Abstract
Background
Influenza infects 5–15% of the global population each year, and obesity has been shown to be an independent risk factor for increased influenza-related complications including hospitalization and death. However, the risk of developing influenza or ILI in a vaccinated obese adult population has not been addressed.
Objective
This study evaluated whether obesity was associated with increased risk of influenza and influenza-like illness among vaccinated adults.
Subjects and Methods
During the 2013–2014 and 2014–2015 influenza seasons, we recruited 1042 subjects to a prospective observational study of trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3) in adults.1022 subjects completed the study. Assessments of relative risk for laboratory confirmed influenza and influenza-like illness were determined based on BMI. Seroconversion and seroprotection rates were determined using pre-vaccination and 26–35 days post-vaccination serum samples. Recruitment criteria for this study were adults 18 years of age and older receiving the seasonal trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3) for the years 2013–2014 and 2014–2015. Exclusion criteria were immunosuppressive diseases, use of immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive drugs, acute febrile illness, history of Guillain-Barre syndrome, use of theophylline preparations, or use of warfarin.
Results
Among obese, 9.8% had either confirmed influenza or influenza-like-illness compared with 5.1% of healthy weight participants. Compared with vaccinated healthy weight, obese participants had double the risk of developing influenza or influenza-like illness (relative risk= 2.01, 95% CI 1.12, 3.60, p=0.020). Seroconversion or seroprotection rates were not different between healthy weight and obese adults with influenza or ILI.
Conclusions
Despite robust serological responses, vaccinated obese adults are twice as likely to develop influenza and influenza-like illness compared to healthy weight adults. This finding challenges the current standard for correlates of protection, suggesting use of antibody titers to determine vaccine effectiveness in an obese population may provide misleading information.
INTRODUCTION
Influenza is a serious worldwide public health problem. Seasonally, 5–10% of adults and 20–30% of children contract influenza virus, resulting in up to 500,000 deaths1 and influenza pandemics greatly increase the number of infections and deaths. Indeed, the 1918 influenza pandemic was estimated to have infected 20–40% of the world’s population, causing approximately 50 million deaths2. Historically, the highest risk groups for increased morbidity and mortality from influenza infection include the elderly3, the very young4, individuals with chronic diseases such as diabetes5 or congestive heart failure6, and pregnant women7. During the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, obesity was recognized as an independent risk factor for complications from influenza8 and continues to be a risk factor for seasonal influenza strains9 as well as for emerging influenza virus strains such as A(H7N9)(ref. 10). Obesity is not only a concern in the US, with 37% of adults obese11, but also affects 14% of the worldwide adult population12. Therefore, with a growing obesity epidemic, complications from influenza infection would be expected to increase.
Influenza vaccine remains the primary method currently available for prevention of influenza infection. Each year, vaccines are formulated based on evaluations of previously circulating influenza strains. Typically, the vaccine contains two influenza A strains and one, or more recently two, influenza B strains. Vaccine-generated antibodies against the viral surface protein hemagglutinin (HA) are considered to be protective, therefore vaccines are standardized to the quantity of HA, generally 15 μg of HA per strain13. A serum hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titer of 40 or greater has historically been considered an immunological correlate of protection from influenza infection, corresponding to 50% protection14. Protection against influenza infection increases up to an HAI titer of 160, beyond which further protective capacity is minimal15. High risk groups for influenza infection, including the elderly and children under 6 years of age, may need to reach titers greater than 40 to achieve protection16. To determine if obesity altered the risk of developing influenza or ILI in a vaccinated adult population, we report the incidence of influenza infection and influenza-like illness (ILI) in vaccinated obese and healthy weight adults as well as the extent to which participants with influenza infection and ILI produced influenza specific antibodies.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Study Design
Participants were recruited as a part of a prospective observational study carried out at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Family Medicine Center, an academic outpatient primary care facility in Chapel Hill, North Carolina. All procedures were approved by the Biomedical Institutional Review Board at the University of North Carolina. At enrollment, informed written consent was received.
Participants
Recruitment criteria for this study were adults 18 years of age and older receiving the seasonal trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3) for the years 2013–2014 and 2014–2015. Exclusion criteria were immunosuppressive diseases including HIV, use of immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive drugs, acute febrile illness, history of hypersensitivity to any influenza vaccine components, history of Guillain-Barre syndrome, use of theophylline preparations, or use of warfarin. Height and weight were measured and a baseline serum sample drawn. BMI for each participant was calculated as weight (kg)/height(m)2. Healthy weight was defined as a BMI of 18.5–24.9, overweight as a BMI of 25–29.9 and obese as a BMI of ≥30.
