Abstract
Background
The authors are aware of only one article investigating amino acid concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms, and this was published 31 years ago. Since then, both management of subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) and amino acid assay techniques have seen radical alterations, yet the pathophysiology of SAH remains unclear.
Objective
To analyse the pattern of concentrations of amino acids and related compounds in patients with different outcomes following aneurysmal SAH.
Methods
49 CSF samples were collected from 23 patients on days 0–3, 5, and 10 post-SAH. Concentrations of 33 amino acids and related compounds were assayed by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in patients with good [Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) 1–3] and poor (GOS 4–5) outcome.
Results
Of the 33 compounds assayed, only hydroxyproline and 3-aminoisobutyric acid appeared not to increase significantly following SAH. In poor outcome patients, we found significantly higher concentrations of aspartic acid (p = 0.038), glutamic acid (p = 0.038), and seven other compounds on days 0–3 post-SAH; glutamic acid (p = 0.041) on day 5 post-SAH, and 2-aminoadipic acid (p = 0.033) on day 10 post-SAH. The most significant correlation with GOS at 3 months was found for aminoadipic acid on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.81).
Conclusion
Aneurysmal rupture leads to a generalised increase of amino acids and related compounds in CSF. The patterns differ between good and poor outcome cases. Increased excitatory amino acids are strongly indicative of poor outcome.
Keywords: subarachnoid haemorrhage, amino acids, early brain injury, delayed cerebral ischaemia, biomarkers
Introduction
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) due to ruptured intracranial aneurysms is a life-threatening condition with an annual incidence of 2–22.5/100,000 population per annum. The average annual attack rate per 100,000 population for men and women aged 25–64 years in Poland is 10.9 and 9.1, respectively, and the 28 day fatality rates 39 and 44% (1, 2). Cumulative morbidity and mortality following SAH remain high, despite the considerable efforts of neuroclinicians worldwide (3, 4). Traditionally, rebleeding and cerebral vasospasm have been regarded as the main causes of poor outcome in these cases (5). Although cerebral vasospasm has been extensively studied, and subjected to numerous drug trials during the past several decades, the outcome appears not to have been improved by its reversal (2, 6, 7). Several recent studies indicate that early brain injury (EBI), which occurs during the 24–72 h following aneurysmal rupture, makes a significant contribution to patient outcome, and may be responsible for the detrimental effects seen in patients after SAH (3, 8–10). EBI was first reported by Kusaka et al. (11). Since then, the knowledge of mechanisms involved in EBI significantly progressed, but it still warrants further investigation (12–20). During EBI, the central nervous system (CNS) suffers from “primary” insults (involving acute changes of intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, and cerebral blood flow with vascular constriction and obstruction of the microcirculation), and “secondary” ischaemic processes (including anaerobic cellular respiration, energy depletion, impaired protein synthesis, excitotoxicity, free radical attack, neuronal stress, and DNA damage, leading to apoptosis and necrosis) (16). Many of these processes may potentially be initiated, mediated, or terminated by amino acids and related compounds. Von Holst and Hagenfeldt in 1985 appear to be the only group to have demonstrated increased levels of amino acids in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) after SAH, and proposed mechanisms leading to it (21). Since then, no new studies analysing CSF amino acids involved in SAH has been published. Our present aim is to look into the role of amino acids and related compounds potentially involved in the process of brain injury following SAH. Determination of amino acid levels in CSF samples may provide a means of determining prognosis at an early stage and extending the knowledge about the pathophysiology of SAH.
Materials and Methods
Ethics and Consent
This is a prospective observational study conducted in a single medical centre in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The local bioethics committee approved the study protocol, consenting protocol, and consent forms. Patients were assessed by two specialists (neurosurgeon and anaesthesiologist) as to their ability to give informed consent. Depending on this assessment, either the patient or next of kin gave consent for entry to the study and use a blinded medical data for analysis and further publication.
Population, Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
132 patients with SAH [confirmed by non-contrast computed tomography (CT)] were referred to our department during study recruitment period (from May 2015 to October 2016). Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) aneurysmal SAH treated endovascularly <24 h post rupture, (2) external ventricular drainage (EVD) placed <48 h post rupture. The aim was early prevention of rebleeding while managing acute hydrocephalus (HCP), but avoiding the trauma associated with open surgery. Exclusion criteria for the study were as follows: (1) history of CNS disease (meningitis, stroke), (2) active CNS infection, (3) active systemic disease (diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, malignancy, cirrhosis, renal failure), (4) age below 18, and (5) pregnancy. Conditions with potential impact on CSF homeostasis as well as subpopulations with distinct SAH features were not enrolled. Control CSF was obtained during spinal anaesthesia from age- and sex-matched patients with a negative history of CNS diseases.
Management, Definitions, and End Points
On admission, the clinical status was assessed using GCS and specific SAH grading scales [Hunt and Hess (HH), World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies (WFNS)]. An initial head CT scan was used to confirm SAH and assess the presence of HCP. EVD was placed secondary to endovascular treatment in patients with GCS score below 15 and: (1) relative bicaudate index >1, (2) focal dilation of ventricular system due to obstruction, or (3) thick intraventricular blood clot. A second CT scan was performed within 24 h of aneurysmal occlusion and EVD placement to assess any procedure related brain injury. Patients received a continuous infusion of nimodipine for at least 10 days, hypotension was avoided using vasopressors, and euvolemia was maintained. Induced hypertension (20–30% above baseline levels) was used to treat patients diagnosed with delayed cerebral ischaemia (DCI), based on the appearance of a new focal deficit, or a drop of at least two points on the GCS lasting at least 2 h after the exclusion of systematic causes EVD infection screening involved CSF cell count at least twice per patient, and CSF culture at least once on day 10 post-SAH. The primary end point was the treatment outcome assessed at 3 months using the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) (22). Patients were divided into two groups according to GOS. Good outcome consisted of those with no disability, moderate disability, and severe disability (GOS grades 5, 4, and 3); poor outcome were those with persistent vegetative state or death (GOS grades 2 and 1). DCI related infarction was defined as a new cerebral infarction identified on a head CT scan within 6 weeks of rupture and not present on the immediate posttreatment scan [as proposed by Vergouwen et al. (23)].
Plasma Assays and CSF Sample Collection
Haemoglobin, white blood cell (WBC) count, C-reactive protein (CRP) level, and fibrinogen level were assessed daily. Automatic analysers XT 2000i (Sysmex, Japan), Cobas 6000 (Roche Diagnostic, USA), and ACL TOP 500 (Instrumentation Laboratory, Italy) were used for measurements. CSF samples were collected from the EVD at three time points, on post-SAH days 0–3, 5, and 10. Each CSF sample was centrifugated and stored at −80°C until assayed.
