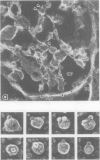
Abstract
Synaptic vesicles from guinea pig brain were highly purified by chromatography on Sephacryl S 1000. They were associated with a Mg-ATPase which could be solubilized with dichloromethane from vesicle membranes, and which elutes upon gel filtration with a mol. wt. approximately 300 kd. Vesicles accumulate [14C]methylamine in the presence of external ATP, indicating an ATP-dependent proton pump. Electron microscopy using a quick freeze, deep etch, rotary shadowing technique showed characteristic 'knob-like' protrusions on the surface of the vesicle. We suggest that these protrusions represent part of a proton ATPase which may be necessary for packaging of neurotransmitter into synaptic vesicles.
Full text
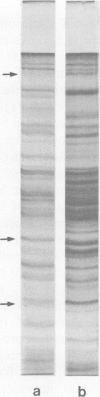
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apps D. K., Schatz G. An adenosine triphosphatase isolated from chromaffin-granulate membranes is closely similar to F1-adenosine triphosphatase of mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. Adenosine triphosphatase activity associated with purified cholinergic synaptic vesicles of Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Schneider D. L. Characterization of the membrane proteins of rat liver lysosomes. Composition, enzyme activities and turnover. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):525–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2040525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNANDEZ MORAN H., ODA T., BLAIR P. V., GREEN D. E. A MACROMOLECULAR REPEATING UNIT OF MITOCHONDRIAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. CORRELATED ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC AND BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF ISOLATED MITOCHONDRIA AND SUBMITOCHONDRIAL PARTICLES OF BEEF HEART MUSCLE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jul;22:63–100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M., Cantley L., Wiedenmann B., Altstiel L., Branton D. Clathrin-coated vesicles contain an ATP-dependent proton pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1300–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füldner H. H., Stadler H. 31P-NMR analysis of synaptic vesicles. Status of ATP and internal pH. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosie R. J. The localization of adenosine triphosphatases in morphologically characterized subcellular fractions of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):404–412. doi: 10.1042/bj0960404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota K., Kadota T. Isolation of coated vesicles, plain synaptic vesicles, and flocculent material from a crude synaptosome fraction of guinea pig whole brain. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):135–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Witzemann V. Photoaffinity labeling of a synaptic vesicle specific nucleotide transport system from Torpedo marmorata. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6123–6130. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Baker R. R., Morris S. J., Whittaker V. P. The preparation and characterization of synaptic vesicles of high purity. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 11;109(2):285–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90531-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi P. K., Irace G., Van Jaarsveld P. P., Lippoldt R. E., Edelhoch H. Instability of coated vesicles in concentrated sucrose solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5881–5885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Coated vesicles from human placenta carry ferritin, transferrin, and immunoglobulin G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):451–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Winkler H., Plattner H. Adrenal chromaffin granules: evidence for an ultrastructural equivalent of the proton-pumping ATPase. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;27(1):96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. L. ATP-dependent acidification of intact and disrupted lysosomes. Evidence for an ATP-driven proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3858–3864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Dowe G. H. Identification of a heparan sulphate-containing proteoglycan as a specific core component of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1381–1384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Fenwick E. M. Cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata contain an atractyloside-binding protein related to the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):377–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Tashiro T. Isolation of synaptosomal plasma membranes from cholinergic nerve terminals and a comparison of their proteins with those of synaptic vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;101(1):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. K., Xie X. S., Racker E. An ATP-driven proton pump in clathrin-coated vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4059–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudzuki T. Mg2+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase in isolated synaptic vesicles. Attribution of most of the enzymic activity to an actomyosin-like protein. J Biochem. 1979 Feb;85(2):567–574. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Usukura J., Tsukita S., Ishikawa H. The cytoskeleton in myelinated axons: a freeze-etch replica study. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2135–2147. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Stadler H., Witzemann V. Calmodulin binding proteins of the cholinergic electromotor synapse: synaptosomes, synaptic vesicles, receptor-enriched membranes, and cytoskeleton. J Neurochem. 1984 Feb;42(2):314–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechel K., Stadler H. Identification of actin in highly purified synaptic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):788–795. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]