Abstract
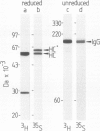
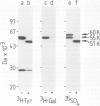
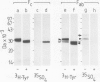
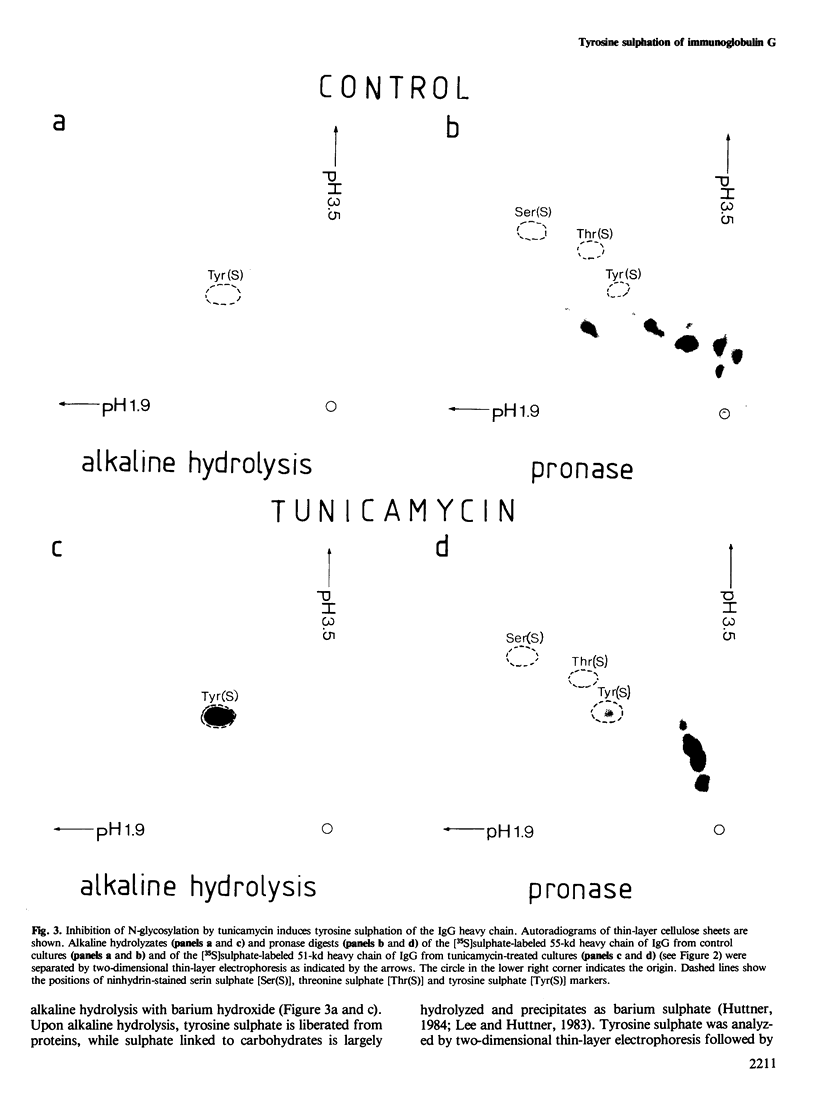
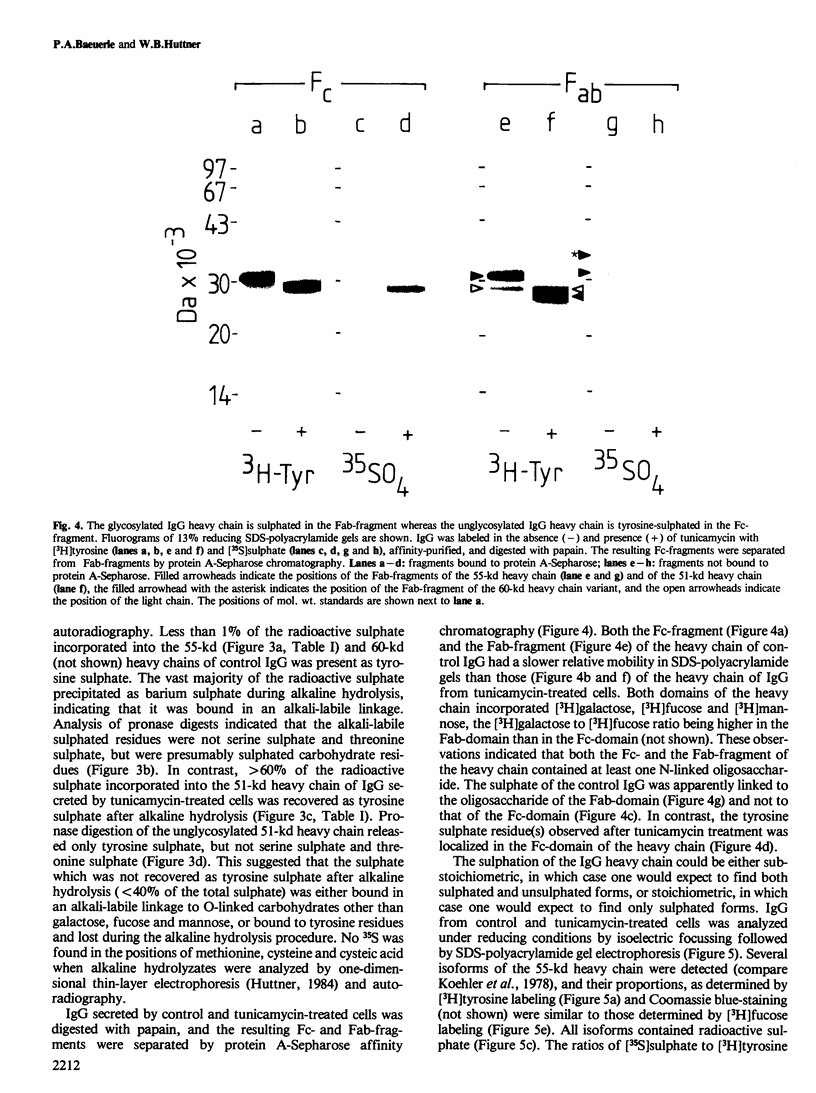
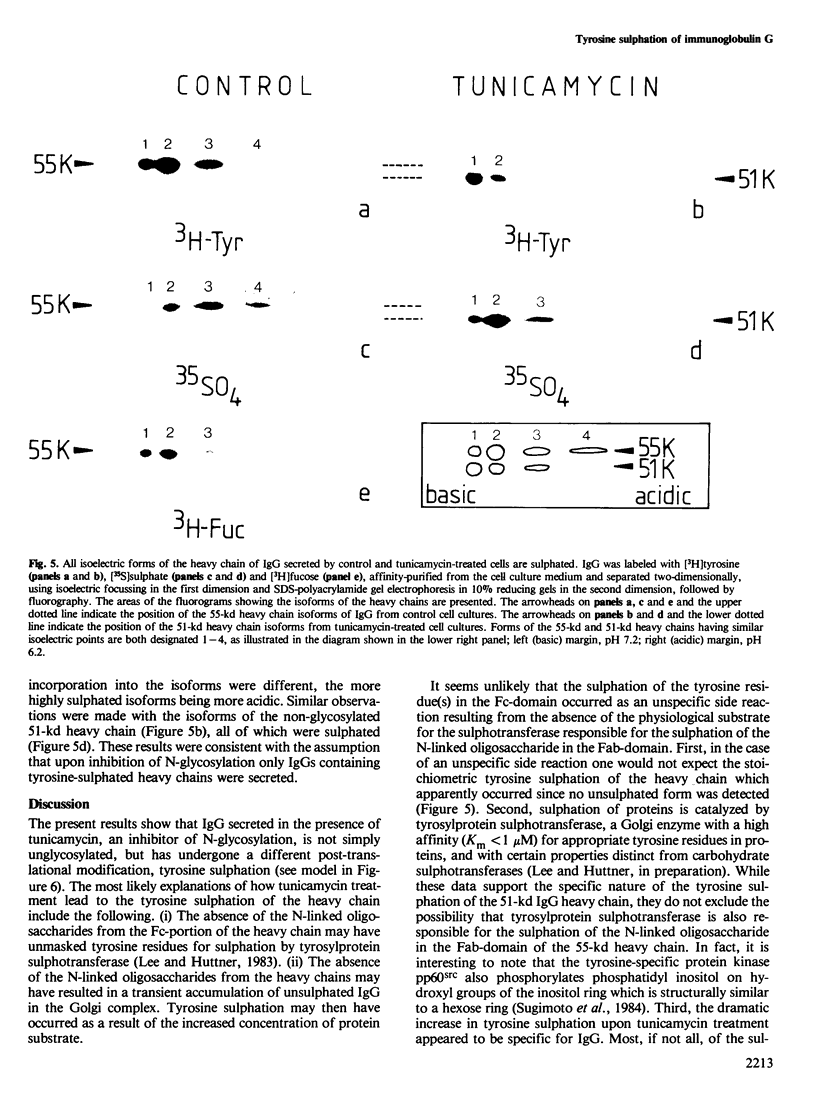
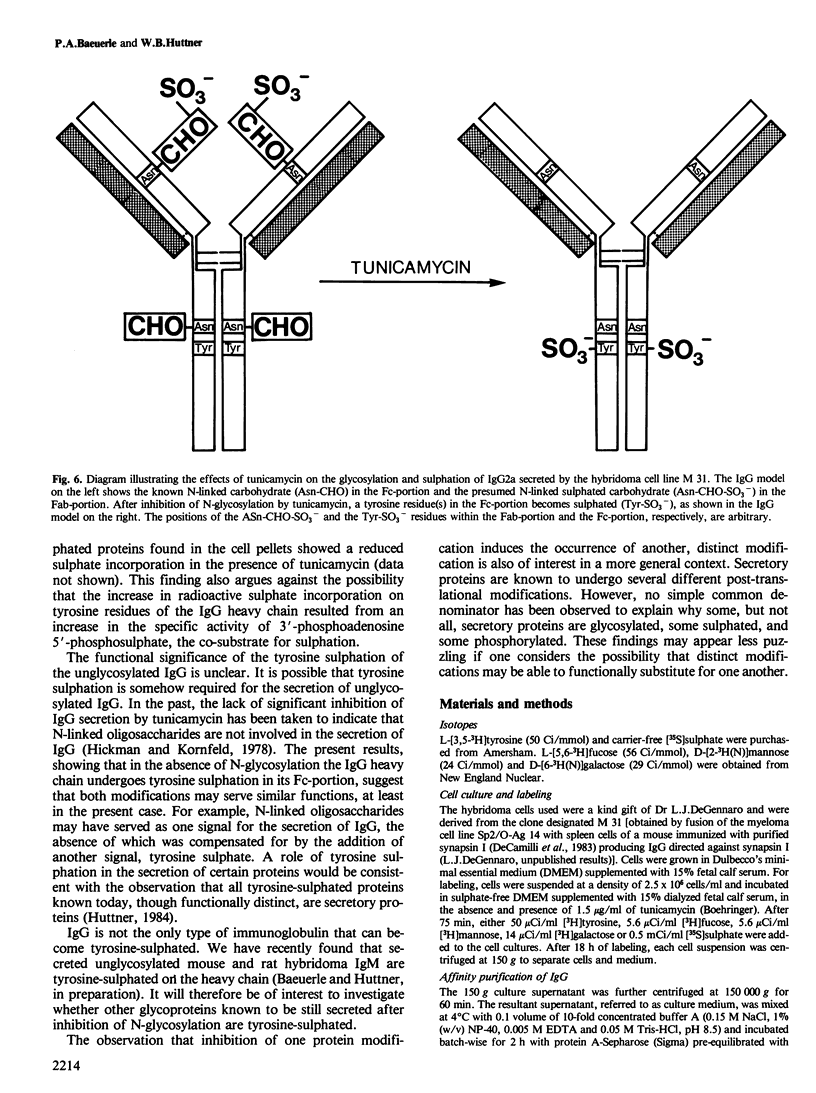
Immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) secreted by the hybridoma line M 31 was found to contain covalently linked sulphate. The sulphate was bound to the heavy chain which existed in several isoelectric variants. All variants were sulphated, the more acidic ones being more highly sulphated. Within the heavy chain the sulphate was not linked to tyrosine, threonine or serine residues, but appeared to be bound to N-linked oligosaccharides located in the Fab-portion. In contrast, the N-linked oligosaccharides in the Fc-portion were unsulphated. Surprisingly, the unglycosylated IgG secreted in the presence of tunicamycin, an inhibitor of N-glycosylation, was not unsulphated, but contained four times as much sulphate on the heavy chain as control IgG. All isoelectric variants of the non-glycosylated heavy chain contained sulphate. This sulphate was localized in the Fc-portion and was largely bound to tyrosine