Determination of Free Amino Acid Profiles
The applied methodology was based on an aTRAQ™ kit (Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA). The detailed description of a sample preparation procedure as well as liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) parameters have been described in our previous report (24). The sample preparation comprised the following steps: protein precipitation by 10% sulphosalicyclic acid, dilution with borate buffer, amino acids labelling with aTRAQ™ reagent, and addition of internal standard mixture. Labelling efficiency was confirmed using norleucine (contained in sulphosalicylic acid solution) and norvaline (contained in borate buffer). LC–MS/MS assays were carried out on a high-performance liquid chromatography instrument 1260 Infinity (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) coupled with 4000 QTRAP triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA). Chromatographic separation of amino acids was performed using a Sciex C18 column (4.6 mm × 150 mm, 5 µm) and a flow rate of 800 µL/min in a gradient elution mode. Solvent A was water and solvent B was methanol, both with 0.1% formic acid and 0.01% heptafluorobutyric acid. The injection volume was 2 µL. The mass spectrometer was equipped with an electrospray ionisation source and operated in positive ionisation mode. For detection and quantification of amino acids, a highly selective schedule multiple reaction monitoring mode was used. Data acquisition and processing were performed with Analyst 1.5 software (Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA). The applied methodology is suitable for simultaneous determination of a wide range of 33 free amino acids, both proteinogenic and non-proteionogenic, with high sensitivity and specificity in time below 20 min (24–26). Due to simplification used in this article, o-phosphoethanolamine and ethylamine are counted to amino acids, yet in fact they are amino acids derivatives.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using STATISTICA 10 (Stat Soft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). Values for normally distributed numerical data have been expressed as mean and SDs; for ordinal or non-normally distributed numerical data as median and interquartile range, and for categorical data as counts and percentages. The normality of data distribution was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Amino acids levels are presented on figures as median and interquartile range since in nearly all cases they do not show normal distribution. Comparisons were made by using (1) Mann–Whitney test, (2) Student’s t-test, (3) Friedman test with Conover–Iman post hoc, and (4) repeated measures ANOVA test with Fisher post hoc. The correlations were assessed by Spearman’s test, and correlation coefficient (cc) >0.6 (cc < −0.6) was considered significant. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant when comparing.
Results
The concentrations of the 33 compounds were established for 49 samples derived from 23 SAH patients (Table 1), and 25 samples collected from 25 control patients. Assays were available from 22 samples at days 0–3 post-SAH, 15 from days 5, and 12 from day 10. Rupture of an aneurysm led to a significant elevation of 27 of the 33 compounds in the CSF at days 0–3 post-SAH (Table 2). On days 0–3 post-SAH, the six exceptions were ethylamine (p = 0.798), gamma-aminobutyric acid (p = 0.699), 3-amino-isobutyric acid (p = 0.668), hydroxyproline (p = 0.164), threonine (p = 0.079), and arginine (p = 0.062). On day 5 post-SAH, three compounds showed no significant difference—aspartic acid (p = 0.175), 3-amino-isobutyric acid (p = 0.563), and hydroxyproline (p = 0.658). On day 10 post-SAH, there were four—aspartic acid (p = 0.054), 3-amino-isobutyric acid (p = 0.806), hydroxyproline (p = 0.289), and ethylamine (p = 0.292). Thus, hydroxyproline and 3-amino-isobutyric acid are the only 2 of the 33 substances assayed which appear to show no increase following SAH.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of study patients.
| Male | 12 (52%) | ||
| Age (years) | 57.26 ± 14.78 | ||
| Aneurysm location | |||
| Anterior communicating artery | 8 (35%) | ||
| Middle cerebral artery | 6 (26%) | ||
| Anterior cerebral artery | 3 (13%) | ||
| Basilar artery | 3 (13%) | ||
| Internal carotid artery | 1 (4%) | ||
| Posterior cerebral artery | 1 (4%) | ||
| Posterior inferior cerebellar artery | 1 (4%) | ||
| Aneurysmal size (mm) | 4.74 ± 1.82 | ||
| Cerebral infarction due to DCI on CT | 15 (65%) | ||
| Intracerebral haemorrhage on CT | 15 (65%) | ||
| Intraventricular blood on CT | 21 (91%) | ||
| Fisher CT score | 4 (4–4) | ||
| Modified Fisher CT score | 4 (3–4) | ||
| WFNS score on admission | 4 (3–5) | ||
| HH score on admission | 4 (3–5) | ||
| GCS on admission | 5 (4–12) | ||
| On admission | Post-SAH day 5 | Post-SAH day 10 | |
| WBC count (106/mm3) | 13.69 ± 5.4 | 11.86 ± 5.7 | 12.51 ± 4.3 |
| CRP level (mg/L) | 119.50 ± 79.5 | 89.42 ± 54.4 | 78.70 ± 119 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 446.70 ± 151 | 608.20 ± 205 | 592.90 ± 249 |
| Hgb (g/dL) | 16.40 ± 17.41 | 11.31 ± 1.9 | 10.93 ± 1.3 |
| Treatment outcome (according to GOS at 3 months) | |||
| Good recovery (score of 5) | 6 (26%) | ||
| Moderate disability (score of 4) | 2 (9%) | ||
| Severe disability (score of 3) | 2 (9%) | ||
| Persistent vegetative state (score of 2) | 5 (22%) | ||
| Death (score of 1) | 8 (35%) | ||
Data presented as mean ± SD; median (interquartile range) or count (percentage).
CRP, C-reactive protein; CT, computed tomography; DCI, delayed cerebral ischaemia; GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; GOS, Glasgow Outcome Scale; HH, Hunt and Hess scale; Hgb, plasma haemoglobin; WBC, white blood cell; WFNS, World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies scale.
Table 2.
Differences in cerebrospinal fluid amino acid level at days 0–3, 5, and 10 post-SAH in healthy individuals (control group) and subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) patients (study group).