Vaccines and Sample Collection
One dose of 2013–2014 trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (0.5 mL Fluzone; Sanofi Pasteur, Swiftwater PA, USA) containing A/California/07/2009 H1N1, A/Texas/50/2012 H3N2, and B/Massachusetts/02/2012 or 2014–2015 trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (0.5 mL Fluvirin; Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics Limited, Basel, Switzerland) containing A/California/07/2009 H1N1, A/Texas/50/2012 H3N2, and B/Massachusetts/02/2012 was administered in the deltoid muscle, using an inch and half needle, at baseline. Participants returned 26–35 days later for a post-vaccination blood draw. In the 2013–2014 vaccine year, vaccination of participants started on September 16, 2013 and the last vaccination was given on November 4, 2013. Influenza was first detected in NC on November 30, 2013, and cases peaked on January 11, 2014, with influenza levels back to baseline on May 17, 2014. In the 2014–2015 vaccine year, vaccination of participants started on September 15, 2014 and were completed on October 28, 2014. Influenza was first detected in NC on November 29, 2014 and cases peaked on December 27, 2014. Influenza levels were back to baseline on April 25, 2015. Serum samples were stored at −80° C until analyzed. During the 2013–2014 season in North Carolina, influenza 2009 A/H1/N1 was the predominant circulating strain, and during the 2014–2015 season, influenza A/H3N2/Switzerland was the predominant circulating strain.
Surveillance and diagnosis of influenza and/or influenza-like illness (ILI)
Participants were contacted weekly beginning with the first report of influenza activity in the community and contact was discontinued when influenza was no longer active. Participants were contacted by phone or email and asked to report any symptoms of fever, cough, runny nose, sore throat, muscle aches, headaches and fatigue to assess for influenza symptoms. Medical records of all study participants, whether they reported ILI or not, were reviewed at the end of each season for medically reported influenza-like illness or laboratory confirmed influenza. Participants were also instructed to contact the study nurse if they developed ILI. Laboratory confirmed influenza infection was determined from the medical records which reported a positive influenza specimen using the FDA cleared Cepheid Xpert Flu assay (Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA). This assay distinguishes between influenza A and influenza B strains, but does not subtype the strains. All participants who tested positive for influenza were diagnosed with influenza A. ILI was defined using the CDC guidelines17 as fever greater than 100° F with a cough and in the absence of any other medical diagnosis. All subjects with laboratory confirmed influenza also met our criteria for ILI.
Immunogenicity
Hemaglutination Inhibition (HAI) Assay
The HAI titer was blindly determined in accordance with World Health Organization guidelines18 for all patients reporting laboratory confirmed influenza or ILI, as well as matched non-illness reporting participants.
Microneutralization (MN) Assay
Standard microneutralizations (MN) were blindly performed against cell-grown A/Texas/50/2012 (H3N2) according to WHO guidelines18. Luminescent MN assays were blindly performed as previously described using a reverse genetics A/California/04/2009 (pdmH1N1) virus containing an NLuc on its polymerase segment19. MN were conducted for participants with laboratory confirmed influenza and matched controls who did not report any ILI during influenza season.
Matched non-illness reporting participants
For every participant who either had laboratory confirmed influenza or reported ILI, we matched them with a non-illness reporting participant. Matching of the non-illness reporting participants was done on a one-to-one basis with the 74 participants with either confirmed influenza or reporting ILI based on the following criteria in the order provided: 1) same vaccine year; 2) sex; 3) Race; 4) weight category; 5) diabetes status; 6) statin use; 7) smoking status; 8) age (within 10 years). All samples were uniquely matched.
Statistics
Individuals were categorized as underweight (BMI < 18.5), healthy weight (BMI 18.5 – 24.9), overweight (BMI 25.0 – 29.9), or obese (BMI ≥ 30). The Jonckheere–Terpstra test was employed to assess associations between baseline covariates and the ordinal weight category. Risk ratios for laboratory confirmed influenza and influenza-like Illness (ILI) were estimated by fitting a log-binomial model using generalized estimating equations (GEE) with an exchangeable working correlation structure to account for repeated observations per individual. Logistic regression models fit using GEE were utilized to examine associations of diabetes and statin use with obesity and risk of influenza/ILI. Microneutralization and HAI results were analyzed via 2-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for comparisons between matched pairs. Seroconversion and seroprotection were analyzed by the chi-square test of independence. P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Data presented in tables were analyzed using R20. Data presented in Figure 1 were analyzed using Graphpad Prism 6.0h for Mac OSX.
