Figure 1.
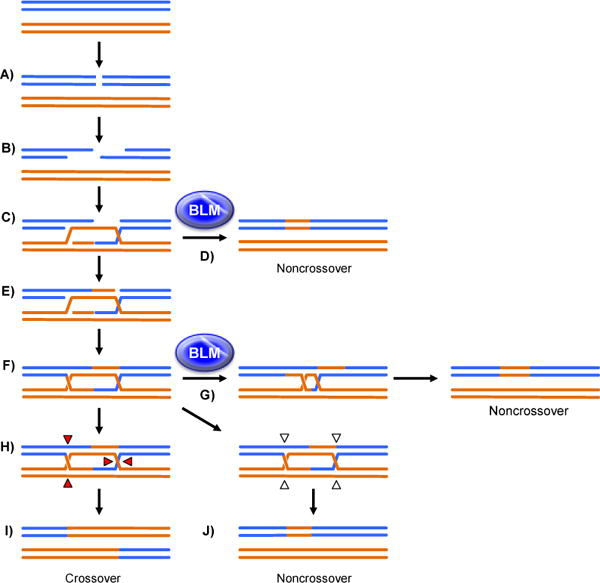
Mitotic Homologous Recombination (HR). A: Mitotic HR begins with a spontaneous DSB. B: The DSB is resected to yield 3′ single-stranded tails. C: A 3′ tail invades a homologous template, displacing a strand to create a D-loop. D: After synthesis off of the template, the nascent strand can be unwound and annealed to the other resected end of the DSB strand through synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA), which is facilitated by BLM, to create a noncrossover. Here and in subsequent figures E: Alternatively, the displaced strand can anneal to the other side of the DSB to prime synthesis. F: After synthesis and ligation, a double-Holliday junction (dHJ) intermediate is formed. G: The dHJ can be unwound in a process called dissolution, facilitated by BLM, to generate a noncrossover. H: If not dissolved, the dHJ can be cleaved by endonucleases at the red triangles (or at the opposite strands at each HJ) to create a crossover. I: dHJs can also be cleaved by endonucleases at the open arrows (or at the opposite strands at each HJ) to generate a noncrossover (J). Dotted lines indicated nascent synthesis. Final products are represented after repair of any mismatches or other heterologies between parental molecules so as to emphasize transfer of sequence information from the template.
