Abstract
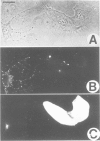
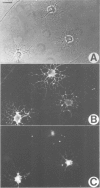
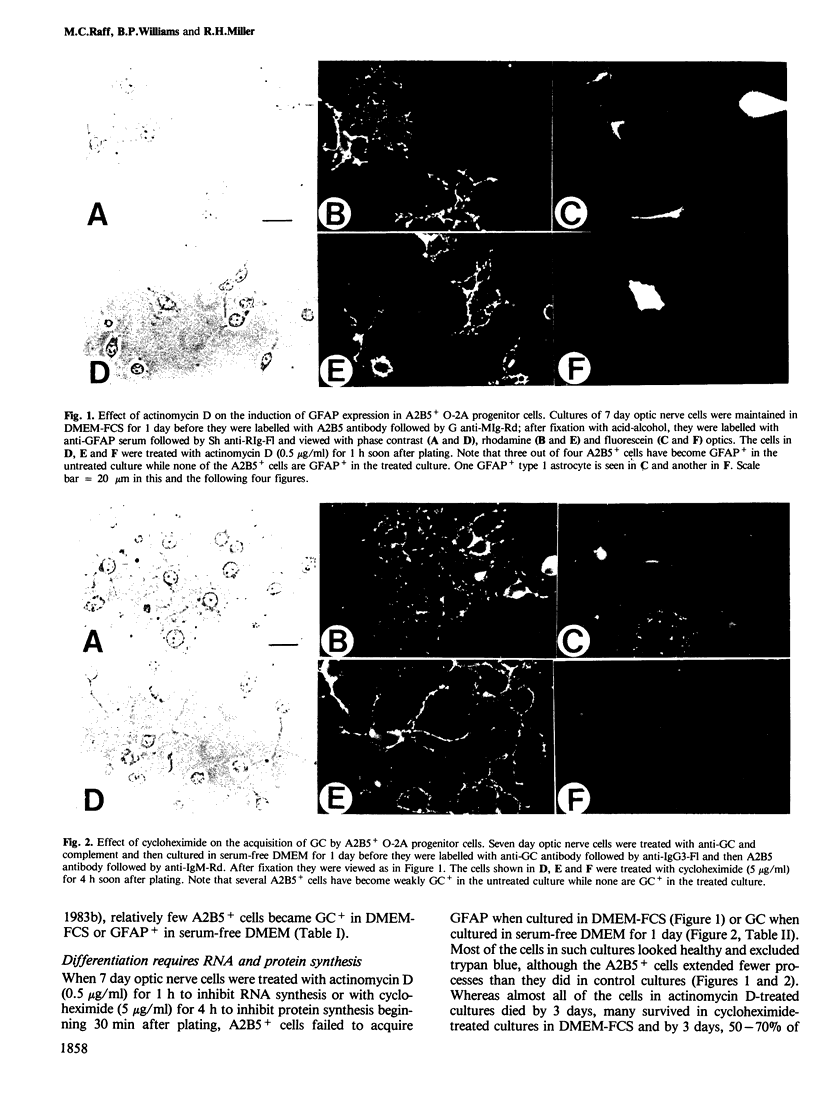
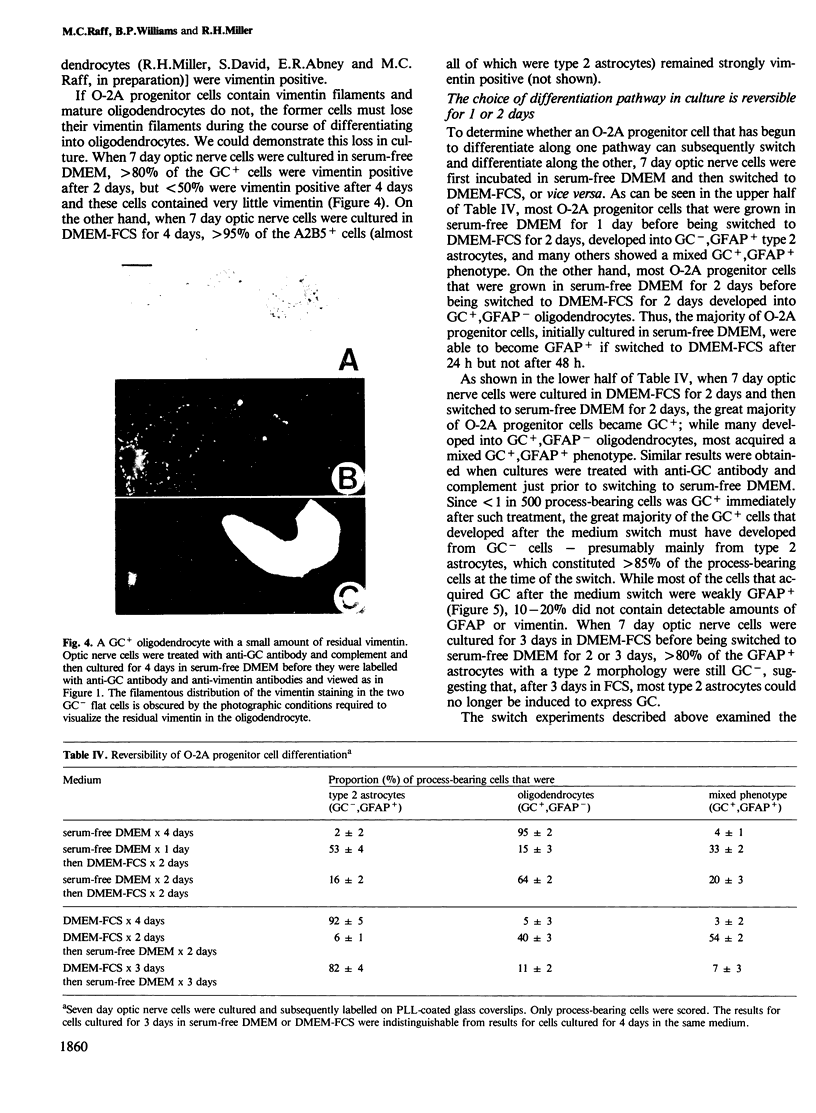
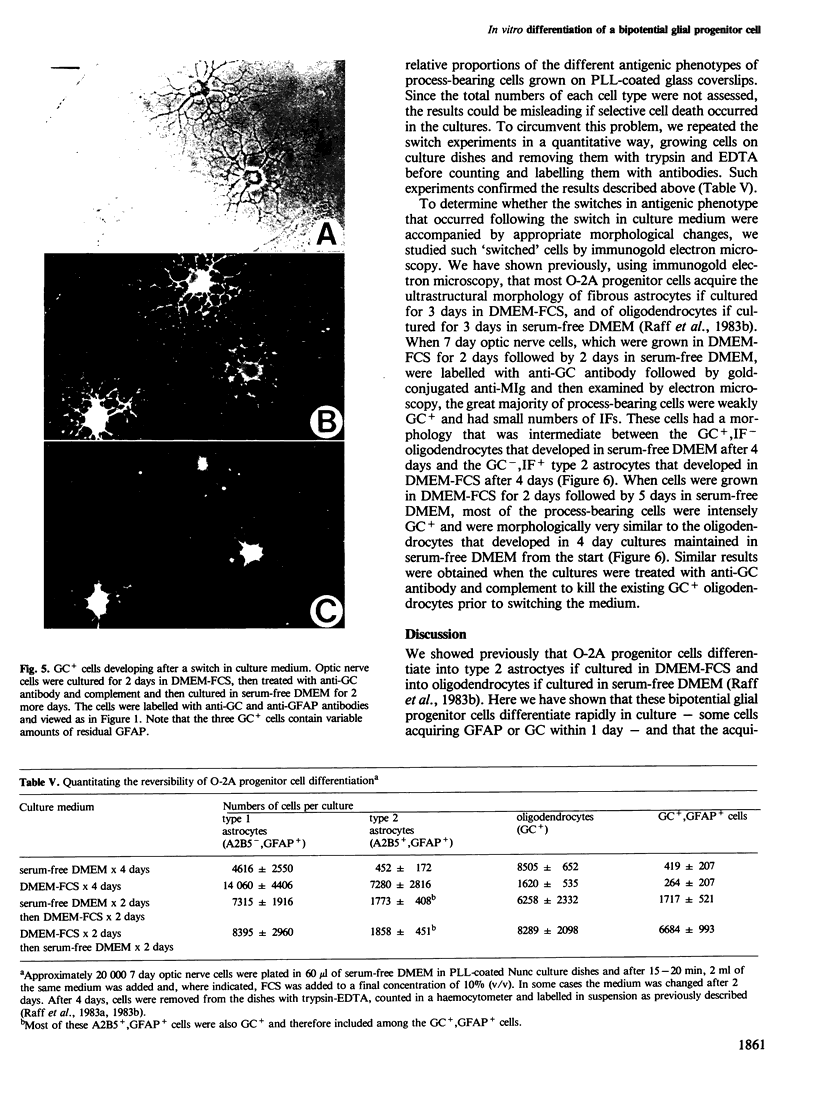
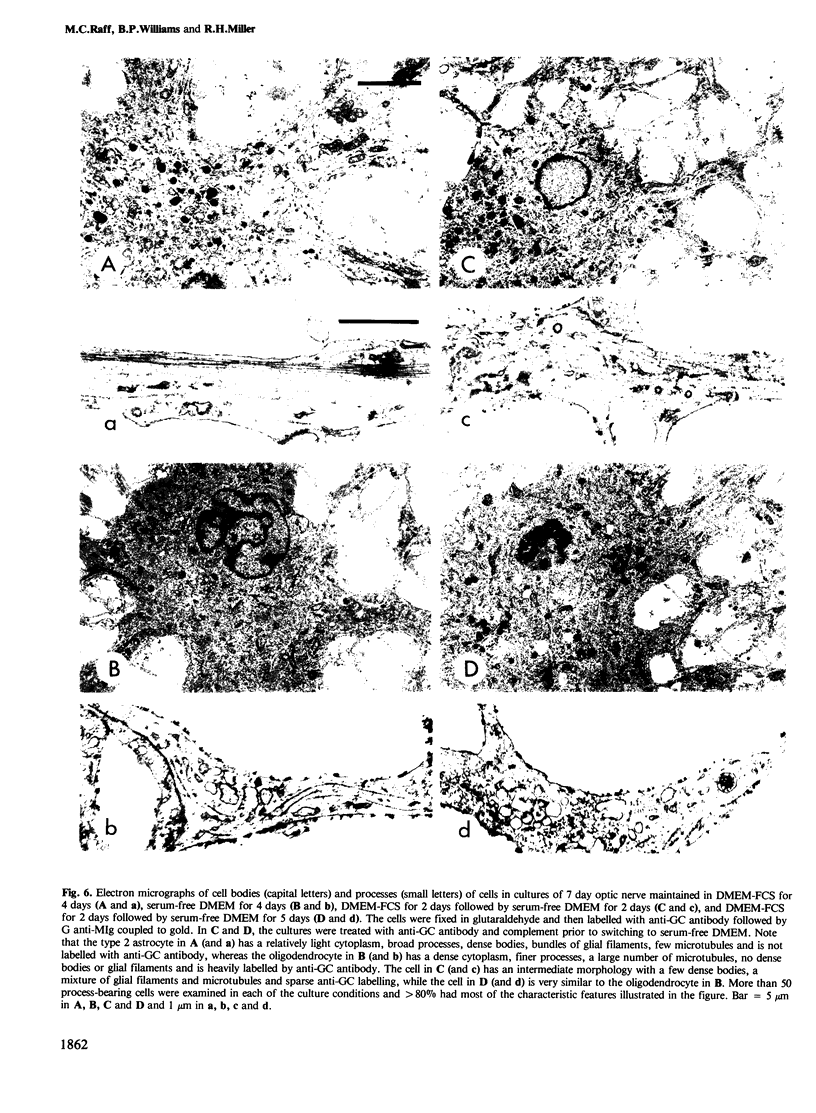
We have studied the properties of a glial progenitor cell from 7-day-old rat optic nerve that differentiates in vitro into an oligodendrocyte if cultured in serum-free medium and into an astrocyte if cultured in foetal calf serum (FCS). Using galactocerebroside as a marker of oligodendrocyte differentiation and glial fibrillary acidic protein as a marker of astrocyte differentiation, we show that the acquisition of these marker molecules occurs rapidly in culture and requires both RNA and protein synthesis. We provide evidence that the effect of FCS on the development of the glial progenitor cell is not due to its influence on cell-substrate adherence or actin filament organization and is not mimicked by an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP or pH. The progenitor cell contains vimentin filaments and retains them on becoming an astrocyte but loses them on becoming an oligodendrocyte. Most importantly, we show that the choice of developmental pathway taken by the bipotential glial progenitor cells in culture is reversible for 1-2 days and then becomes fixed, at least under the conditions we studied.