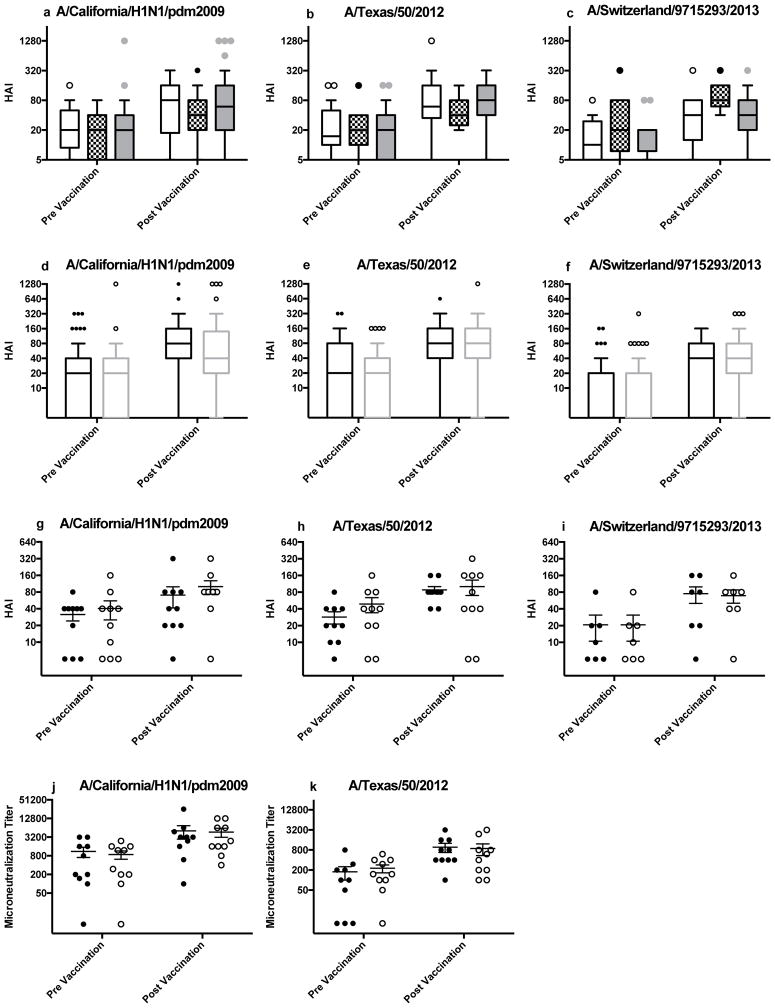
Figure 1.
Influenza HAI and MN antibody titers for influenza confirmed and ILI participants and uninfected controls. Pre and post influenza vaccination HAI titers of participants with influenza confirmed and ILI against (a) A/California/pdm2009, (b) A/Texas/50/2012 and (c) A/Switzerland/9715293/2013. Pre and post vaccination titers were not statistically different among healthy weight (white with open circles), overweight (checkered with black circles) or obese (grey with grey circles) participants. Pre and post influenza vaccination HAI titers in participants with ILI (open circles and grey boxes) and demographically matched uninfected controls (black circles and black boxes) for (d) A/California/pdm2009, (e) A/Texas/50/2012 and (f) A/Switzerland/9715293/2013. Pre and post vaccination titers were not statistically different between ILI participants and non-illness reporting matched controls. Pre and post influenza vaccination HAI (g, h, i) and MN (j,k) titers in participants with confirmed influenza (open circles) and matched uninfected controls (black circles). Pre and post HAI or MN vaccination titers were not statistically different between confirmed influenza participants and matched controls. a,b: n=14 for healthy weight, n=16 for overweight, n=44 obese; c: n=9 healthy weight, n=9 for overweight, n=25 for obese. d, e: n=74; f: n=43, g, h, j, k: n=10; I: n=7.
RESULTS
Demographics of Participants
During the 2013–2014 vaccine year, we enrolled 587 participants and 575 (98.0%) completed the study. During the 2014–2015 vaccine year, we enrolled 455 participants and 447 (98.2%) completed the study. As shown in Table 1, overall, our participants were 27% healthy weight, 28% overweight and 44% obese. In both years of the study, approximately 60% of the participants were Caucasian and 30% African-American. Female participants represented approximately 63% of the total participants. As has been reported for other studies, African-Americans21, and diabetics22 were more likely to be obese, and statin use was associated with higher BMIs. However, statin use and diabetes was not independently associated with influenza or influenza-like illness. Most of the participants were either non-smokers, or had never smoked, with approximately 17% current smokers. There were 184 study subjects who participated in both years of the study, fifteen of which reported ILI in one or both years of the study.
Table 1.
