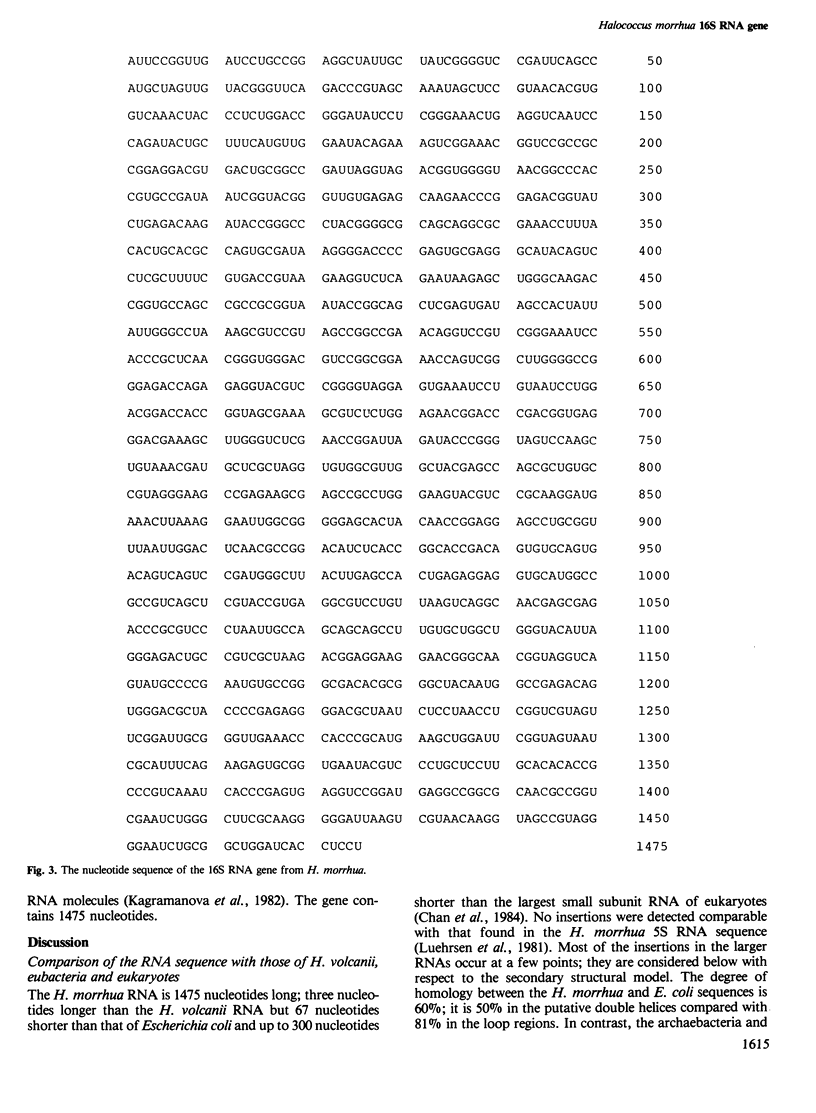
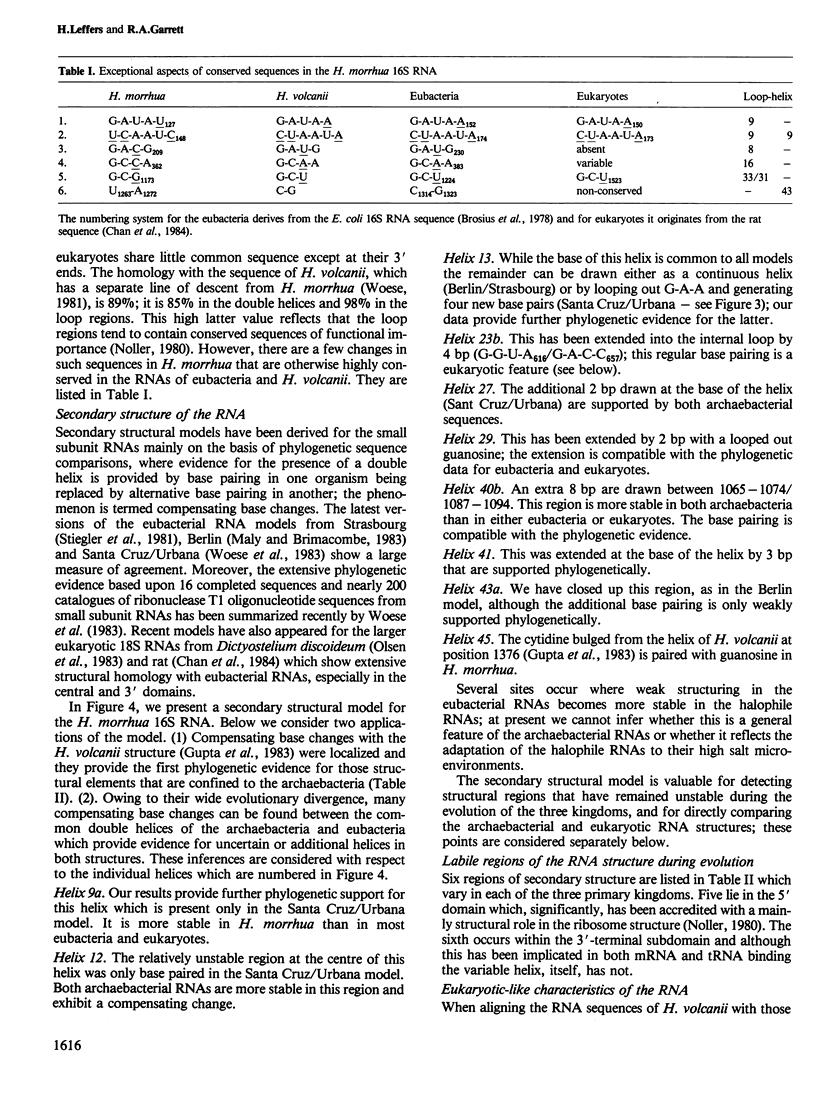


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Gutell R., Noller H. F., Wool I. G. The nucleotide sequence of a rat 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene and a proposal for the secondary structure of 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellner P. Nucleotide sequences from specific areas of the 16S and 23S ribosomal RNAs of E. coli. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):12–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R., Lanter J. M., Woese C. R. Sequence of the 16S Ribosomal RNA from Halobacterium volcanii, an Archaebacterium. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):656–659. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Schnabel R., Sentenac A., Zillig W. Archaebacteria and eukaryotes possess DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of a common type. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1291–1294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagramanova V. K., Mankin A. S., Baratova L. A., Bogdanov A. A. The 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of the Halobacterium halobium 16 S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 19;144(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Klink F. Archaebacterial elongation factor is ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):250–251. doi: 10.1038/287250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok Y., Wong J. T. Evolutionary relationship between Halobacterium cutirubrum and eukaryotes determined by use of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases as phylogenetic probes. Can J Biochem. 1980 Mar;58(3):213–218. doi: 10.1139/o80-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Nicholson D. E., Eubanks D. C., Fox G. E. An archaebacterial 5S rRNA contains a long insertion sequence. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):755–756. doi: 10.1038/293755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrum L. J., Luehrsen K. R., Woese C. R. Are extreme halophiles actually "bacteria"? J Mol Evol. 1978 May 12;11(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01768019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly P., Brimacombe R. Refined secondary structure models for the 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7263–7286. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson A. T., Yaguchi M., Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. Sequence homologies in the N-terminal region of the ribosomal 'A' proteins from Methanobacterium Thermoautotrophicum and Halobacterium cutirubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., McCarroll R., Sogin M. L. Secondary structure of the Dictyostelium discoideum small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):8037–8049. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.8037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. A general secondary-structure model for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNAs from the small ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gupta R. Are archaebacteria merely derived 'prokaryotes'? Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):95–96. doi: 10.1038/289095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Fox G. E. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978 Aug 2;11(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01734485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]