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abney E. R., Williams B. P., Raff M. C. Tracing the development of oligodendrocytes from precursor cells using monoclonal antibodies, fluorescence-activated cell sorting, and cell culture. Dev Biol. 1983 Nov;100(1):166–171. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer C. W., Rooney P., Wolpert L. Cell shape and cartilage differentiation of early chick limb bud cells in culture. Cell Differ. 1982 Jun;11(4):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(82)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Eng L. F., Dahl D., Uyeda C. T. Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Schlesinger M. Absorption of guinea pig serum with agar. A method for elimination of itscytotoxicity for murine thymus cells. Transplantation. 1970 Jul;10(1):130–132. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197007000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Monoclonal antibody to a plasma membrane antigen of neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epel D., Steinhardt R., Humphreys T., Mazia D. An analysis of the partial metabolic derepression of sea urchin eggs by ammonia: the existence of independent pathways. Dev Biol. 1974 Oct;40(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Davidson R. S., McNamee K. C., Russell G., Goodwin D., Holborow E. J. Fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy: a study of the phenomenon and its remedy. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 17;55(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Raff M. C. Fibrous and protoplasmic astrocytes are biochemically and developmentally distinct. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):585–592. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00585.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M. Thy-1 antigen on astrocytes in long-term cultures of rat central nervous system. Nature. 1979 Aug 23;280(5724):688–690. doi: 10.1038/280688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E. R., Cohen J., Lindsay R., Noble M. Two types of astrocytes in cultures of developing rat white matter: differences in morphology, surface gangliosides, and growth characteristics. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1289–1300. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Fields K. L., Hakomori S. I., Mirsky R., Pruss R. M., Winter J. Cell-type-specific markers for distinguishing and studying neurons and the major classes of glial cells in culture. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):283–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90851-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Miller R. H., Noble M. A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending on culture medium. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):390–396. doi: 10.1038/303390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Mirsky R., Fields K. L., Lisak R. P., Dorfman S. H., Silberberg D. H., Gregson N. A., Leibowitz S., Kennedy M. C. Galactocerebroside is a specific cell-surface antigenic marker for oligodendrocytes in culture. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranscht B., Clapshaw P. A., Price J., Noble M., Seifert W. Development of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells studied with a monoclonal antibody against galactocerebroside. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2709–2713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachner M., Faissner A., Kruse J., Lindner J., Meier D. H., Rathjen F. G., Wernecke H. Cell-type specificity and developmental expression of neural cell-surface components involved in cell interactions and of structurally related molecules. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):557–568. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Osborn M., Weber K. An immunofluorescence microscopical study of the neurofilament triplet proteins, vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein within the adult rat brain. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):68–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Ginty C. A. Fibronectin modulation of cell shape and lipogenic gene expression in 3T3-adipocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):657–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swalla B. J., Solursh M. Inhibition of limb chondrogenesis by fibronectin. Differentiation. 1984;26(1):42–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K. Immunological studies on collagen type transition in chondrogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1980;14(Pt 2):199–225. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]