Demographics of all participants by study year and of participants with influenza or influenza like illness
| Underweight: BMI<18.5 | Healthy Weight: BMI18.5–24.9 | Overweight: BMI 25.0–29.9 | Obese: BMI≥30 | Total | P-Valueb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013–2014 | Overall | N | 6 (1) | 143 (25) | 170 (29) | 256 (45) | 575 | 0.57 |
|
| ||||||||
| Agea | 53 ± 20 | 55 ± 18 | 54 ± 16 | 54 ± 12 | 54 ± 15 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Sex | Female | 3 (1) | 92 (25) | 98(26) | 178 (48) | 371 | 0.09 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Male | 3 (2) | 51 (25) | 72 (35) | 78 (38) | 204 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Race | Caucasian | 6 (2) | 104(29) | 114 (31) | 140 (38) | 364 | 0.001 | |
|
| ||||||||
| African American | 0 (0) | 23 (13) | 45 (26) | 107 (61) | 175 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Other | 0 (0) | 16 (45) | 11 (33) | 9 (22) | 36 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Diabetes | Pre Diabetes | 1 (2) | 9 (15) | 10 (21) | 27 (62) | 47 | 0.00002 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Type 1 | 0 (0) | 3 (60) | 1 (20) | 1 (20) | 5 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Type 2 | 0 (0) | 12 (9) | 29 (23) | 86 (68) | 127 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Non-Diabetic | 5 (1) | 119 (31) | 130 (33) | 142 (35) | 396 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Smoking | Current Smoker | 1 (1) | 29 (28) | 33 (32) | 38 (39) | 101 | 0.4 | |
| Previous Smoker | 1 (1) | 36 (24) | 50 (31) | 74 (44) | 161 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Non Smoker | 4 (1) | 78 (25) | 87 (27) | 144 (47) | 313 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Statin Use | Current Statin Use | 0 (0) | 41 (18) | 63 (28) | 119 (53) | 223 | 0.0001 | |
|
| ||||||||
| No Statin | 6 (2) | 102 (29) | 107 (30) | 137 (31) | 352 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| 2014–2015 | Overall | N | 6 (1) | 134 (30) | 113 (26) | 194 (43) | 447 | 0.64 |
|
| ||||||||
| Agea | 54 ± 21 | 54 ± 18 | 60 ± 17 | 55 ± 14 | 56 ± 16 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Sex | Female | 4 (1) | 89 (31) | 58 (20) | 139 (48) | 290 | 0.15 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Male | 2 (1) | 45 (29) | 55 (35) | 55 (35) | 157 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Race | Caucasian | 3 (1) | 98 (34) | 74 (26) | 112 (39) | 287 | 0.06 | |
|
| ||||||||
| African American | 0 (0) | 20 (16) | 34 (27) | 73 (57) | 127 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Other | 3 (1) | 16 (4) | 5(1) | 9 (2) | 33 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Diabetes | Pre Diabetes | 1 (3) | 2 (7) | 6 (21) | 19 (69) | 28 | 0.00002 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Type 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (33) | 2 (67) | 3 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Type 2 | 0 (0) | 9 (11) | 19 (22) | 57 (67) | 85 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Non Diabetic | 5 (2) | 123 (37) | 87 (26) | 116 (35) | 331 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Smoking | Current Smoker | 2 (3) | 24 (33) | 15 (21) | 31 (43) | 72 | 0.4 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Previous Smoker | 1 (1) | 31 (23) | 40 (29) | 64 (47) | 136 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Non Smoker | 3 (1) | 79 (33) | 58 (24) | 99 (41) | 239 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Statin Use | Current Statin Use | 0 (0) | 34 (19) | 50 (28) | 94 (53) | 178 | 0.00006 | |
|
| ||||||||
| No Statin | 6 (2) | 100 (37) | 63 (23) | 100 (37) | 269 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| 2013–2015 Confirmed Influenza or ILI | Overall | N | 0 (0) | 14 (19) | 16 (22) | 44 (59) | 74 | 0.41 |
|
| ||||||||
| Agea | 52 ± 17 | 59 ± 15 | 57 ± 12 | 56 ± 14 | ||||
|
| ||||||||
| Sex | Female | 0 (0) | 10 (14) | 10 (16) | 36 (70) | 56 | 0.2 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Male | 0 (0) | 4 (33) | 6 (39) | 8 (28) | 18 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Race | Caucasian | 0 (0) | 12 (23) | 11 (25) | 25 (52) | 48 | 0.05 | |
|
| ||||||||
| African American | 0 (0) | 2 (12) | 5 (12) | 18 (76) | 25 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Other (Asian) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (1) | 1 (0) | 1 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Diabetes | Pre Diabetes | 0 (0) | 2 (0) | 0 (11) | 7 (89) | 9 | 0.04 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Type 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Type 2 | 0 (0) | 1 (0) | 3 (24) | 13 (76) | 17 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Non Diabetic | 0 (0) | 11 (29) | 13 (23) | 24 (48) | 48 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Smoking | Current Smoker | 0 (0) | 3 (23) | 4 (31) | 6 (46) | 13 | 0.8 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Previous Smoker | 0 (0) | 2 (7) | 7 (24) | 20 (69) | 29 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Non Smoker | 0 (0) | 9 (28) | 5 (12) | 18 (60) | 32 | |||
|
| ||||||||
| Statin Use | Current Statin Use | 0 (0) | 5 (17) | 6 (20) | 19 (63) | 30 | 0.64 | |
|
| ||||||||
| No Statin Use | 0 (0) | 9 (21) | 10 (23) | 25 (57) | 44 | |||
Age is reported in years +/− SD
The p-values are shown for an overall test of association between the covariate and the weight category using the Jonckheere-Terpstra test. As previously reported and also found here, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and statin use is associated with weight, and overweight/obesity is present at a higher rate in African-Americans21 and females are frequently more at risk for influenza infection than males37.
All other values reported as number of participants within each weight class with the indicated demographic.
Relative Risk for Influenza and ILI
In the total vaccinated adult participants for both vaccine years, there were 10 laboratory confirmed cases of influenza A and 64 cases of ILI (Table 2). Of the 74 participants with either confirmed influenza or ILI, 19% were healthy weight, 22% were overweight and 59% were obese. Relative to influenza incidence in vaccinated healthy weight adults, vaccinated obese adults had double the risk for laboratory confirmed influenza considered together with ILI (estimated risk ratio 2.06 with 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.14, 3.71). The risk ratio estimate was similar when adjusting for vaccine year, age, sex, and smoking status using log-binomial regression (2.01, 95% CI 1.12, 3.60). Diabetes and statin use were not associated with influenza or influenza-like illness, however, as expected, BMI category was a significant predictor of diabetes and statin use.
