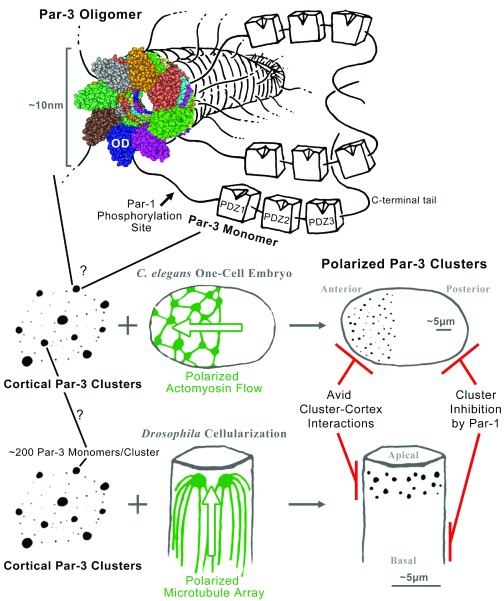
Figure 1. The organization and polarization of Par-3 clusters.
The oligomerization domain of a Par-3 monomer mediates the formation of a helical fiber from which the linker regions and PDZ domains of Par-3 would emanate like branches of a tree. The space-filling structural model is a Cn3D view of the model of Zhang et al. (PDB: 3ZEE) 14. Somehow these fibers are organized into local Par-3 clusters scattered across the cell cortex. In the Caenorhabditis elegans one-cell embryo, a polarized actomyosin flow sweeps the Par-3 puncta to one pole, forming the anterior end of the embryo. In the cellularizing Drosophila embryo, a polarized microtubule array positions the Par-3 puncta to one end of each cell, forming the apicolateral domain. Once the polarity of Par-3 clusters is established, it can be maintained by avid interactions between the clusters and the cell cortex combined with inhibition of Par-3 complex formation at the opposite pole by Par-1 phosphorylation. See main text for further details.