residues. These results show that, upon inhibition of N-glycosylation, the IgG is not simply secreted in non-glycosylated form, but has undergone a different post-translational modification, tyrosine sulphation. We discuss the possibility that tyrosine sulphate residues functionally compensate for the absence of N-linked (sulphated) oligosaccharides in IgG. One common function for these two protein modifications could be to serve as signals for the secretion of IgG.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY H., HARDY P. M., JONES D. S., KENNER G. W., SHEPPARD R. C. THE ANTRAL HORMONE GASTRIN. STRUCTURE OF GASTRIN. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:931–933. doi: 10.1038/204931a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Kornfeld S. Effect of tunicamycin on IgM, IgA, and IgG secretion by mouse plasmacytoma cells. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):990–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B. Determination and occurrence of tyrosine O-sulfate in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:200–223. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B. Sulphation of tyrosine residues-a widespread modification of proteins. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):273–276. doi: 10.1038/299273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R. Post-translational modification of the fourth component of complement. Sulfation of the alpha-chain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12745–12748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Hengartner H., Shulman M. J. Immunoglobulin production by lymphocyte hybridomas. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):82–88. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. W., Huttner W. B. Tyrosine-O-sulfated proteins of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells and their sulfation by a tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11326–11334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutt V., Jorpes J. E. Structure of porcine cholecystokinin-pancreozymin. 1. Cleavage with thrombin and with trypsin. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Oct 17;6(1):156–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth C. D., Hughes J., Morely J. S. O-sulphated Leu-enkephalin in brain. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):519–522. doi: 10.1038/295519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]