Table 2.
Obesity is associated with greater risk for influenza and influenza like illness
| Underweight (BMI<18.5) | Healthy Weight (BMI 18.5–25) | Overweight (BMI 25–30) | Obese (BMI>30) | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013–2014 | Laboratory confirmed influenza | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Influenza-like Illness | 0 | 5 | 6 | 17 | 28 | |
| No flu-like Illness | 6 | 138 | 163 | 237 | 544 | |
| 2014–2015 | Laboratory confirmed influenza | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| Influenza-like Illness | 0 | 8 | 6 | 22 | 36 | |
| No flu-like Illness | 6 | 125 | 104 | 169 | 404 | |
| Total | 12 | 277 | 283 | 450 | 1022 | |
| Risk Ratio vs Healthy Weighta | - | - | 1.27 | 2.01 | ||
| 95% CIb | - | - | (0.64,2.52) | (1.12,3.60) | ||
| Significance | - | - | NSc | p=0.020 | ||
Risk ratio estimates are for laboratory confirmed influenza and influenza-like Illness (ILI) combined. Estimates were obtained using a log-binomial model fit using generalized estimating equations (GEE) with an exchangeable working correlation structure to account for repeated observations per individual. The model was adjusted for vaccine year, age, sex and smoking. Underweight and healthy weight individuals were combined into a single referent category due to the small number of underweight individuals.
CI: confidence interval.
NS: not significant, p>0.05.
Seroprotection and Seroconversion
Among the 74 cases of confirmed influenza or ILI during 2013–2014 and 2014–2015, 30 (41%) seroconverted (four-fold increase from pre- to post-vaccination HAI titer) to vaccine strain A/H1N1/California/pdm2009 and 34 (46%) seroconverted to vaccine strain A/H3N2/Texas/50/2012. For these same 74 participants, 70% reached a seroprotective titer (26–35 day post vaccination HAI titer ≥ 40) for A/H1N1/California/pdm2009 and 80% reached a seroprotective titer for A/H3N2/Texas/50/2012. However, no differences were observed in seroprotective or seroconversion rates based on BMI (Table 3 and Figures 1a–b).
Table 3.
Obesity was not associated with seroconversion and seroprotection levels in participants with confirmed influenza and ILI
| Healthy Weight (BMI 18.5–24.9) | Overweight (BMI 25–29.9) | Obese (BMI ≥ 30) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/H1N1 California/pdm2009 | a Seroconversion | 4-Fold Increase or greater | 43% | 38% | 41% | 41% |
| b Seroprotection | HAI ≥ 40 | 71% | 79% | 68% | 70% | |
| HAI ≥ 80 | 64% | 31% | 50% | 49% | ||
| HAI ≥ 160 | 36% | 13% | 25% | 24% | ||
| HAI ≥ 320 | 14% | 6% | 11% | 11% | ||
| Nc | 14 | 16 | 44 | 74 | ||
| A H3N2 Texas 50/2012 | Seroconversion | 4-Fold Increase or greater | 50% | 44% | 46% | 46% |
| Seroprotection | HAI ≥ 40 | 86% | 69% | 82% | 80% | |
| HAI ≥ 80 | 57% | 44% | 55% | 53% | ||
| HAI ≥ 160 | 43% | 25% | 32% | 32% | ||
| HAI ≥ 320 | 14% | 6% | 11% | 11% | ||
| Nc | 14 | 16 | 44 | 74 | ||
| A/H3N2 Switzerland 9715293/2013 | Seroconversion | 4-Fold Increase or greater | 67% | 56% | 32% | 44% |
| Seroprotection | HAI ≥ 40 | 67% | 100% | 60% | 70% | |
| HAI ≥ 80 | 33% | 78% | 28% | 40% | ||
| HAI ≥ 160 | 11% | 33% | 8% | 14% | ||
| HAI ≥ 320 | 11% | 11% | 4% | 7% | ||
| c N | 9 | 9 | 25 | 43 |
Seroconversion is defined as a ≥4-fold increase in HAI titer 25–35 days post vaccination from pre-vaccination titer.
Seroprotection is typically defined as an HAI of ≥40, however multiple cut-off points were assessed as indicated. There were no significant associations between weight and the odds of seroconversion for the multiple cut-off points considered.
N is number of subjects by column and varies by virus as A/H3N2/Switzerland/9715293 was not assessed in participants from the 2013–2014 influenza vaccine season.
During the 2014–2015 influenza season, the H3N2 vaccine strain was a poor match for the circulating strain23. Therefore, for the 43 cases of laboratory confirmed influenza or ILI during 2014–2015, we measured HAI titers pre and post vaccination against the circulating influenza A/H3N2/Switzerland/9715293/2013 strain. Seroconversion for this strain occurred in 19 (44%) participants, and seroprotection was present in 30 (70%) participants. Again, no differences were observed based on BMI (Table 3 and Figures 1c). Higher, alternative cutoffs for seroprotection levels of HAIs at 80, 160 and 320 were also determined, and no differences were observed based on BMI (Table 3).
