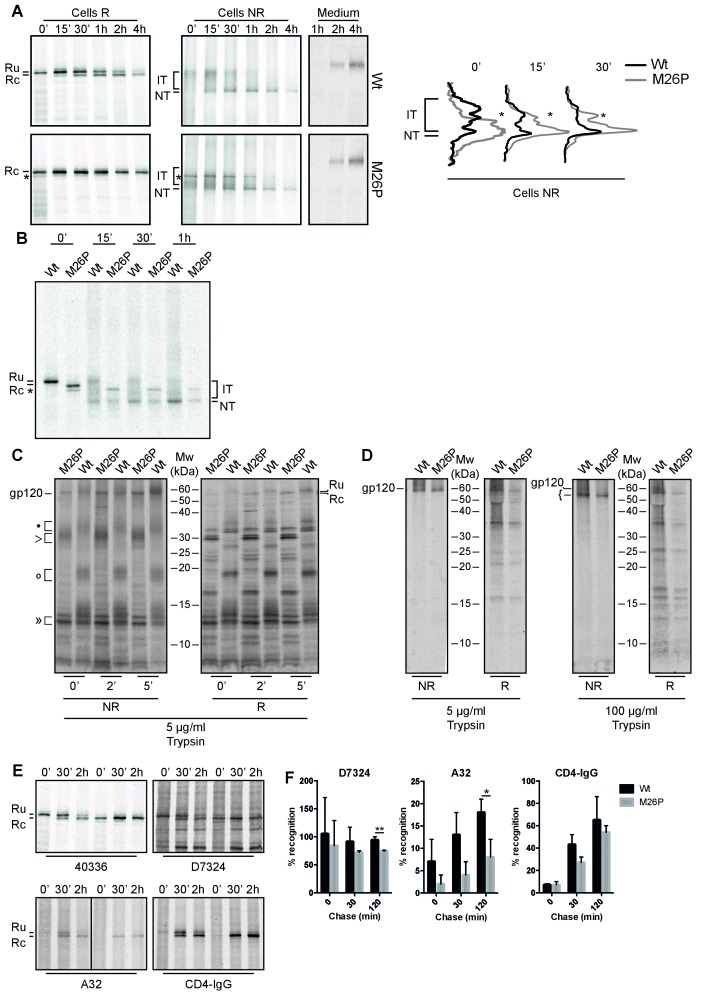
Figure 7. M26P leads to co-translational signal-peptide cleavage.
Experiments were done as in Figure 1. (A) HeLa cells expressing wild-type and M26P gp160 were radiolabeled for 10 min and chased for the indicated times. Samples were deglycosylated with endoH and subjected to reducing (Cells R) and non-reducing (Cells NR) 7.5% SDS-PAGE. Medium samples were reduced and not deglycosylated. Lane profiles depicting the folding-intermediate (NR) smear of wild-type and M26P gp160 were determined from autoradiographs. (B) As in A except that wild-type and M26P gp120 were used and samples were pulse labeled for 5 min in the presence of 5 mM DTT and chased in the absence of DTT. (C + D) HeLa cells expressing wild-type and M26P gp120 were pulse labeled as above and chased for either 0, 2, or 5 min (C) or 2 h (D). At the end of each time point, detergent cell lysates were proteolyzed with 5 or 100 µg/ml trypsin for exactly 15 min on ice. Proteolyzed samples were processed as in Figure 1 and analyzed by 15% SDS-PAGE. (E) HeLa cells expressing wild-type or M26P gp160 were pulse labeled and chased as above. Detergent cell lysates were immunoprecipitated in parallel with either polyclonal antibody 40336 or antibodies A32, D7324, or CD4-IgG. After immunoprecipitation, samples were processed as in Figure 1. (F) Quantifications of experiments from E. Values were normalized compared to immunoprecipitation by 40336. Statistics were calculated using an unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. Exact p values can be found in Figure 7—source data 1. IT: folding intermediates; NT: native gp160; *: uncleaved unglycosylated M26P gp160 that had not targeted properly to the ER, likely due to its suboptimal signal sequence. Gels shown are representative of at least 3 independent experiments (biological replicates).