| Amino acid | Control group | Study group, day 0–3 post-SAH | Control group vs study group, days 0–3 post-SAH. p value | Study group, day 5 post-SAH | Control group vs study group, day 5 post-SAH. p value | Study group, day 10 post-SAH | Control group vs study group, day 10 post-SAH. p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-phosphoethanolamine (μM) | 3.00 | 5.95 | <0.01 | 5.15 | <0.001 | 6.60 | <0.001 |
| Ethylamine (μM) | 9.80 | 9.40 | 0.798 | 9.65 | <0.001 | 11.10 | 0.292 |
| Taurine (μM) | 7.00 | 16.00 | <0.001 | 14.30 | <0.001 | 10.75 | <0.01 |
| Asparagine (μM) | 5.70 | 10.35 | 0.01 | 19.50 | <0.001 | 21.75 | <0.001 |
| Serine (μM) | 24.20 | 55.70 | <0.001 | 75.40 | <0.001 | 83.75 | <0.001 |
| Glycine (μM) | 8.90 | 38.75 | <0.001 | 34.85 | <0.001 | 35.20 | <0.001 |
| Hydroxyproline (μM) | 0.60 | 1.00 | 0.164 | 1.35 | 0.658 | 1.35 | 0.289 |
| Glutamine (μM) | 407.60 | 520.65 | <0.01 | 791.10 | <0.001 | 796.30 | <0.001 |
| Aspartic acid (μM) | 0.50 | 1.55 | <0.001 | 0.80 | 0.175 | 0.95 | 0.054 |
| Citruline (μM) | 1.60 | 2.75 | 0.011 | 2.55 | <0.01 | 3.30 | <0.01 |
| Threonine (μM) | 24.80 | 29.05 | 0.079 | 56.10 | <0.001 | 63.40 | <0.001 |
| Beta-alanine (μM) | 20.30 | 22.00 | 0.040 | 29.00 | <0.01 | 27.30 | <0.01 |
| Alanine (μM) | 35.00 | 88.05 | <0.001 | 114.55 | <0.001 | 122.55 | <0.001 |
| Glutamic acid (μM) | 1.20 | 5.40 | <0.001 | 3.00 | < 0.001 | 2.35 | <0.01 |
| Histidine (μM) | 11.40 | 28.20 | <0.001 | 43.35 | <0.001 | 40.20 | <0.001 |
| 3-Methylhistidine (μM) | 0.50 | 1.00 | <0.01 | 1.40 | <0.001 | 1.05 | <0.01 |
| 2-Aminoadipic acid (μM) | 0.00 | 1.65 | <0.001 | 2.10 | <0.001 | 1.45 | <0.001 |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid (μM) | 0.40 | 0.50 | 0.699 | 0.30 | 0.012 | 0.20 | 0.051 |
| 3-Aminoisobutyric acid (μM) | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.668 | 0.30 | 0.563 | 0.35 | 0.806 |
| 2-Aminobutyric acid (μM) | 3.20 | 6.20 | <0.01 | 6.60 | <0.001 | 7.30 | <0.001 |
| Arginine (μM) | 15.70 | 19.25 | 0.062 | 26.60 | <0.001 | 24.35 | <0.01 |
| Proline (μM) | 0.80 | 11.80 | <0.001 | 13.95 | <0.001 | 16.15 | <0.001 |
| Ornithine (μM) | 4.30 | 19.80 | <0.001 | 17.95 | <0.001 | 17.75 | <0.001 |
| Cystathionine (μM) | 0.30 | 2.05 | <0.001 | 1.05 | <0.001 | 1.40 | <0.001 |
| Cysteine (μM) | 0.40 | 2.05 | <0.001 | 1.75 | <0.001 | 1.65 | <0.001 |
| Lysine (μM) | 22.50 | 53.80 | <0.001 | 73.05 | <0.001 | 72.40 | <0.001 |
| Methionine (μM) | 3.10 | 6.20 | <0.01 | 11.70 | <0.001 | 13.65 | <0.001 |
| Valine (μM) | 16.20 | 38.65 | <0.01 | 66.20 | <0.001 | 76.30 | <0.001 |
| Tyrosine (μM) | 7.80 | 26.70 | <0.001 | 36.20 | <0.001 | 37.30 | <0.001 |
| Isoleucine (μM) | 4.40 | 9.65 | 0.001 | 13.05 | <0.001 | 15.05 | <0.001 |
| Leucine (μM) | 11.40 | 29.20 | <0.001 | 43.50 | <0.001 | 56.80 | <0.001 |
| Phenylalanine (μM) | 9.40 | 26.45 | <0.001 | 43.25 | <0.001 | 44.45 | <0.001 |
| Tryptophan (μM) | 1.90 | 9.70 | <0.001 | 13.60 | <0.001 | 12.85 | <0.001 |
Median levels of the amino acids are presented in the table. p values were calculated either by Mann–Whitney or Student’s t-test. Amino acids increasing significantly during SAH (on days 0–3, 5, or 10) are shown in bold.
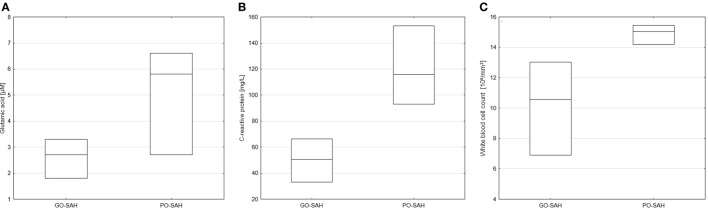
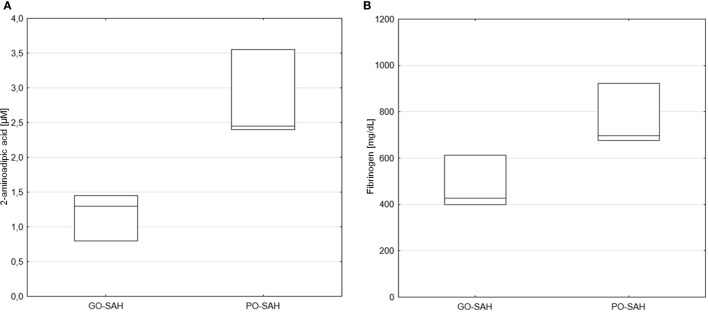
Patients were now divided into two groups as good and poor outcomes as defined above (Table 3). On days 0–3 post-SAH, concentrations of nine amino acids were significantly higher in patients with poor outcome than those with good outcome: taurine (p = 0.038), aspartic acid (p = 0.038), citrulline (p = 0.035), glutamic acid (p = 0.038), gamma-amino-butyric acid (p = 0.043), 3-methyl-histidine (p = 0.01), ornithine (p = 0.033), cystathionine (p = 0.01), and isoleucine (p = 0.045). WBC level (p = 0.01) also differentiated these two groups (Figure 1). On day 5 post-SAH, glutamic acid (p = 0.041) was the only amino acid showing significantly higher levels in the poor outcome group. At this stage, CRP (p = 0.020) and WBC (p = 0.044) were also significantly higher in the poor outcome group (Figure 2). On day 10 post-SAH, 2-amino-adipic acid (p = 0.033) and fibrinogen (p = 0.014) were the only parameters showing significantly higher levels in the poor outcome group (Figure 3).
Table 3.