Laboratory confirmed Influenza and ILI compared to non-illness reporting matched controls
All 74 participants with either laboratory confirmed or ILI were matched with non-illness reporting participants and their demographics are shown in Supplemental Table 1. There were no differences in pre or post HAI titers for the vaccine strains A/California/H1N1/pdm2009 (Figure 1d) and A/Texas/H3N2/50/2012 (Figure 1e) or for the circulating 2015 influenza strain A/H3N2/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (Figure 1f) between participants reporting ILI and their non-reporting matched controls. Similarly, there was no difference in HAI (Figures 1g–h) or MN influenza titers (Figures 1 j-k) between participants with laboratory confirmed influenza and their matched, uninfected controls.
DISCUSSION
The first influenza pandemic of the 21st century resulted in identifying obesity as an independent risk factor for increased severity from infection with Influenza A/pH1H1/20098. Since that time, obesity has also been identified as a risk factor for seasonal and emerging influenza strains. This is highly significant, in that obesity levels in the US population are at epidemic proportions, with 37% of adults overall obese11 and even higher rates in non-Hispanic blacks (48%)21. Obesity rates worldwide have doubled since 1980 and currently 13% of the world’s adult population is obese12, leaving a large number of obese adults in the US and worldwide at significant risk for infection with influenza virus.
Influenza vaccination represents the best method of protection from infection with influenza virus. Several studies have suggested that overweight and obesity impairs vaccine response to several pathogens. For example, non-responders to hepatitis B vaccination are overrepresented in obese adults24, while tetanus toxoid response in overweight children is similarly impaired25. A recent review on the association of obesity with vaccine responses points to a number of studies that demonstrate diminished vaccine-induced immune responses in both obese adults and children26. We have also documented impaired vaccine-specific T cell responses in influenza vaccinated obese adults27, and a waning serological response one year post vaccination28. Despite the growing number of studies implicating obesity in poor responses to vaccination, and specifically influenza vaccination, a key question remains unanswered: in obesity and healthy weight, does vaccination offer the same protection from influenza and ILI?
Here, for the first time, we demonstrate that obese adult recipients of IIV3 have two times greater incidence of influenza and/or ILI despite being vaccinated. One obvious hypothesis for the increase in influenza and ILI in obese adult participants is a failure to seroconvert or reach seroprotective levels of antibody. Serological responses to influenza vaccination are typically assessed as seroprotection, defined as an HAI titer of 40 or greater post vaccination, or seroconversion, defined as a 4 fold or greater increase in HAI from prevaccination titer to post vaccination titer. However, we found that the increased susceptibility to influenza and ILI in the obese adults was not associated with a failure to reach a seroprotective titer or to seroconvert. Indeed, we found no statistical differences in serological responses to vaccine between healthy weight and obese vaccinated adults. For the H1N1 strain, 36% of healthy weight adults seroconverted compared with 43% of obese adults. Similarly, seroconversion rates to the H3N2 vaccine strain were 43% of healthy weight adults and 50% of obese adults. When using the commonly defined seroprotective HAI titer of ≥40, more than 70% of the healthy weight and obese participants reached this HAI level.
The presence of a “seroprotective” level of antibody against influenza A strains demonstrates that, despite the vaccine inducing this this correlate of protection, the obese adults were still 2X more likely to develop influenza and ILI. This lack of protection, even with a seroprotective antibody titer, has also been observed in elderly adults29 and children16, where a higher HAI definition as a correlate of protection has been proposed. Our data, however, do not suggest an elevated definition is protective for obese adults. Raising the seroprotective cutoff level to 80, 160 and 320 still failed to differentiate healthy weight adults from obese adults.
The 2014–2015 influenza vaccine effectiveness overall was reduced (13% vs 61% in 2013–2014) due to the circulating Influenza A H3N2 strain having drifted from the H3N2 vaccine strain23. Therefore, for all participants who had influenza or ILI during the 2014–2015 vaccine season, we measured HAI antibody titer against the circulating A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 strain. Despite the mismatch with the vaccine strain, IIV3 induced seroconversion among 67% of the healthy weight and 32% of the obese participants. For a seroprotective level of ≥40 HAI, 67% of healthy weight and 60% of obese participants achieved this level. There were no statistical differences in seroprotection or seroconversion rates between healthy weight and obese adults.
We found no differences in HAI titers between non-illness reporting participants and participants reporting ILI. In addition to HAI, virus microneutralization (MN) titers are a highly sensitive and specific method for detecting antibodies that inhibit viral entry or exit out of the cell. Cheng et al.30 reported that, compared to HAI titers, MN titers demonstrated a greater seroconversion rate and fold increase and suggested that neutralizing antibody titers may be a better correlate of protection for understanding influenza vaccine effectiveness. However, as was found for HAI titers, there were no differences in MN titers between uninfected controls and infected participants.
