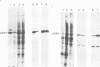Abstract
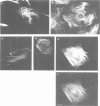
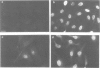
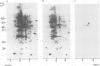
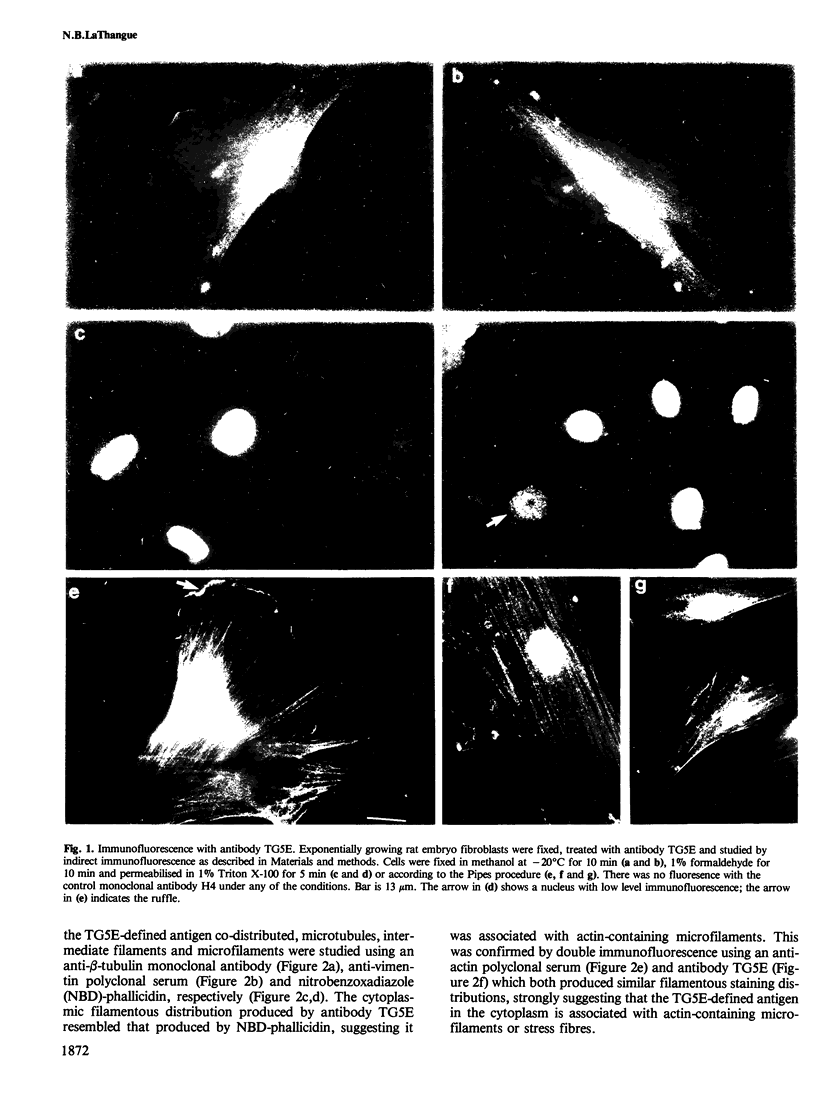
A monoclonal antibody reacts with a polypeptide of 68 000 mol. wt. (p68) that accumulates to high levels during heat shock. The intracellular distribution of this antigen in normal and heat-shocked cells has been studied. It is a major component of non-stressed cells, where it is located predominantly in the cytoplasm, but also occurs in the nucleus. The nuclear accumulation is growth regulated, in that exponentially growing cells have strong nuclear immunofluorescence and confluent cells little. It is concentrated at the leading edge of motile fibroblasts and co-distributes with actin-containing microfilaments. Heat shock causes cytoplasmic and nuclear accumulation and there is new deposition in the periphery of cells. In normal cells the antigen in the nucleus is located in the nuclear lamina and matrix which increases during heat shock. The distribution of this molecule and the structures with which it interacts suggests that it is important in mediating the effects of heat shock.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Immunofluorescence localization of a small heat shock protein (hsp 23) in salivary gland cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00271198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Fakan S., Tissières A. Localization of the heat shock-induced proteins in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Jul;78(1):86–103. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensaude O., Babinet C., Morange M., Jacob F. Heat shock proteins, first major products of zygotic gene activity in mouse embryo. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):331–333. doi: 10.1038/305331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensaude O., Morange M. Spontaneous high expression of heat-shock proteins in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells and ectoderm from day 8 mouse embryo. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):173–177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear protein matrix: association with newly synthesized DNA. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):291–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1145202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E. Newcastle disease virus stimulates the cellular accumulation of stress (heat shock) mRNAs and proteins. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):703–707. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.703-707.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Holmgren R., Freund R., Morimoto R., Meselson M. Four heat shock proteins of Drosophila melanogaster coded within a 12-kilobase region in chromosome subdivision 67B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5390–5393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findly R. C., Pederson T. Regulated transcription of the genes for actin and heat-shock proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):323–328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S. Two-dimensional gel analysis of HSV type 1-induced polypeptides and glycoprotein processing. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):77–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E. Cultured animal cells exposed to amino acid analogues or puromycin rapidly synthesize several polypeptides. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Mar;102(3):407–427. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Livak K., Morimoto R., Freund R., Meselson M. Studies of cloned sequences from four Drosophila heat shock loci. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1359–1370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Clark E. A., Smith E., Mitchison N. A. Mouse hybrid cell lines produce antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):81–87. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. Antibodies to two major chicken heat shock proteins cross-react with similar proteins in widely divergent species. