Abstract
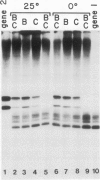
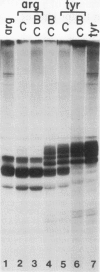
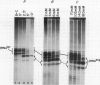
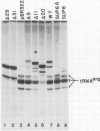
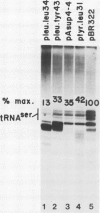
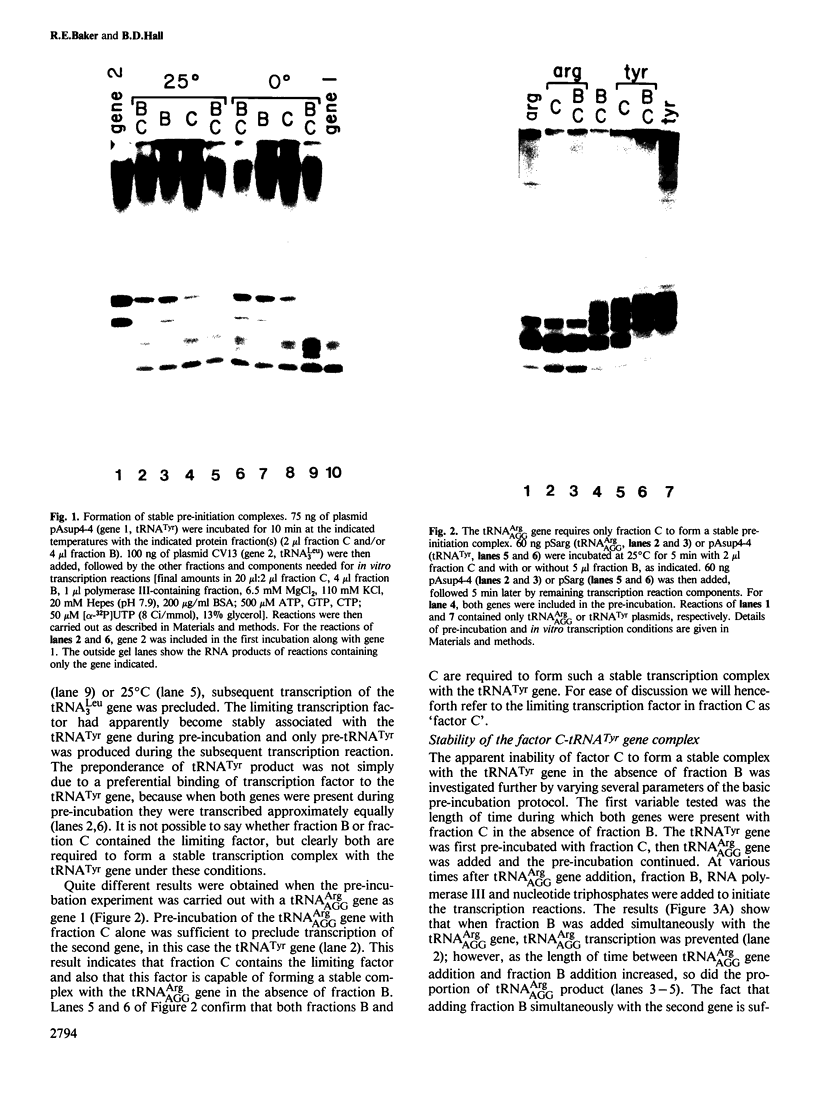
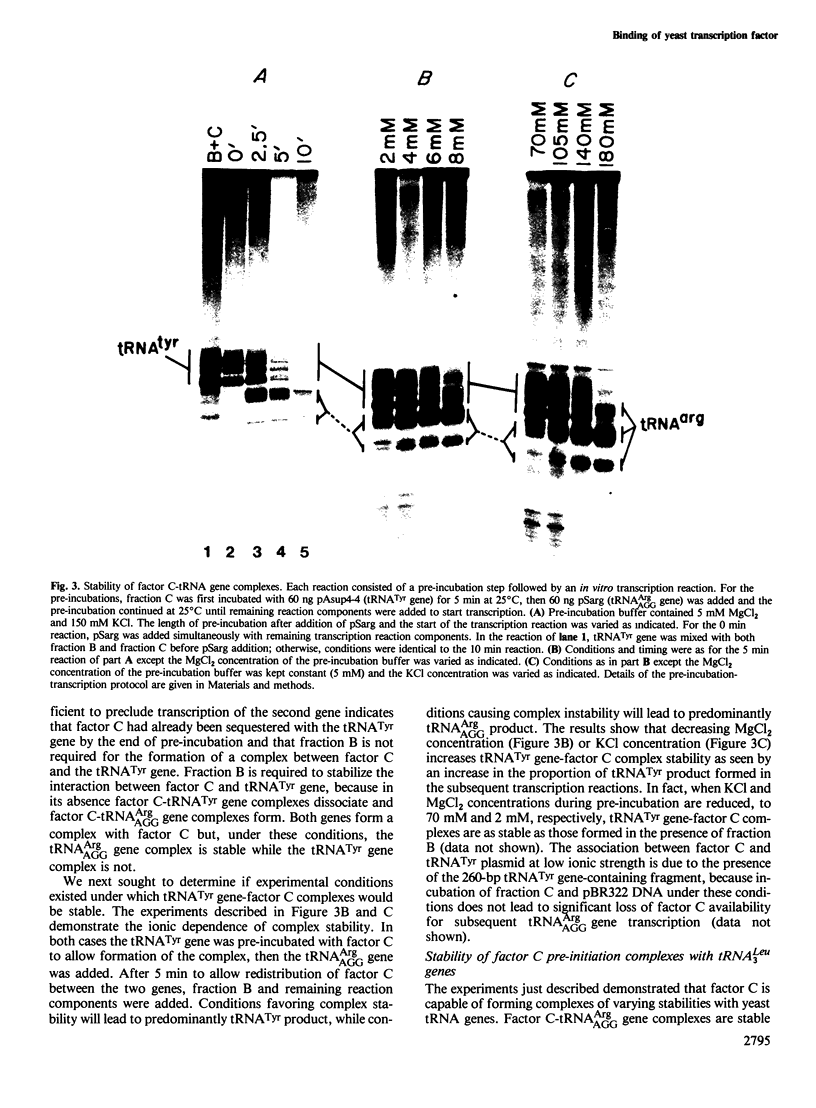
Transcription of yeast tRNA genes in vitro requires, in addition to RNA polymerase III, two accessory factors which are resolved by ion-exchange chromatography. One of these transcription factors (factor C) binds to tRNA genes. The stability of factor C-tRNA gene complexes is gene-dependent: the tRNAAGGArg gene forms a highly stable complex while tRNA3Leu and tRNATyr gene complexes are unstable under our standard assay conditions. To determine how differences in tRNA gene structure affect factor C binding, mutant tRNATyr genes, internally deleted tRNA3Leu genes and hybrid transcription units containing both tRNATyr and tRNA3Leu segments were compared in their abilities to stably bind factor C. Sequence changes in either of the two highly conserved promoter elements (A block and B block) affect factor C complex stability. Changes towards the consensus sequence increase complex stability while changes away from the consensus sequence drastically reduce stability. Also, the distance separating the A and B blocks affects complex stability; 34-53 bp gives highest stability. These results indicate that the stable binding of transcription factor C to tRNA genes involves interactions with both A block and B block sequences.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Goh S. H., Hall B. D. The promoter sequence of a yeast tRNAtyr gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreadis A., Hsu Y. P., Kohlhaw G. B., Schimmel P. Nucleotide sequence of yeast LEU2 shows 5'-noncoding region has sequences cognate to leucine. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. Stable transcription complex formation of eukaryotic tRNA genes is dependent on a limited separation of the two intragenic control regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10395–10402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafner J., Robertis E. M., Philippsen P. Delta sequences in the 5' non-coding region of yeast tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):583–591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Specific