Differences in monitored parameters at days 0–3, 5, and 10 post-SAH in patients with good (GO-SAH) and poor (PO-SAH) treatment outcome.
| Monitored parameter | Days 0–3 post-SAH |
Day 5 post-SAH |
Day 10 post-SAH |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO-SAH | PO-SAH | GO-SAH vs PO-SAH. p value | GO-SAH | PO-SAH | GO-SAH vs PO-SAH. p value | GO-SAH | PO-SAH | GO-SAH vs PO-SAH. p value | |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 125.00 | 130.00 | 0.715 | 50.70 | 115.80 | 0.020 | 22.40 | 109.70 | 0.139 |
| White blood cell count (106/mm3) | 9.86 | 17.47 | <0.001 | 10.57 | 15.03 | 0.044 | 9.66 | 16.84 | 0.445 |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.10 | 13.10 | 0.212 | 11.30 | 10.90 | 0.262 | 10.60 | 11.50 | 0.672 |
| Temperature (°C) | 37.00 | 37.00 | 0.736 | 37.40 | 37.20 | 0.273 | 36.90 | 35.70 | 0.512 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 485.00 | 550.00 | 0.879 | 509.00 | 676.00 | 0.257 | 428.00 | 698.00 | 0.014 |
| O-phosphoethanolamine (μM) | 4.10 | 6.80 | 0.161 | 4.90 | 7.70 | 0.161 | 5.95 | 8.50 | 0.019 |
| Taurine (μM) | 13.10 | 19.40 | 0.038 | 14.60 | 13.40 | 0.514 | 12.20 | 7.35 | 0.138 |
| Asparagine (μM) | 9.00 | 11.50 | 0.256 | 30.20 | 12.50 | 0.397 | 22.90 | 20.45 | 0.423 |
| Serine (μM) | 45.10 | 76.50 | 0.161 | 77.00 | 61.40 | 0.947 | 79.50 | 94.75 | 0.503 |
| Glycine (μM) | 29.60 | 41.00 | 0.182 | 30.00 | 43.00 | 0.204 | 35.20 | 35.65 | 0.671 |
| Hydroxyproline (μM) | 0.70 | 1.30 | 0.066 | 1.70 | 0.80 | 0.518 | 1.35 | 1.10 | 0.793 |
| Ethylaminev (μM) | 5.80 | 15.80 | 0.102 | 7.90 | 12.10 | 0.134 | 8.85 | 14.50 | 0.35 |
| Glutamine (μM) | 489.90 | 602.50 | 0.182 | 837.30 | 505.10 | 0.585 | 852.50 | 715.60 | 0.483 |
| Aspartic acid (μM) | 0.80 | 2.20 | 0.038 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 0.071 | 0.95 | 1.30 | 0.551 |
| Citruline (μM) | 1.90 | 5.90 | 0.035 | 2.50 | 3.10 | 0.396 | 3.30 | 3.30 | 1 |
| Threonine (μM) | 25.90 | 50.00 | 0.35 | 86.30 | 34.20 | 0.327 | 63.40 | 57.95 | 0.298 |
| Beta-alanine (μM) | 28.30 | 22.00 | 0.07 | 30.00 | 28.60 | 0.497 | 26.85 | 27.85 | 0.893 |
| Alanine (μM) | 70.70 | 138.10 | 0.109 | 115.50 | 113.60 | 0.447 | 120.30 | 141.70 | 0.954 |
| Glutamic acid (μM) | 3.40 | 9.30 | 0.038 | 2.70 | 5.80 | 0.024 | 2.00 | 17.10 | 0.269 |
| Histidine (μM) | 18.90 | 38.10 | 0.256 | 63.60 | 23.70 | 0.711 | 43.55 | 37.45 | 0.753 |
| 3-Methylhistidine (μM) | 0.70 | 1.50 | <0.01 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 0.958 | 1.35 | 1.05 | 0.733 |
| 2-Aminoadipic acid (μM) | 1.30 | 1.70 | 0.076 | 1.50 | 4.10 | 0.071 | 1.30 | 2.45 | 0.033 |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid (μM) | 0.30 | 0.90 | 0.043 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.932 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.266 |
| 3-Aminoisobutyric acid (μM) | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.066 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.958 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.93 |
| 2-Aminobutyric acid | 4.60 | 8.20 | 0.088 | 11.40 | 5.50 | 0.542 | 10.75 | 6.50 | 0.124 |
| Arginine (μM) | 18.50 | 22.30 | 0.182 | 30.90 | 26.00 | 0.525 | 24.35 | 20.45 | 0.21 |
| Proline (μM) | 4.50 | 14.80 | 0.204 | 18.70 | 10.90 | 0.672 | 16.15 | 18.40 | 0.759 |
| Ornithine (μM) | 7.60 | 27.50 | 0.033 | 17.30 | 28.30 | 0.09 | 17.35 | 33.05 | 0.552 |
| Cystathionine (μM) | 0.80 | 2.80 | <0.01 | 1.00 | 1.80 | 0.089 | 1.30 | 1.50 | 0.199 |
| Cysteine (μM) | 1.60 | 2.30 | 0.141 | 1.50 | 2.20 | 0.243 | 1.95 | 1.40 | 0.329 |
| Lysine (μM) | 43.00 | 74.50 | 0.095 | 87.10 | 55.90 | 0.341 | 72.40 | 72.60 | 0.612 |
| Methionine (μM) | 4.60 | 12.30 | 0.204 | 16.20 | 7.70 | 0.491 | 13.65 | 13.70 | 0.687 |
| Valine (μM) | 31.80 | 62.40 | 0.109 | 102.50 | 33.60 | 0.397 | 87.75 | 72.20 | 0.377 |
| Tyrosine (μM) | 23.00 | 32.50 | 0.083 | 36.60 | 35.80 | 0.876 | 38.60 | 37.30 | 0.676 |
| Isoleucine (μM) | 6.00 | 13.00 | 0.045 | 17.60 | 11.80 | 0.597 | 15.05 | 13.70 | 0.45 |
| Leucine (μM) | 22.90 | 39.70 | 0.109 | 80.30 | 29.80 | 0.397 | 60.95 | 50.55 | 0.532 |
| Phenylalanine (μM) | 21.20 | 38.80 | 0.062 | 51.30 | 32.40 | 0.665 | 45.40 | 44.45 | 0.913 |
| Tryptophan (μM) | 8.00 | 12.20 | 0.066 | 13.60 | 13.60 | 0.606 | 12.60 | 13.55 | 0.804 |
Median levels of the amino acids are presented in the table. p values were calculated either by Mann–Whitney or Student’s t-test. Significant differences are shown in bold.
Figure 1.
Significant differences in monitored parameters on days 0–3 post-SAH between patients with good (GO-SAH) and poor (PO-SAH) treatment outcome. Mann–Whitney test revealed significantly higher levels of (A) taurine (p = 0.038), (B) aspartic acid (p = 0.038), (C) citruline (p = 0.035), (D) glutamic acid (p = 0.038), (E) 3-methylhistidine (p < 0.01), (F) gamma-aminobutyric acid (p = 0.043), (G) ornithine (p = 0.033), (H) cystathionine (p < 0.01), and (I) isoleucine (p = 0.045) in patients with poor outcome. Student’s t-test revealed significantly higher level of white blood cell count (p < 0.01) in patients with poor outcome (J). In all cases, median levels and the 25th and 75th percentiles are presented.
Figure 2.
Significant differences in monitored parameters on day 5 post-SAH between patients with good (GO-SAH) and poor (PO-SAH) treatment outcome. (A) Student’s t-test revealed significantly higher levels of glutamic acid (p = 0.041) in patients with poor outcome. Mann–Whitney test revealed significantly higher C-reactive protein level (p 0.020) (B) and white blood cell count (p = 0.044) (C) in patients with poor outcome. In all cases, median levels and the 25th and 75th percentiles are presented.
