Abstract
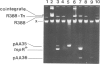
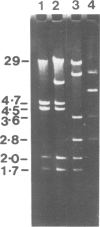
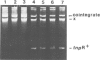
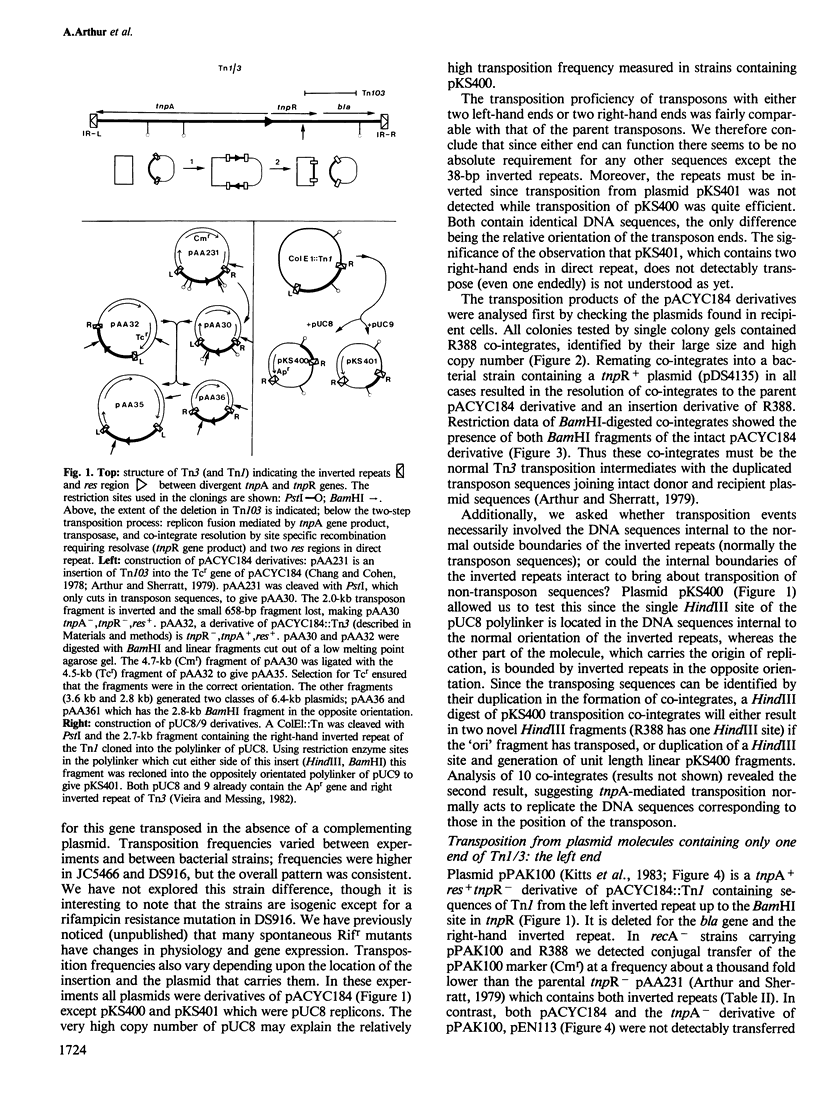
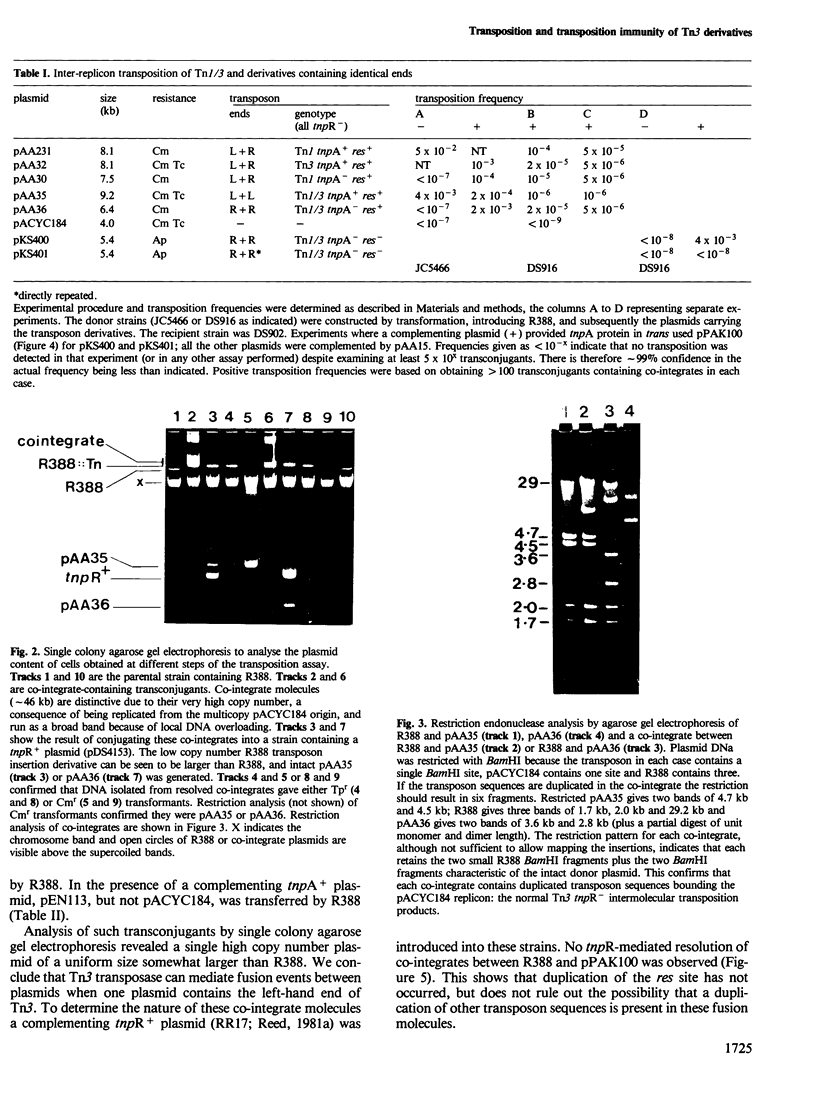
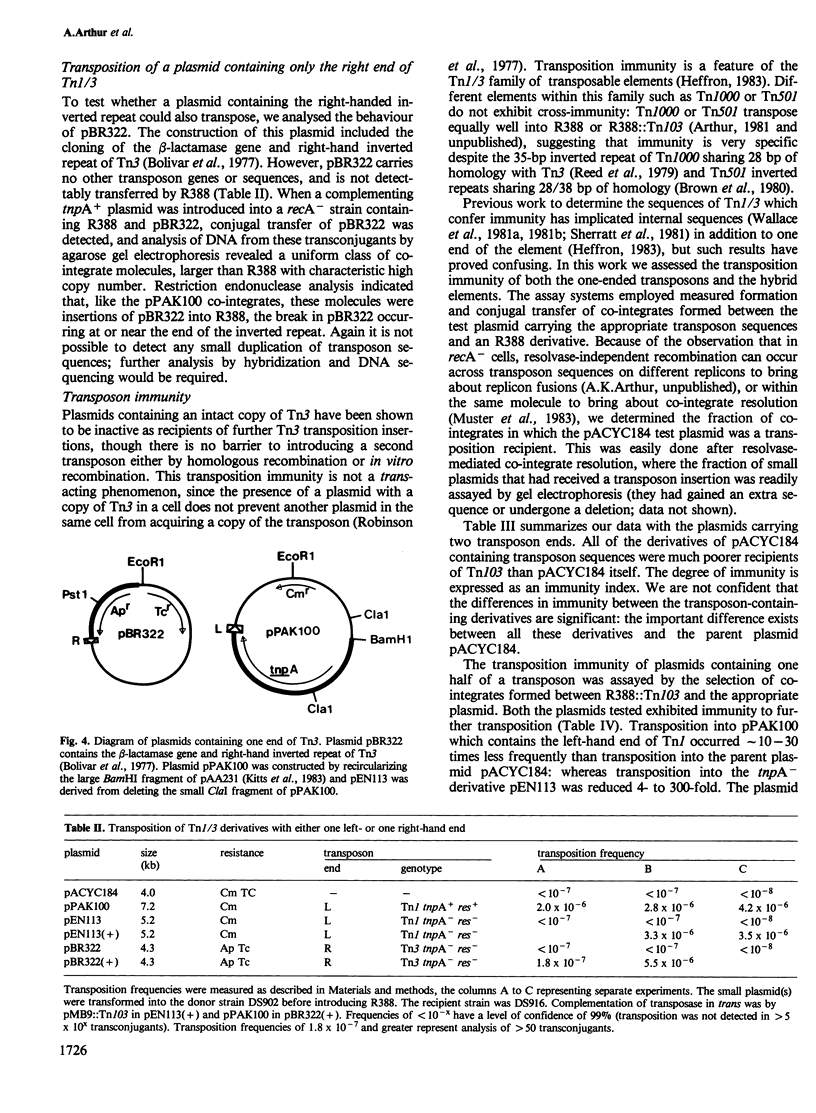
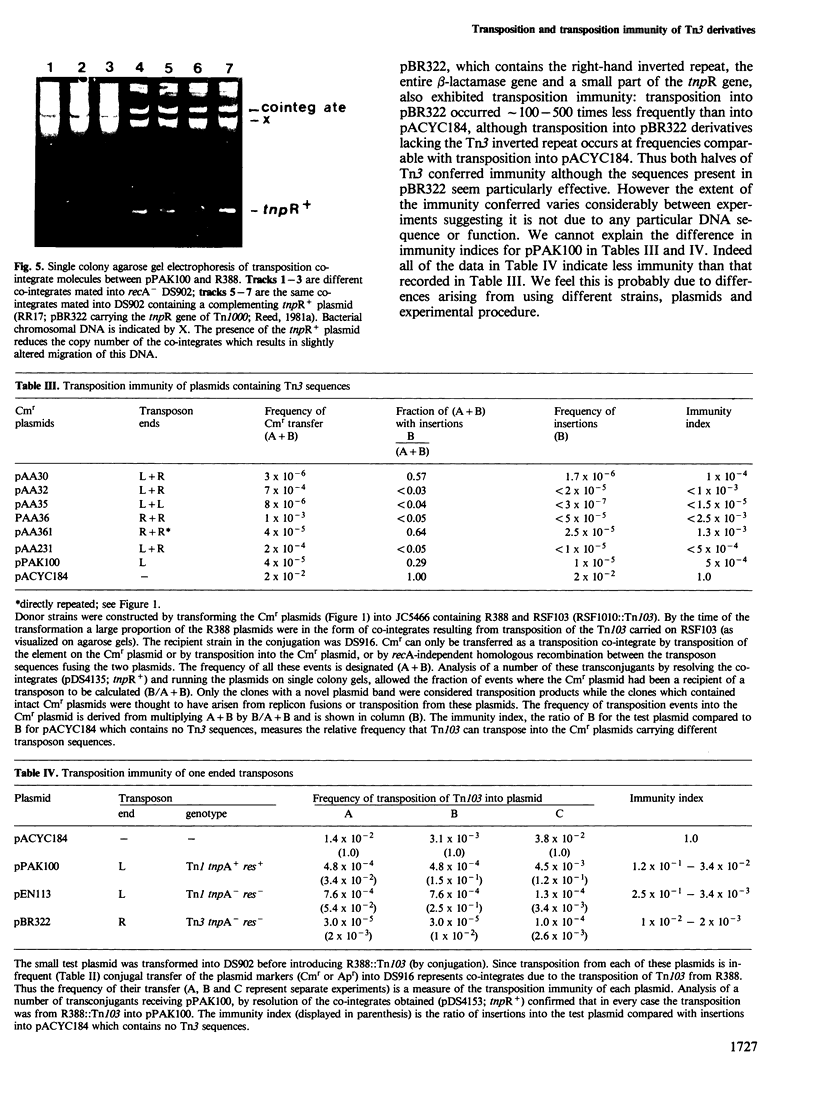
Novel Tn1/3 derivatives that contained either two left- or two right-hand ends of the transposon were constructed in a small plasmid. Both transposed at reasonable frequencies to give normal transposition products, suggesting that only the 38-bp inverted repeats of Tn3 are essential for transposition. Plasmids containing transposon derivatives with only one end (either left or right) undergo transposase-dependent transposition between replicons at much lower frequencies, resulting in co-integrate molecules in which there is no substantial duplication of transposon DNA and that appear to be simple fusions of the two plasmids. Both the right and left halves of the transposon are separately able to confer transposition immunity to the plasmid, this immunity being inseparably linked to transposition proficiency and specificity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur A., Sherratt D. Dissection of the transposition process: a transposon-encoded site-specific recombination system. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):267–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00397226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Choi C. L., Grinsted J., Richmond M. H., Whitehead P. R. Nucleotide sequences at the ends of the mercury resistance transposon, Tn501. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1933–1945. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan J., Sherratt D. Plasmid ColE1 conjugal mobility: the nature of bom, a region required in cis for transfer. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(2):344–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00330810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Chandler M. On the molecular mechanisms of transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4858–4862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Heffron F., Dougan G., Falkow S. Analysis of sequences transposed by complementation of two classes of transposition-deficient mutants of Tn3. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):742–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.742-756.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Sherratt D. J. Sequence analysis at IS1 insertion sites: models for transposition. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1257–1261. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshey R. M., Bukhari A. I. A mechanism of DNA transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1090–1094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Bedinger P., Champoux J. J., Falkow S. Deletions affecting the transposition of an antibiotic resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):702–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Lamond A., Sherratt D. J. Inter-replicon transposition of Tn1/3 occurs in two sequential genetically separable steps. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):626–628. doi: 10.1038/295626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Symington L. S., Dyson P., Sherratt D. J. Transposon-encoded site-specific recombination: nature of the Tn3 DNA sequences which constitute the recombination site res. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1055–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P., Symington L., Burke M., Reed R., Sherratt D. Transposon-specified site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Bhagwat A., Heffron F. Identification of a transposon Tn3 sequence required for transposition immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6765–6769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida Y., Machida C., Ohtsubo E. A novel type of transposon generated by insertion element IS102 present in a pSC101 derivative. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muster C. J., MacHattie L. A., Shapiro J. A. p lambda CM system: observations on the roles of transposable elements in formation and breakdown of plasmids derived from bacteriophage lambda replicons. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):976–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.976-990.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Resolution of cointegrates between transposons gamma delta and Tn3 defines the recombination site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Young R. A., Steitz J. A., Grindley N. D., Guyer M. S. Transposition of the Escherichia coli insertion element gamma generates a five-base-pair repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4882–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. K., Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H. Inhibition of TnA translocation by TnA. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):407–414. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.407-414.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Carle G. F., Berg D. E. Sequences essential for transposition at the termini of IS50. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7293–7297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Molecular model for the transposition and replication of bacteriophage Mu and other transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherratt D., Arthur A., Burke M. Transposon-specified, site-specific recombination systems. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):275–281. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Ward J. M., Richmond M. H. The location of sequences of TnA required for the establishment of transposition immunity. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):80–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00271199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Ward J. M., Richmond M. H. The tnpR gene product of TnA is required for transposition immunity. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):87–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00271200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Schaus N. A., Grindley N. D. Insertion sequence duplication in transpositional recombination. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):755–765. doi: 10.1126/science.6314502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]