interactions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with a promoter region of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Allison D. S., Worthington M., Hall B. D. An in vitro RNA polymerase III system from S. cerevisiae: effects of deletions and point mutations upon SUP4 gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8127–8143. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Gillam S., Smith M. Mutations at the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: DNA sequence changes in mutants lacking suppressor activity. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladiges W. C., Raff R. F., Brown S., Deeg H. J., Storb R. The canine major histocompatibility complex. Supertypic specificities defined by the primed lymphocyte test (PLT). Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00345410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Page G. S., Sentenac A., Piper P. W., Worthington M., Weiss R. B., Hall B. D. Only one of two closely related yeast suppressor tRNA genes contains an intervening sequence. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):464–469. doi: 10.1038/291464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price H. J., Stebbins G. L. The Developmental Genetics of the CALCAROIDES Gene in Barley, II. Peroxidase Activity in Mutant and Normal Plants at Progressive Stages of Development. Genetics. 1971 Aug;68(4):539–546. doi: 10.1093/genetics/68.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Camier S., Smagowicz W., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of a class C transcription factor which forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. II. Formation of stable complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Differential binding of a S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase III transcription factor to two promoter segments of a tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):847–853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson P. F., Tanaka S., Schöld M., Itakura K., Abelson J. Directed deletion of a yeast transfer RNA intervening sequence. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1396–1400. doi: 10.1126/science.6997991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]