Figure 3.
Significant differences in monitored parameters on day 10 post-SAH between patients with good (GO-SAH) and poor (PO-SAH) treatment outcome. Mann–Whitney test revealed significantly higher 2-aminoadipic acid (p = 0.033) (A) and fibrinogen (p = 0.014) (B) levels in patients with poor outcome. Median levels and the 25th and 75th percentiles are presented.
In the course of the study, it was possible to undertake assays at all three time points in 10 of the subjects; 7 of these were in the good outcome group. In this group, the Friedman test with Conover–Iman post hoc, or ANOVA test with Fisher post hoc, revealed significant changes in the concentrations of 18 of the compounds tested (Table 4). The number of poor outcome patients was too small to carry out such testing.
Table 4.
Amino acid level changes in time in good outcome SAH patients with (GO-SAH).
| Monitored parameter | Days 0–3 post-SAH | Day 5 post-SAH | Day 10 post-SAH | Omnibus test p value | Days 0–3 vs Day 5 p value post hoc | Days 0–3 vs Day 10 p value post hoc | Day 5 vs Day 10 p value post hoc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 125.00 | 50.70 | 27.00 | 0.049 | 0.345 | 0.012 | 0.073 |
| White blood cell count (106/mm3) | 9.86 | 10.57 | 9.34 | 0.631 | |||
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.10 | 10.60 | 10.50 | 0.066 | |||
| Temperature (°C) | 37.00 | 37.30 | 36.90 | 0.382 | |||
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 485.00 | 442.00 | 423.00 | 0.327 | |||
| O-phosphoethanolamine (μM) | 6.20 | 5.00 | 5.80 | 0.325 | |||
| Taurine (μM) | 13.90 | 14.60 | 10.80 | 0.867 | |||
| Asparagine (μM) | 8.40 | 18.30 | 21.20 | 0.180 | |||
| Serine (μM) | 45.10 | 73.80 | 76.10 | 0.031 | 0.039 | 0.013 | 0.566 |
| Glycine (μM) | 29.60 | 32.60 | 42.50 | 0.565 | |||
| Hydroxyproline (μM) | 0.70 | 1.10 | 1.40 | 0.094 | |||
| Ethylaminev (μM) | 5.70 | 10.10 | 9.80 | 0.039 | 0.078 | <0.01 | 0.187 |
| Glutamine (μM) | 454.30 | 818.70 | 828.30 | 0.001 | <0.01 | <0.001 | 0.565 |
| Aspartic acid (μM) | 0.70 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.215 | |||
| Citruline (μM) | 1.90 | 2.40 | 2.80 | 0.069 | |||
| Threonine (μM) | 22.90 | 52.50 | 61.20 | 0.012 | 0.128 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Beta-alanine (μM) | 28.30 | 26.80 | 26.70 | 0.553 | |||
| Alanine (μM) | 70.70 | 106.20 | 120.30 | 0.124 | |||
| Glutamic acid (μM) | 4.50 | 2.70 | 2.10 | 0.898 | |||
| Histidine (μM) | 16.80 | 38.10 | 37.40 | 0.156 | |||
| 3-Methylhistidine (μM) | 0.60 | 1.50 | 0.90 | 0.369 | |||
| 2-Aminoadipic acid (μM) | 1.30 | 1.50 | 1.30 | 0.129 | |||
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid (μM) | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.633 | |||
| 3-Aminoisobutyric acid (μM) | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.215 | |||
| 2-Aminobutyric acid (μM) | 4.60 | 11.40 | 11.40 | 0.010 | 0.019 | <0.01 | 0.427 |
| Arginine (μM) | 18.50 | 26.50 | 24.10 | 0.050 | 0.073 | 0.012 | 0.345 |
| Proline (μM) | 3.40 | 11.90 | 15.20 | 0.062 | |||
| Ornithine (μM) | 7.60 | 17.30 | 14.30 | 0.368 | |||
| Cystathionine (μM) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.20 | 0.648 | |||
| Cysteine (μM) | 1.60 | 1.70 | 2.10 | 0.368 | |||
| Lysine (μM) | 43.00 | 83.20 | 70.80 | 0.017 | 0.017 | <0.01 | 0.735 |
| Methionine (μM) | 4.60 | 10.00 | 11.90 | 0.008 | 0.029 | <0.01 | 0.200 |
| Valine (μM) | 28.20 | 61.60 | 78.10 | 0.015 | 0.017 | <0.01 | 0.683 |
| Tyrosine (μM) | 23.00 | 35.10 | 28.50 | 0.020 | 0.023 | <0.01 | 0.647 |
| Isoleucine (μM) | 5.90 | 11.10 | 13.60 | 0.024 | 0.081 | <0.01 | 0.219 |
| Leucine (μM) | 22.60 | 39.70 | 60.50 | 0.024 | 0.022 | 0.013 | 0.801 |
| Phenylalanine (μM) | 20.90 | 35.20 | 37.50 | 0.038 | 0.040 | 0.018 | 0.700 |
| Tryptophan (μM) | 8.00 | 11.80 | 11.10 | 0.072 |
Median levels of the amino acids are presented in the table. Omnibus statistical test (Friedman or repeated measures ANOVA) revealed significant changes in concentration of 13 amino acids (shown in bold). Next, post hoc analysis (Conover–Iman for Friedman test and Fisher for repeated measures ANOVA) was run for those 13 amino acids to specify between what time points (days 0–3, 5, or 10 post-SAH) the differences in concentration were significant (shown in bold).
