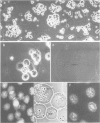
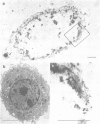
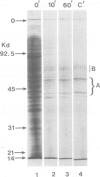
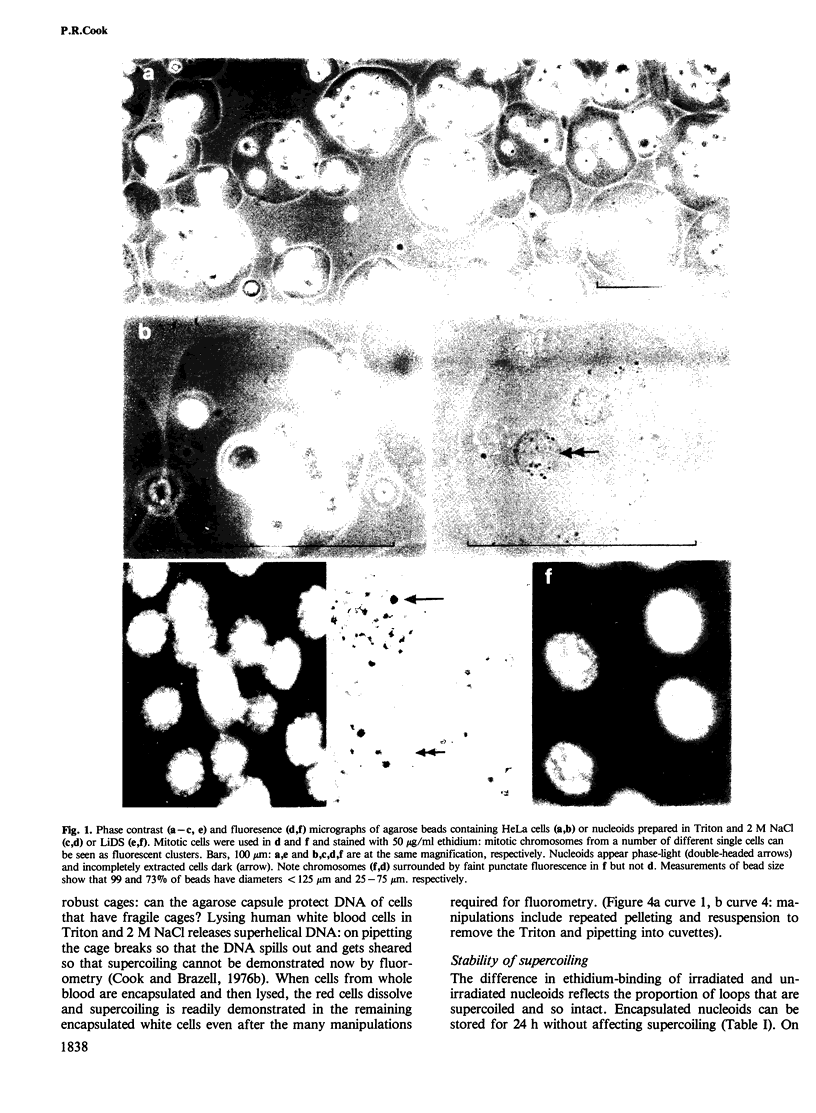
Abstract
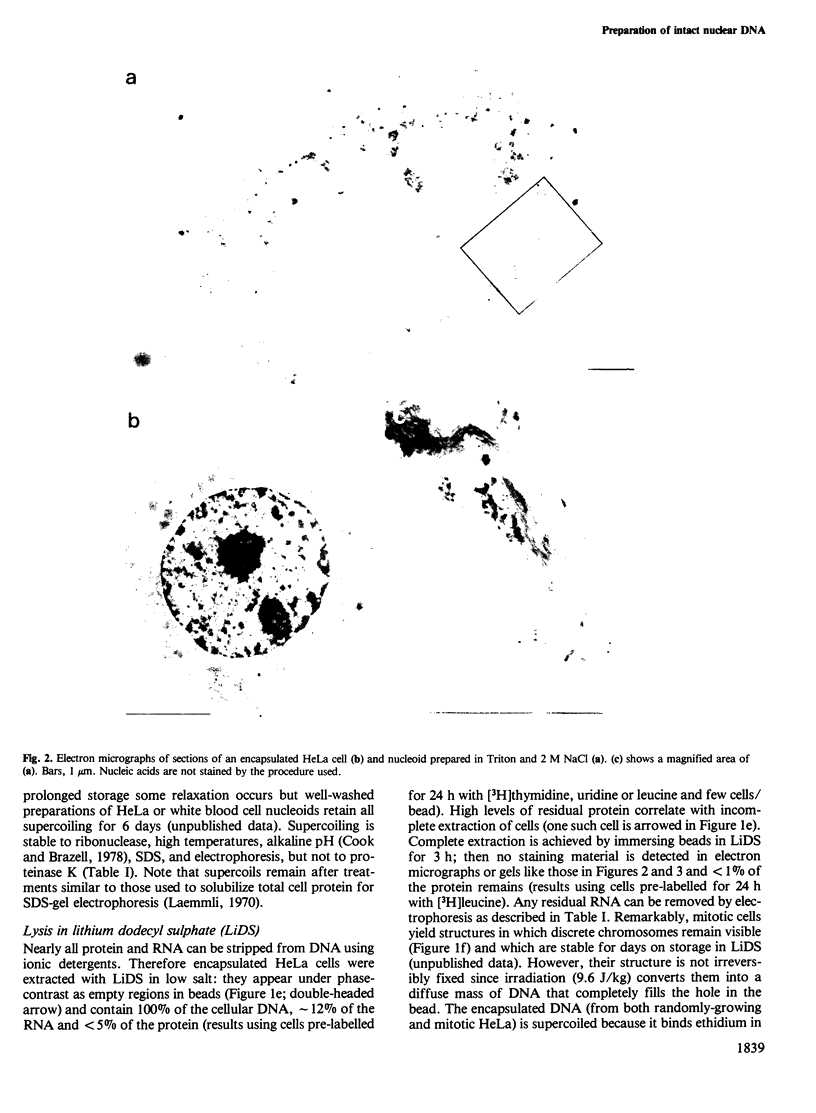
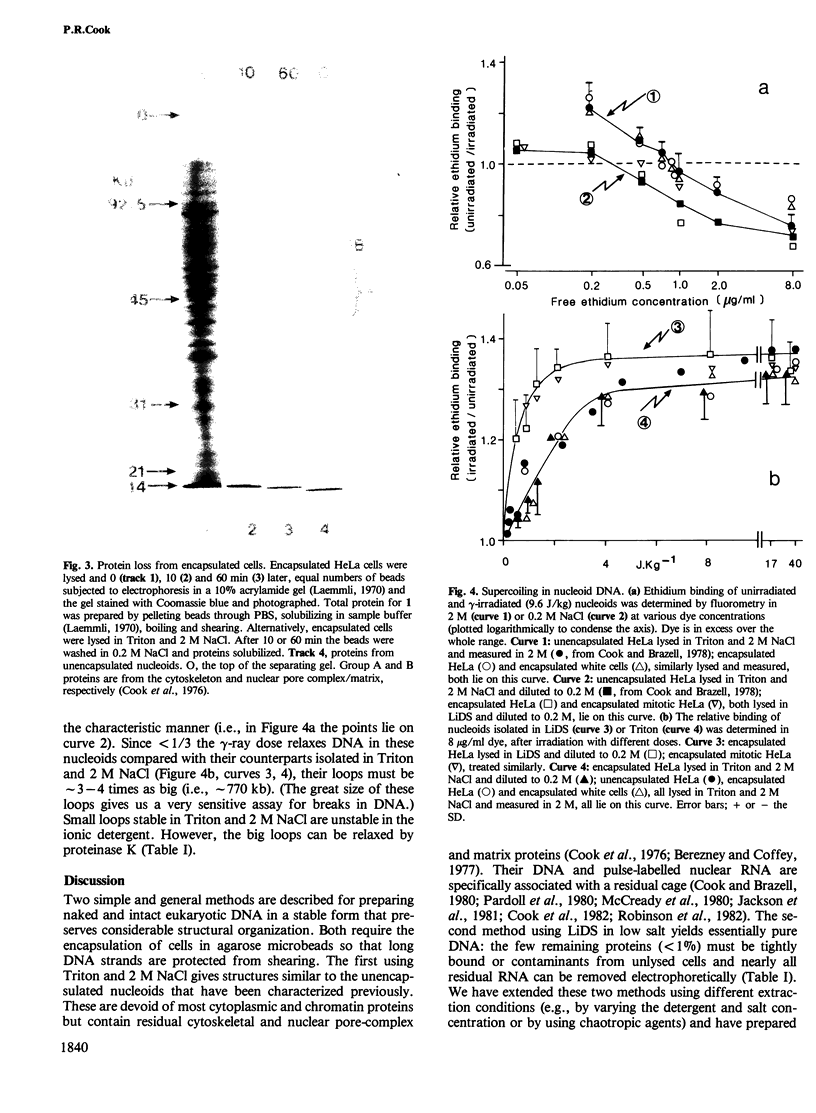
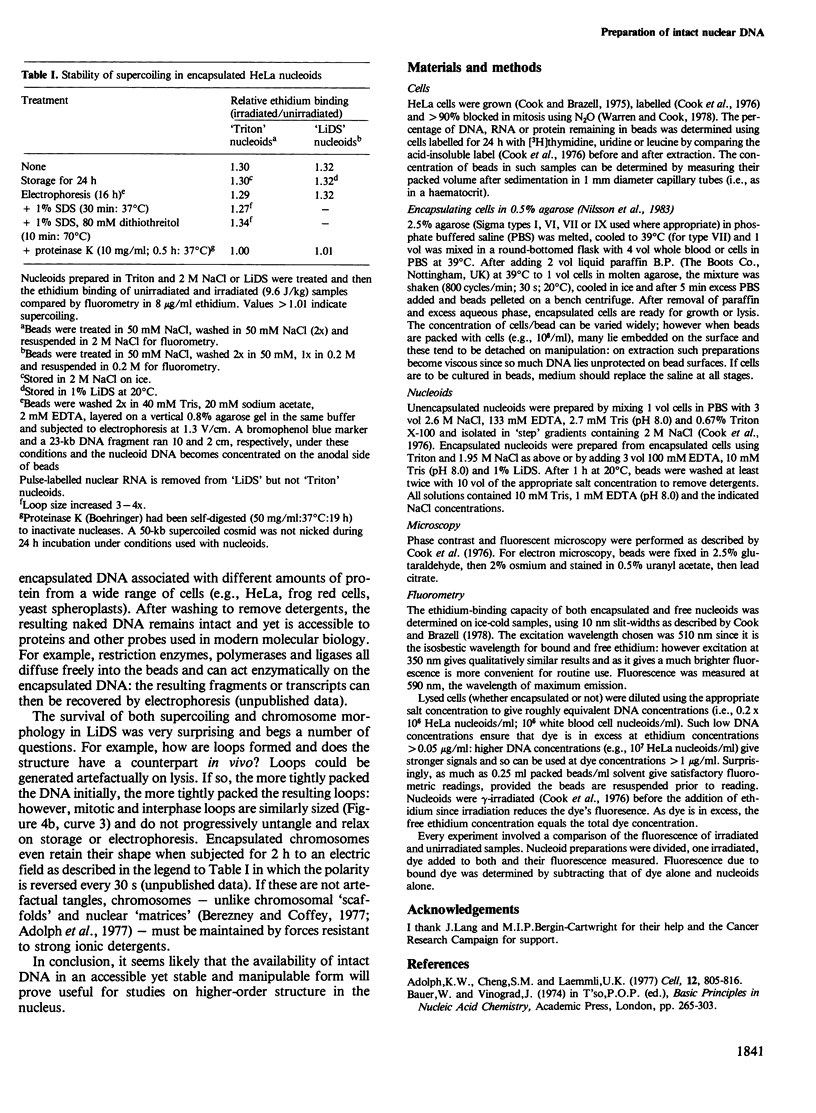
Naked nuclear DNA is easily sheared. Two general methods are described for preparing intact DNA in a stable form that can be pipetted without breaking it. Cells are encapsulated in agarose microbeads and then lysed in a non-ionic detergent (i.e., Triton X-100) and 2 M NaCl or an ionic detergent (e.g., sodium or lithium dodecyl sulphate) in low salt. Most cellular protein and RNA then diffuse out through pores in the beads to leave encapsulated and naked DNA which is nevertheless accessible to enzymes and other probes. Remarkably, considerable structure is preserved since the DNA is supercoiled and chromosomes retain their shape.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolph K. W., Cheng S. M., Laemmli U. K. Role of nonhistone proteins in metaphase chromosome structure. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. A relative molecular weight series derived from the nucleic acid of bacteriophage T2. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:458–472. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear matrix. Isolation and characterization of a framework structure from rat liver nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):616–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Cook P. R. Transcription of superhelical DNA from cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):63–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Conformational constraints in nuclear DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):287–302. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Detection and repair of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):679–682. doi: 10.1038/263679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A., Jost E. Characterization of nuclear structures containing superhelical DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):303–324. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Mapping sequences in loops of nuclear DNA by their progressive detachment from the nuclear cage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2895–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Spectrofluorometric measurement of the binding of ethidium to superhelical DNA from cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):465–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Supercoils in human DNA. J Cell Sci. 1975 Nov;19(2):261–279. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Lang J., Hayday A., Lania L., Fried M., Chiswell D. J., Wyke J. A. Active viral genes in transformed cells lie close to the nuclear cage. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., McCready S. J., Cook P. R. RNA is synthesized at the nuclear cage. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):552–555. doi: 10.1038/292552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavenoff R., Zimm B. H. Chromosome-sized DNA molecules from Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1973;41(1):1–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00284071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready S. J., Godwin J., Mason D. W., Brazell I. A., Cook P. R. DNA is replicated at the nuclear cage. J Cell Sci. 1980 Dec;46:365–386. doi: 10.1242/jcs.46.1.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Scheirer W., Merten O. W., Ostberg L., Liehl E., Katinger H. W., Mosbach K. Entrapment of animal cells for production of monoclonal antibodies and other biomolecules. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):629–630. doi: 10.1038/302629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. I., Nelkin B. D., Vogelstein B. The ovalbumin gene is associated with the nuclear matrix of chicken oviduct cells. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Saffran W., Welsh J., Haas R., Goldenberg M., Cantor C. R. New techniques for purifying large DNAs and studying their properties and packaging. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):189–195. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Cook P. R. Supercoiling of DNA and nuclear conformation during the cell-cycle. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:211–226. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]