Abstract
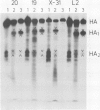
The amino acid sequences and biological properties of the haemagglutinin of three variants of the influenza virus X-31 (H3N2) selected for their capacity to grow in MDCK cells are reported. In two variants, amino acid substitutions at HA1 residues 8 and 144 correlated with the loss of a site for glycosylation and specific changes in antigenicity, respectively. In all three variants substitution of an arginine residue for histidine at HA1 position 17 was correlated with increased pH optima of haemolysis. The importance of this substitution for cleavage of the haemagglutinin precursor required to produce infectious virus is discussed in relation to the three-dimensional structure of X-31 haemagglutinin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baez M., Palese P., Kilbourne E. D. Gene composition of high-yielding influenza vaccine strains obtained by recombination. J Infect Dis. 1980 Mar;141(3):362–365. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Analyses of the antigenicity of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH optimum for virus-mediated membrane fusion. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1657–1662. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Lomniczi B., Bellamy A. R., Skehel J. J. Transcription of the influenza virus genome. Virology. 1977 Dec;83(2):337–355. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Rott R., Wahn K., Klenk H. D., Kohama T. The function of the neuraminidase in membrane fusion induced by myxoviruses. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90299-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M. Further studies on the activation of influenza virus by proteolytic cleavage of the haemagglutinin. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):151–161. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Gerhard W., Ward C. W., Dopheide T. A. Antigenic drift in type A influenza virus: sequence differences in the hemagglutinin of Hong Kong (H3N2) variants selected with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90540-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunier B., Kilker R. D., Jr, Tkacz J. S., Quaroni A., Herscovics A. Inhibition of N-linked complex oligosaccharide formation by 1-deoxynojirimycin, an inhibitor of processing glucosidases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14155–14161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild G. C., Oxford J. S., de Jong J. C., Webster R. G. Evidence for host-cell selection of influenza virus antigenic variants. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):706–709. doi: 10.1038/303706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeyen M., Fang R., Jou W. M., Devos R., Huylebroeck D., Saman E., Fiers W. Antigenic drift between the haemagglutinin of the Hong Kong influenza strains A/Aichi/2/68 and A/Victoria/3/75. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):771–776. doi: 10.1038/286771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. W., Brown L. E., Downie J. C., Jackson D. C. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus hemagglutinin. VII. The carbohydrate side chains of A/Memphis/102/72 hemagglutinin heavy chain which cross-react with host antigen. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]