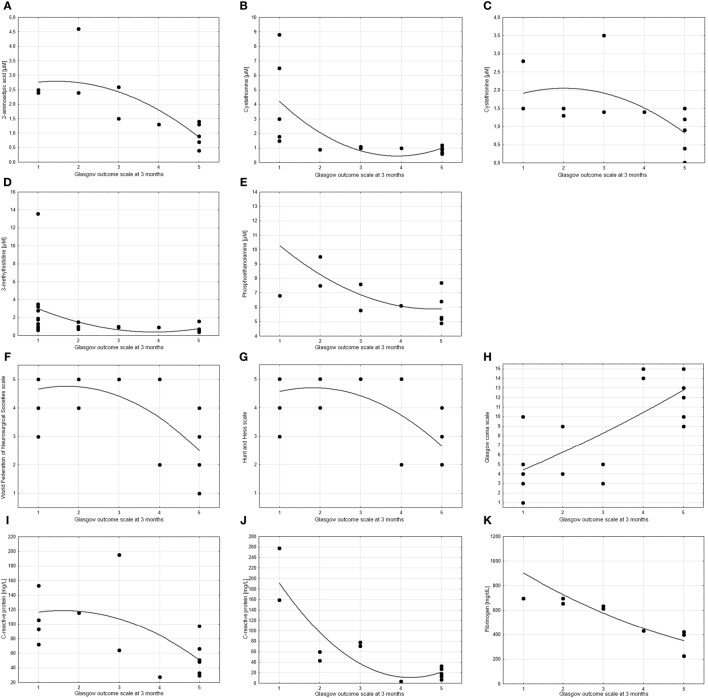
The levels of four of the compounds tested showed a significant correlation with GOS at 3 months. These were 2-amino-adipic acid on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.81), cystathionine on day 5 post-SAH (cc = −0.72) and day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.67), 3-methylhistidine on days 0–3 post-SAH (cc = −0.64), and o-phosphoethanolamine on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.62). As might be expected, there was a correlation between all three admission assessments (WFNS, HH, and GCS) and outcome. There were also correlations between outcome and CRP on days 5 and 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.64 and cc = −0.79, respectively) as well as fibrinogen level on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.97) (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Scatter charts showing the correlation between treatment outcome (measured by Glasgow Outcome Scale at 3 months) and other parameters. Spearman’s test revealed significant correlations (cc > 0.6 or cc < −0.6) for (A) 2-aminoadipic acid on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.81), (B,C) cystathionine on day 5 post-SAH (cc = −0.72) and day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.67), (D) 3-methylhistidine on days 0–3 post-SAH (cc = −0.64), (E) o-phosphoethanolamine on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.62), (F) World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies scale (cc = −0.64), (G) Hunt and Hess scale (cc = −0.61), (H) Glasgow coma scale (cc = 0.72), (I,J) C-reactive protein on day 5 post-SAH (cc = −0.64) and day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.79), and (K) fibrinogen on day 10 post-SAH (cc = −0.97). p values are <0.05 in all cases.
Discussion
In this study, we have analysed the profiles of amino acids and related compounds in the CSF of patients following SAH. The most significant findings are as follows:
-
(1)
Increase in 31 of 33 compounds in the days following SAH, with 26 increasing in the first 3 days after rupture
-
(2)
Significant increase in 18 of these compounds between days 0–3 and days 5 and 10
-
(3)
Higher levels of excitatory amino acids (EAAs) (glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and 2-amino-adipic acid) appear to predict a poor outcome.
As far as we are aware, it is 31 years since an article investigating amino acids in SAH has been published. In view of the paucity of publications, knowledge of this subject remains rudimentary. With the introduction of microdialysis, interest in this subject has been renewed since it allows in vivo sampling of brain interstitial fluid (27). This method allows continuous monitoring of brain metabolism, but this is limited to the tissue around the probe (28). On the other hand, the commonly available CSF analysis gives a more general picture of conditions in the brain. Physiologically, the exchange between brain interstitial fluid and CSF is bidirectional (29). In mice, levels of amino acids in brain interstitial fluid were found to be approximately 5–10 times lower than in the CSF (30). Although the latest studies of amino acids in SAH have focussed on microdialysis, widespread use of this monitoring technique is limited by its high cost. By contrast, EVD is a relatively inexpensive procedure commonly performed in patients following SAH. In the clinical setting, CSF seems to be a more convenient source for examining biomarkers.
In our patients, rupture of an aneurysm led to an increase in 31 of 33 amino acids and related compounds we assayed. In the study by von Holst et al., there was no increase in taurine levels following SAH. Because the concentration of taurine in whole blood is four to eight times greater than in blood plasma alone, von Holst et al. concluded that red blood cell (RBC) lysis did not contribute to the amino acid concentrations (31). We do not agree with this statement as in our series, the CSF taurine levels increased by a factor of 2. RBC lysis begins within 2–4 h of SAH and continues at least until the clot has cleared (32, 33). In our opinion, this process contributes to the amino acid levels at every stage following SAH. Microdialysis studies indicate that an early increase of taurine in the brain interstitial fluid is a reliable marker of poor outcome (34, 35). In the both articles, brain cells activated in the course of SAH were indicated as a potential source of taurine in the interstitial fluid. In our series, significantly higher taurine levels were observed on days 0–3 post-SAH in patients with a poor outcome. This observation suggests that taurine may have some value as a clinical marker and encourage further studies. In experimental settings, both detrimental and beneficial roles for taurine have been described. Kofler et al. have extensively discussed this matter in the context of SAH (34). Our study suggests predominantly harmful effects from taurine.
Among 33 assayed compounds, only 2 did not increase at any stage; these were hydroxyproline and 3-aminoisobutyric acid, neither of which is encoded in the eukaryotic genetic code. Hydroxyproline is produced by hydroxylation of proline and incorporated into collagen protein (36). In patients with blood–CSF barrier dysfunction, hydroxyproline has a smaller biological variation in CSF when compared with other amino acids (37). Hydroxyproline is increased in the blood plasma in Alzheimer’s disease, but shows no increase in Parkinson’s disease (38, 39). High protein bound of hydroksyproline in human erythrocytes could be an explanation of its elevation absence in CSF following SAH (40). Even less data are available for 3-aminoisobutyric acid, although it is known that it is a product of thymine catabolism and plays a role in fatty acid metabolism (41). The alterations of 3-aminoisobutyric acid could be a potential marker for the monitoring of the blood–brain barrier condition in the future studies (42).
Immediately after aneurysmal rupture, significantly higher levels of nine of the compounds investigated identified the patients with a poorer prognosis. Furthermore, none of the substances showed a significant decrease in CSF following SAH. We suspect that the initial increase is due to extravasated blood, and its extent related to the amount of blood. The main source is likely to be plasma, since the majority of amino acids (except glutamine and glutamic acid) have a CSF:plasma ratio of 0.1–0.2 (43). This is consistent with the fact that patients with a greater volume of subarachnoid blood have a poorer outcome (44).
In 18 of the compounds we investigated, there was a significant increase from days 0–3 post-SAH to days 5 and 10. There are several possible mechanisms for this delayed rise: (1) increased amino acid turnover as a response to injury. Zetterling et al. proposed this mechanism as an explanation for an increase in the concentrations of eight non-transmitter amino acids in brain interstitial fluid (45). (2) Cytokine-stimulated amino acid release. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1), which is a proinflammatory cytokine [found in CSF of SAH patients (46)], which induces the release of the glutamate analogue from gliosomes (glial resealed subcellular particles) in a concentration-dependent manner (47). Conversely, HMGB1 was found to accumulate in glutamate treated primary cortical culture media, and supernatants collected from these cultures were found to trigger microglial activation (48). (3) Disruption of CSF homeostasis affecting transport with both the bloodstream and the interstitial fluid. (4) Lysis of RBCs (mentioned above) subsequent to their continuous release from the clot during its clearance (33).