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):267–274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Türler H. Simian virus 40 and polyoma virus induce synthesis of heat shock proteins in permissive cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloetzel P. M., Bautz E. K. Heat-shock proteins are associated with hnRNA in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):705–710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Spang A. E. Definition of a series of stages in the association of two herpesviral proteins with the cell nucleus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):314–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.314-324.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaThangue N. B., Shriver K., Dawson C., Chan W. L. Herpes simplex virus infection causes the accumulation of a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. Epinemin: a new protein associated with vimentin filaments in non-neural cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1891–1905. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Heat-shock proteins of Drosophila are associated with nuclease-resistant, high-salt-resistant nuclear structures. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):793–796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Mikelens P., Oppermann H., Jackson J. Effect of antabuse (disulfiram) on Rous sarcoma virus and on eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 22;519(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long B. H., Huang C. Y., Pogo A. O. Isolation and characterization of the nuclear matrix in Friend erythroleukemia cells: chromatin and hnRNA interactions with the nuclear matrix. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Wheeler S. Heat shock response of Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Pederson T. Heat shock alters nuclear ribonucleoprotein assembly in Drosophila cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):161–171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Alterations in translatable ribonucleic acid after heat shock of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):603–612. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.603-612.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Huang C. Y., Pogo A. O. Rat liver nuclear skeleton and ribonucleoprotein complexes containing HnRNA. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):675–691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T., Davis N. G. Messenger RNA processing and nuclear structure: isolation of nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles containing beta-globin messenger RNA precursors. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):47–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Nuclear RNA-protein interactions and messenger RNA processing. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1321–1326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stévenin J., Gattoni R., Keohavong P., Jacob M. Mild nuclease treatment as a probe for a non-random distribution of adenovirus-specific RNA sequences and of cellular RNA in nuclear ribonucleoprotein fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):185–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subjeck J. R., Shyy T., Shen J., Johnson R. J. Association between the mammalian 110,000-dalton heat-shock protein and nucleoli. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1389–1395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Welch W. J., Mathews M. B., Feramisco J. R. Molecular and cellular effects of heat-shock and related treatments of mammalian tissue-culture cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):985–996. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez J. M., Sonoda S., Bugaisky G., Lindquist S. Is the major Drosophila heat shock protein present in cells that have not been heat shocked? J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):286–290. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig S., Hensse S., Keitel C., Elsner C., Wittig B. Heat shock gene expression is regulated during teratocarcinoma cell differentiation and early embryonic development. Dev Biol. 1983 Apr;96(2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]