Our study has several limitations. Although we used the CDC’s stringent definition for ILI and ILI is widely used for influenza surveillance reporting, we did not do specific testing for influenza in subjects with ILI. Therefore we could be over-reporting, as some of the ILI subjects may be positive for a respiratory virus other than influenza, or under-reporting, as the more stringent CDC criteria may miss some milder ILI symptoms that are influenza positive. By only collecting ILI data during times of influenza circulating in the community, this helps to reduce over-reporting, but it doesn’t eliminate this possibility. In addition, our study does not address the possibility that obese adults may be more exposed to influenza compared with healthy weight adults. Under this possibility, the influenza vaccine may equally protect healthy weight and obese adults, however an increased rate of infection exposure in obese adults could lead to an increased rate of infection in vaccinated obese adults compared with healthy weight adults. However, Murphy et al.31 used data from the 2010 Health Survey for England, which asked in a survey question administered during the year following the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic whether participants had experienced “flu-like illness where [respondents] felt feverish and had a cough or sore throat,” and considered cases between May and December 2009 to be flu-like illness in that study. The investigators found no relationship between ILI (including laboratory confirmed influenza) and obesity. This finding may suggest that influenza infection rates in healthy weight and obese adults are similar, and therefore our findings are related to a failure of the vaccine to protect obese adults to the same extent as healthy weight adults. Indeed, in an animal model, Karlsson et al.32 reported that although lean mice were protected from influenza infection following vaccination, diet-induced obese mice were still susceptible to influenza infection despite vaccination. This contrasts with school aged children, where live attenuated influenza vaccination was shown to reduce risk for laboratory confirmed influenza similarly for healthy weight and obese33. These contrasting findings may be driven by differences in vaccine preparation (live versus inactivated), or by differences between obese adults and children.
The findings reported here demonstrate that, compared to vaccinated healthy weight adults, vaccinated obese adults were 2X more likely to develop influenza infection and ILI. Notably, HAI antibody titers, widely viewed as correlates of protection against influenza, were unreliable as predictive of disease protection in obese adults. Previously, we28 and others34–36 have reported that HAI antibody titers 30 days post vaccination in obese adults or children are either slightly higher or no different from vaccinated healthy weight individuals. The present study confirmed these earlier reports on vaccine-induced antibody titers. However, here we found that an HAI antibody titer of 40 or higher was not a serological correlate for vaccine-induced protection and did not prevent laboratory confirmed influenza and ILI in obese adults. Additionally, MN titers in obese adults were also inadequate predictors of protection and these studies directly correlate with studies conducted in obese mice32. Although our study does not compare vaccinated obese adults with unvaccinated obese adults, it is clear that vaccinated obese adults are at a higher risk for influenza and ILI compared to vaccinated healthy weight adults.
The mechanism for increased risk of influenza and ILI in the obese population may be due to poor T cell function. As we have reported previously, compared with T cells from vaccinated healthy weight adults, T cells from influenza vaccinated obese adults are less activated when stimulated with vaccine strains of influenza26,27. As T cells are necessary for protection and recovery from influenza, impaired T cell function, despite a robust serological response, may render vaccinated obese adults more susceptible to influenza infection. Indeed, vaccinated elderly adults are also less protected from influenza infection despite having an adequate serological response, which has been attributed to poor T cell responses29.
Taken together, these results suggest that the effectiveness of influenza vaccines, and perhaps other vaccines as well, should be fully assessed in obese adults. For example, use of adjuvanted influenza vaccines such as MF59 (FLUAD, Seqirus) or high-dose vaccine preparations that are designed for vaccinating adults over 65 may be warranted for use in an obese population. However, animal studies suggest that even adjuvanted vaccines or increased dosage may not overcome the increased susceptibility of the obese host32. Therefore, alternative approaches may be needed to protect obese adults from both seasonal and pandemic influenza virus infection.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank our study coordinator, Kim Bartholomew, RN, MPH and all the study participants for their contribution. We thank Savanna Ledford and Qing Shi for technical assistance. This work was funded by NIH grants R01AI078090 and P30DK056350 to MAB and ALSAC to SSC.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.WHO/Influenza (Seasonal) WHO; 2016. [Accessed November 10, 2016]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/ [Google Scholar]
- 2.Patterson KD, Pyle GF. The geography and mortality of the 1918 influenza pandemic. Bull Hist Med. 1991;65:4–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E, et al. Mortality associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in the United States. JAMA. 2003;289:179–186. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Izurieta HS, Thompson WW, Kramarz P, et al. Influenza and the rates of hospitalization for respiratory disease among infants and young children. New Engl J Med. 2000;342:232–239. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200001273420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Valdez R, Narayan KM, Geiss LS, Engelgau MM. Impact of diabetes mellitus on mortality associated with pneumonia and influenza among non-Hispanic black and white US adults. AJPH. 1999;89:1715–1721. doi: 10.2105/ajph.89.11.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sandoval C, Walter SD, Krueger P, et al. Risk of hospitalization during influenza season among a cohort of patients with congestive heart failure. Epidemiol Infect. 2007;135:574–582. doi: 10.1017/S095026880600714X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Neuzil KM, Reed GW, Mitchel EF, Simonsen L, Griffin MR. Impact of influenza on acute cardiopulmonary hospitalizations in pregnant women. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;148:1094–1102. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Louie JK, Acosta M, Winter K, et al. Factors associated with death or hospitalization due to pandemic 2009 influenza A(H1N1) infection in California. JAMA. 2009;302:1896–1902. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mertz D, Kim TH, Johnstone J, et al. Populations at risk for severe or uncomplicated influenza illness: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f5061. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu B, Havers F, Chen E, et al. Risk factors for influenza A(H7N9) disease-China, 2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:787–794. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [Acessed November 10, 2016];Adult Obesity Facts. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html.