Glutamic acid, as an important EAA, is the most extensively studied amino acid in SAH. Levels of glutamic acid in the interstitial fluid increase within minutes of SAH, peak at 40 min, and remain elevated for days (49). The increase is most pronounced in patients with acute ischaemic neurological deficit (50). Increase in interstitial glutamic acid was identified as one of the earliest markers of impending ischaemia, typically increasing before the onset of clinical symptoms (27, 50). Our results are in line with these observations. Glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and 2-aminoadipic acid levels increase on days 0–3 post-SAH, and are all significantly higher at some point in the poor outcomes group of patients. In fact, in this group, outcome was most accurately predicted by 2-aminoadipic acid levels in CSF on day 10 post-SAH. 2-Aminoadipic acid is a structural homologue of glutamic acid and a natural product of lysine metabolism in mammalian cells (51). Huck et al. described gliotoxic properties of this amino acid (52), while Kato et al. observed enhanced susceptibility of glial cell to oxidative stress after 2-aminoadipic acid administration (53).
In this prospective observational study, some limitations need to be considered. First, specific enrolment criteria (acute HCP and EVD insertion) interfere with typical SAH pathophysiology. They will aggravate the SAH-associated brain injury and may well alter amino acid concentrations. Consequently, our observations may only be applicable to this subpopulation of SAH patients. Second, the relatively small number of examined samples and enrolled patients limits the extent of our conclusions. Nevertheless, the statistical relationships in our study follow the pattern of large scale studies (e.g., high correlation between admission status and treatment outcome). Third, EVD infection and CNS microbial inflammation could potentially affect the results, but our protocols specifically aim to minimise such problems. We have assumed a relationship between CSF and interstitial fluid, but this may itself be corrupted by the pathology. Future studies should include more good-grade patients without severe complications (e.g., acute HCP) with CSF drawn by LP.
Conclusion
Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage leads to a generalised increase of amino acids and related compounds in CSF. The patterns of concentrations differ between good and poor outcome patients. Increased EAAs are strongly indicative of poor outcome.
Ethics Statement
This is a prospective observational study conducted in a single medical centre in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The local bioethics committee approved the study protocol, consenting protocol, and consent forms.
Author Contributions
BS conceived and designed the study. BS, NW, RJa, and RJu analysed and interpreted the patient clinical data. BU, SP, AK, and ZK performed the amino acid assay and interpreted the laboratory data. BW performed statistical analysis. BS, NW, BW, and BU wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr Paul H. Walter—Consultant Neurosurgeon for the thorough review and valuable suggestions. They are also grateful to the nursing staff of ICU of Heliodor Swiecicki Clinical Hospital of the Poznan University of Medical Sciences.
References
- 1.Ingall T, Asplund K, Mähönen M, Bonita R. A multinational comparison of subarachnoid hemorrhage epidemiology in the WHO MONICA stroke study. Stroke (2000) 31:1054–61. 10.1161/01.STR.31.5.1054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Connolly ES, Rabinstein A, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke (2012) 43:1711–37. 10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schubert GA, Seiz M, Hegewald AA, Manville J, Thomé C. Hypoperfusion in the acute phase of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl (2011) 110:35–8. 10.1007/978-3-7091-0353-1_6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schwartz C, Pfefferkorn T, Ebrahimi C, Ottomeyer C, Fesl G, Bender A, et al. Long-term neurological outcome and quality of life after World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies Grades IV and V Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in an Interdisciplinary Treatment Concept. Neurosurgery (2017) 39:2722–7. 10.1093/neuros/nyw138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Veldeman M, Höllig A, Clusmann H, Stevanovic A, Rossaint R, Coburn M, et al. Delayed cerebral ischaemia prevention and treatment after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic review. Br J Anaesth (2016) 117(1):17–40. 10.1093/bja/aew095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pickard JD, Murray GD, Illingworth R, Shaw MD, Teasdale GM, Foy PM, et al. Effect of oral nimodipine on cerebral infarction and outcome after subarachnoid haemorrhage: British aneurysm nimodipine trial. BMJ (1989) 298:636–42. 10.1136/bmj.298.6674.636 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fisher CM, Roberson GH, Ojemann RG. Cerebral vasospasm with ruptured saccular aneurysm – the clinical manifestations. Neurosurgery (1977) 1:245–8. 10.1227/00006123-197711000-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lin B, Dan W, Jiang L, Yin X, Wu H, Sun X. Association of APOE polymorphism with the change of brain function in the early stage of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl (2011) 110:39–42. 10.1007/978-3-7091-0353-1_7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cahill WJ, Calvert JW, Zhang JH. Mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab (2006) 26:1341–53. 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sabri M, Lass E, Macdonald RL. Early brain injury: a common mechanism in subarachnoid hemorrhage and global cerebral ischemia. Stroke Res Treat (2013) 2013:394036. 10.1155/2013/394036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kusaka G, Ishikawa M, Nanda A, Granger DN, Zhang JH. Signaling pathways for early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab (2004) 24:916–25. 10.1097/01.WCB.0000125886.48838.7E [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ma CX, Yin WN, Cai BW, Wu J, Wang JY, He M, et al. Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling detected in brain after early subarachnoid hemorrhage. Chin Med J (Engl) (2009) 122(13):1575–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sehba FA, Friedrich V. Early micro vascular changes after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl (2011) 110:49–55. 10.1007/978-3-7091-0353-1_9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM, Zhang JH. The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol (2012) 97:14–37. 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.02.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Friedrich V, Flores R, Sehba FA. Cell death starts early after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosci Lett (2012) 512(1):6–11. 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.01.036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sehba FA, Bederson JB. Mechanisms of acute brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res (2006) 28:381–98. 10.1179/016164106X114991 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sokół B, Wasik N, Jankowski R, Hołysz M, Więckowska B, Jagodziński P. Soluble toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute hydrocephalus following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0156171. 10.1371/journal.pone.0156171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sokół B, Woźniak A, Jankowski R, Jurga S, Wasik N, Shahid H, et al. HMGB1 level in cerebrospinal fluid as a marker of treatment outcome in patients with acute hydrocephalus following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis (2015) 24(8):1897–904. 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.05.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Feng H, Mao Y, Zhang JH, editors. Early Brain Injury or Cerebral Vasospasm, Acta Neurochirurgica, Wien: Springer; (Vol. 110/1) (2011). p. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Helbok R, Kurtz P, Vibbert M, Schmidt MJ, Fernandez L, Lantigua H, et al. Early neurological deterioration after subarachnoid haemorrhage: risk factors and impact on outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry (2013) 84:266–70. 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.von Holst H, Hagenfeldt L. Increased levels of amino acids in human lumbar and central cerebrospinal fluid after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (1985) 78:46–56. 10.1007/BF01808696 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jennett B, Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. A Practical Scale. Lancet (1975) 305:480–4. 