Abstract
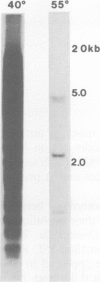
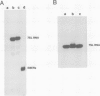
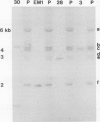
Of the several hundred 7SL RNA-like sequences that are dispersed in human DNA, no more than four are likely to represent genes for 7SL RNA; the majority are 7SL pseudogenes which appear to result from the reverse flow of genetic information from 7SL RNA back into genomic DNA. We present the sequence of five 7SL pseudogenes displaying an unprecedented diversity of structures. All are truncated copies of 7SL RNA, but the site of truncation can occur at either the 5' end, the 3' end or at both ends of the RNA sequence. We suggest that such diverse 7SL pseudogenes are generated by different but related pathways. In particular, we argue that two of the loci are secondary 7SL pseudogenes which derive from RNA polymerase III transcripts of primary (preexisting) 7SL pseudogenes. We also report the isolation and characterisation of a human genomic clone carrying two linked 7SL RNA coding regions, 7L30.1 and 7L30.2. The 7L30.2 locus differs by several single base changes from the known human 7SL RNA sequences and does not appear to be expressed at a detectable level in HeLa cells. The 7L30.1 locus is an authentic 7SL RNA gene encoding one of the three sequence variants of human 7SL RNA.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein L. B., Mount S. M., Weiner A. M. Pseudogenes for human small nuclear RNA U3 appear to arise by integration of self-primed reverse transcripts of the RNA into new chromosomal sites. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundelfinger E. D., Krause E., Melli M., Dobberstein B. The organization of the 7SL RNA in the signal recognition particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7363–7374. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Sharp S., Yamada H., Söll D. Analysis of a drosophila tRNA gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):889–895. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Y., Reddy R., Henning D., Epstein P., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of 7 S RNA. Homology to Alu DNA and La 4.5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5136–5142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D., Gottlieb E., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Striking similarities are exhibited by two small Epstein-Barr virus-encoded ribonucleic acids and the adenovirus-associated ribonucleic acids VAI and VAII. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):785–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. Globin mRNA sequences: analysis of base pairing and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):985–1002. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos T., Zasloff M. Comparative analysis of human chromosomal segments bearing nonallelic dispersed tRNAimet genes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Nishizawa R., Matsuda K., Taya Y., Nishimura S. A rat tRNA gene cluster containing the genes for tRNAPro and tRNALys. Analysis of nucleotide sequences of the genes and the surrounding regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6411–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Dingermann T., Farrell P., Söll D. Internal control regions for transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6657–6661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. A novel method for site-directed mutagenesis: its application to an eukaryotic tRNAPro gene promoter. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):415–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Melli M. Cloning and characterization of cDNA copies of the 7S RNAs of HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2209–2223. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Murphy S., Melli M. Human 7SL RNA consists of a 140 nucleotide middle-repetitive sequence inserted in an alu sequence. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Weiner A. M. Pseudogenes for human U2 small nuclear RNA do not have a fixed site of 3' truncation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1463–1471. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Weiner A. M. The small nuclear RNAs of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):956–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Genes for two small cytoplasmic Ro RNAs are adjacent and appear to be single-copy in the human genome. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):735–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Synthesis of two classes of small RNA species in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4520–4525. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]