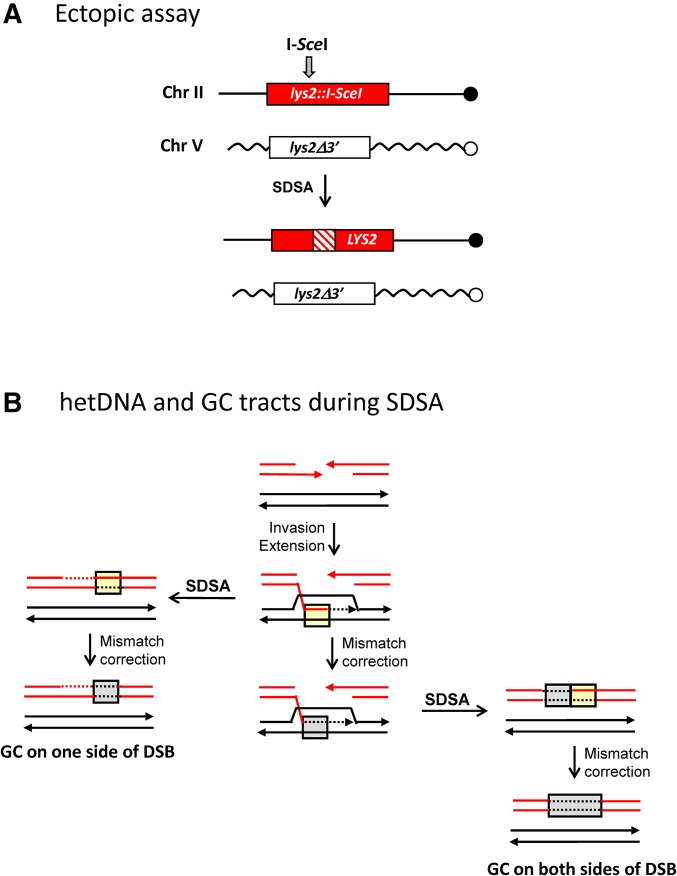
Figure 7.
Mismatch repair during SDSA. (A) The ectopic assay uses diverged, 4.3-kb lys2 repeats on chromosomes II and V. The full-length, recipient allele contains an intact I-SceI cleavage site and the truncated, donor allele contains a mutated site; the I-SceI gene was fused to pGAL and integrated at HIS3. Following galactose induction of I-SceI, repair of the broken allele produces a selectable, Lys+ phenotype. SDSA is inferred when the repaired allele contains a hetDNA tract (cross-hatched region) on only one side of the DSB and the donor allele is unchanged. hetDNA and GC tract positions were determined by sequencing products obtained in an MMR-defective (mlh1Δ) or wild-type background, respectively. (B) Products predicted from SDSA-mediated repair are illustrated. Strands of the broken recipient allele are red and those of the donor allele are black. hetDNA is in yellow boxes and GC tracts resulting from hetDNA repair are in gray boxes. If MMR occurs only after repair is complete, GC will be confined to one side of the initiating DSB (left side). If MMR can occur before the D-loop is dismantled, however, then there will a GC tract that spans the DSB (right side).