10.1016/S0140-6736(75)92830-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vergouwen MDI, Vermeulen M, van Gijn J, Rinkel GJE, Wijdicks EF, Muizelaar JP, et al. Definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as an outcome event in clinical trials and observational studies: proposal of a multidisciplinary research group. Stroke (2010) 41:2391–5. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.589275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Matysiak J, Dereziński P, Klupczyńska A, Matysiak J, Kaczmarek E, Kokot ZJ. Effects of a honeybee sting on the serum free amino acid profile in humans. PLoS One (2014) 9:e103533. 10.1371/journal.pone.0103533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Klupczynska A, Dereziński P, Dyszkiewicz W, Pawlak K, Kasprzyk M, Kokot ZJ. Evaluation of serum amino acid profiles’ utility in non-small cell lung cancer detection in Polish population. Lung Cancer (2016) 100:71–6. 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Held PK, White L, Pasquali M. Quantitative urine amino acid analysis using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and aTRAQ® reagents. J Chromatogr B (2011) 879:2695–703. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.07.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Unterberg AW, Sakowitz OW, Sarrafzadeh AS, Benndorf G, Lanksch WR. Role of bedside microdialysis in the diagnosis of cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg (2001) 94:740–9. 10.3171/jns.2001.94.5.0740 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Helbok R, Schiefecker AJ, Beer R, Dietmann A, Antunes AP, Sohm F, et al. Early brain injury after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a multimodal neuromonitoring study. Crit Care (2015) 19:75. 10.1186/s13054-015-0809-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Matsumae M, Sato O, Hirayama A, Hayashi N, Takizawa K, Atsumi H, et al. Research into the physiology of cerebrospinal fluid reaches a new horizon: intimate exchange between cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid may contribute to maintenance of homeostasis in the central nervous system. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) (2016) 56:416–41. 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dolgodilina E, Imobersteg S, Laczko E, Welt T, Verrey F, Makrides V. Brain interstitial fluid glutamine homeostasis is controlled by blood–brain barrier SLC7A5/LAT1 amino acid transporter. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab (2016) 36:1929–41. 10.1177/0271678X15609331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Trautwein EA, Hayes KC. Taurine concentrations in plasma and whole blood in humans: estimation of error from intra- and interindividual variation and sampling technique. Am J Clin Nutr (1990) 52:758–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McPherson RA, Pincus MR, Henry JB. Cerebrospinal, synovial, serous body fluids. 22nd ed In: McPherson RA, Pincus M, editors. Henry’s Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders; (2011). p. 480–506. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Whitmore RG, Grant RA, Leroux P, El-Falaki O, Stein SC. How large is the typical subarachnoid hemorrhage? A review of current neurosurgical knowledge. World Neurosurg (2012) 77:686–97. 10.1016/j.wneu.2011.02.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kofler M, Schiefecker A, Ferger B, Beer R, Sohm F, Broessner G, et al. Cerebral Taurine levels are associated with brain edema and delayed cerebral infarction in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care (2015) 23:321–9. 10.1007/s12028-015-0140-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Staub F, Graf R, Gabel P, Köchling M, Klug N, Heiss W-D. Multiple interstitial substances measured by microdialysis in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery (2000) 47:1106–16. 10.1097/00006123-200011000-00016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jenkins CL, Bretscher LE, Guzei IA, Raines RT. Effect of 3-hydroxyproline residues on collagen stability. J Am Chem Soc (2003) 125:6422–7. 10.1021/ja034015j [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kruse T, Reiber H, Neuhoff V. Amino acid transport across the human blood-CSF barrier. J Neurol Sci (1985) 70:129–38. 10.1016/0022-510X(85)90082-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Molina JA, Jiménez-Jiménez FJ, Vargas C, Gómez P, de Bustos F, Ortí-Pareja M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of non-neurotransmitter amino acids in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) (1998) 105:279–86. 10.1007/s007020050057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Antonio Molina J, Javier Jiménez-Jiménez F, Gómez P, Vargas C, Antonio Navarro J, Ortí-Pareja M, et al. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid levels of neutral and basic amino acids in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci (1997) 150:123–7. 10.1016/S0022-510X(97)00069-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Siddiqi NJ, Alhomida AS. Distribution of total, free, peptide-bound and protein- bound hydroxyproline in the erythrocytes from different species. Comp Clin Path (2002) 11:123–8. 10.1007/s005800200010 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Roberts LD, Boström P, O’Sullivan JF, Schinzel RT, Lewis GD, Dejam A, et al. β-Aminoisobutyric acid induces browning of white fat and hepatic β-oxidation and is inversely correlated with cardiometabolic risk factors. Cell Metab (2014) 19:96–108. 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Choi YH, Fletcher PJ, Wong CCS, Anderson GH. Measurement of blood-brain barrier permeability of rats with alpha-aminoisobutyric acid during microdialysis: possible application to behavioral studies. Physiol Behav (1999) 67:587–98. 10.1016/S0031-9384(99)00110-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Benarroch EE. Basic Neurosciences with Clinical Applications. Butterworth: Heinemann/Elsevier; (2006). [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hijdra A, van Gijn J, Nagelkerke NJ, Vermeulen M, van Crevel H. Prediction of delayed cerebral ischemia, rebleeding, and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke (1988) 19(10):1250–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zetterling M, Hillered L, Samuelsson C, Karlsson T, Enblad P, Ronne-Engström E. Temporal patterns of interstitial pyruvate and amino acids after subarachnoid haemorrhage are related to the level of consciousness—a clinical microdialysis study. Acta Neurochir (2009) 151:771–80; discussion 780. 10.1007/s00701-009-0384-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nakahara T, Tsuruta R, Kaneko T, Yamashita S, Fujita M, Kasaoka S, et al. High-mobility group box 1 protein in CSF of patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care (2009) 11:362–8. 10.1007/s12028-009-9276-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pedrazzi M, Raiteri L, Bonanno G, Patrone M, Ledda S, Passalacqua M, et al. Stimulation of excitatory amino acid release from adult mouse brain glia subcellular particles by high mobility group box 1 protein. J Neurochem (2006) 99:827–38. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04120.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kim J-B, Sig Choi J, Yu Y-M, Nam K, Piao C-S, Kim S-W, et al. HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. J Neurosci (2006) 26:6413–21. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3815-05.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sehba FA, Pluta RMR, Zhang JJH. Metamorphosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage research: from delayed vasospasm to early brain injury. Mol Neurobiol (2011) 43:27–40. 10.1007/s12035-010-8155-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sarrafzadeh AS, Sakowitz OW, Kiening KL, Benndorf G, Lanksch WR, Unterberg AW. Bedside microdialysis: a tool to monitor cerebral metabolism in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients? Crit Care Med (2002) 30:1062–70. 10.1097/00003246-200205000-00018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Guidetti P, Schwarcz R. Determination of α-aminoadipic acid in brain, peripheral tissues, and body fluids using GC/MS with negative chemical ionization. Mol Brain Res (2003) 118:132–9. 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Huck S, Grass F, Hatten ME. Gliotoxic effects of alpha-aminoadipic acid on monolayer cultures of dissociated postnatal mouse cerebellum. Neuroscience (1984) 12:783–91. 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90170-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kato S, Ishita S, Sugawara K, Mawatari K. Cystine/glutamate antiporter expression in retinal Müller glial cells: implications for DL-alpha-aminoadipate toxicity. Neuroscience (1993) 57:473–82. 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90080-Y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]