- 12.World Health Organization. [Accessed November 10, 2016];Adult obesity facts. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
- 13.Sridhar S, Brokstad KA, Cox RJ. Influenza vaccination strategies: comparing inactivated and live attenuated influenza vaccines. Vaccines (Basel) 2015;3:373–389. doi: 10.3390/vaccines3020373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Trombetta CM, Montomoli E. Influenza immunology evaluation and correlates of protection: a focus on vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016;15:967–976. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1164046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Coudeville L, Bailleux F, Riche B, Megas F, Andre P, Ecochard R. Relationship between haemagglutination-inhibiting antibody titres and clinical protection against influenza: development and application of a Bayesian random-effects model. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-10-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Black S, Nicolay U, Vesikari T, et al. Hemagglutination inhibition antibody titers as a correlate of protection for inactivated influenza vaccines in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011;30:1081–1085. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182367662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [Accessed November 10, 2016];Overview of Influenza Surveillance in the United States. http://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/overview.htm.
- 18.Webster R, Cox N, Stohr K. World Health Organization Manual on Animal Influenza Diagnosis and Surveillance. WHO; Geneva: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karlsson EA, Meliopoulos VA, Savage C, Livingston B, Mehle A, Schultz-Cherry S. Visualizing real-time influenza virus infection, transmission and protection in ferrets. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6378. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2016. https://www.R-project.org/ [Google Scholar]
- 21.Flegal KM, Kruszon-Moran D, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Trends in obesity among adults in the United States, 2005–2014. JAMA. 2016;315:2284–2291. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.6458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289:76–79. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xie H, Wan XF, Ye Z, et al. H3N2 mismatch of 2014–15 northern hemisphere influenza vaccines and head-to-head comparison between human and ferret antisera derived antigenic maps. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15279. doi: 10.1038/srep15279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fan W, Chen XF, Shen C, Guo ZR, Dong C. Hepatitis B vaccine response in obesity: A meta-analysis. Vaccine. 2016;34:4835–4841. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.08.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eliakim A, Schwindt C, Zaldivar F, Casali P, Cooper DM. Reduced tetanus antibody titers in overweight children. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:137–141. doi: 10.1080/08916930600597326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Painter SD, Ovsyannikova IG, Poland GA. The weight of obesity on the human immune response to vaccination. Vaccine. 2015;33:4422–4429. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.06.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Paich HA, Sheridan PA, Handy J, et al. Overweight and obese adult humans have a defective cellular immune response to pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus. Obesity. 2013;21:2377–2386. doi: 10.1002/oby.20383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sheridan PA, Paich HA, Handy J, et al. Obesity is associated with impaired immune response to influenza vaccination in humans. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012;36:1072–1077. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McElhaney JE, Xie D, Hager WD, et al. T cell responses are better correlates of vaccine protection in the elderly. J Immunol. 2006;176:6333–6339. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.6333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cheng LW, Huang SW, Huang LM, et al. Comparison of neutralizing and hemagglutination-inhibiting antibody responses for evaluating the seasonal influenza vaccine. J Virol Methods. 2012;182:43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Murphy R, Fragaszy EB, Hayward AC, Warren-Gash C. Investigating obesity as a risk factor for influenza-like illness during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic using the Health Survey for England. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2017;11:66–73. doi: 10.1111/irv.12420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Karlsson EA, Hertz T, Johnson C, Mehle A, Krammer F, Schultz-Cherry S. Obesity outweighs protection conferred by adjuvanted influenza vaccination. MBio. 2016;7:e01144–16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01144-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Smit MA, Wang HL, Kim E, et al. Influenza vaccine is protective against laboratory-confirmed influenza in obese children. Ped Infect Dis J. 2016;35:440–445. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Callahan ST, Wolff M, Hill HR, et al. Impact of body mass index on immunogenicity of pandemic H1N1 vaccine in children and adults. J Infect Dis. 2014;210:1270–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Esposito S, Giavoli C, Trombetta C, et al. Immunogenicity, safety and tolerability of inactivated trivalent influenza vaccine in overweight and obese children. Vaccine. 2016;34:56–60. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Talbot H, Coleman L, Crimin K, et al. Association between obesity and vulnerability and serologic response to influenza vaccination in older adults. Vaccine. 2012;30:3937–3943. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.03.071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.