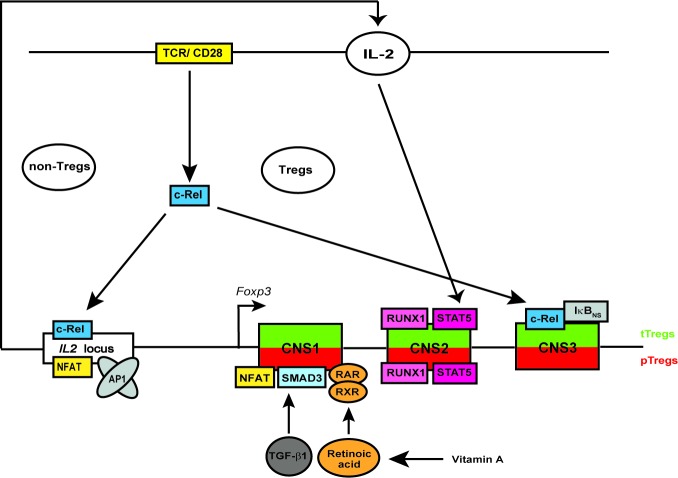
Figure 6. Schematic overview of the proposed mechanism of c-Rel-mediated regulation of Tregs.
c-Rel regulates the Treg development and homeostasis by binding to the IL2 locus in non-Tregs and to the Foxp3 locus in developing thymic Tregs, respectively. c-Rel binds together with IκBNS to conserved non-coding sequence 3 (CNS3) of Foxp3 locus. Several other transcription factors such as STAT5, RUNX1 as well as NFAT, SMAD3, RAR and RXR can bind to CNS2 and CNS1, respectively. Tregs in the peripheral organs and in in vitro CD4+ T cell cultures develop independently of c-Rel. Abbreviations: TCR, T cell receptor; TGF, transforming growth factor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; AP1, activator protein 1; RUNX1, runt-related transcription factor 1; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; RXR, retinoid X receptor.