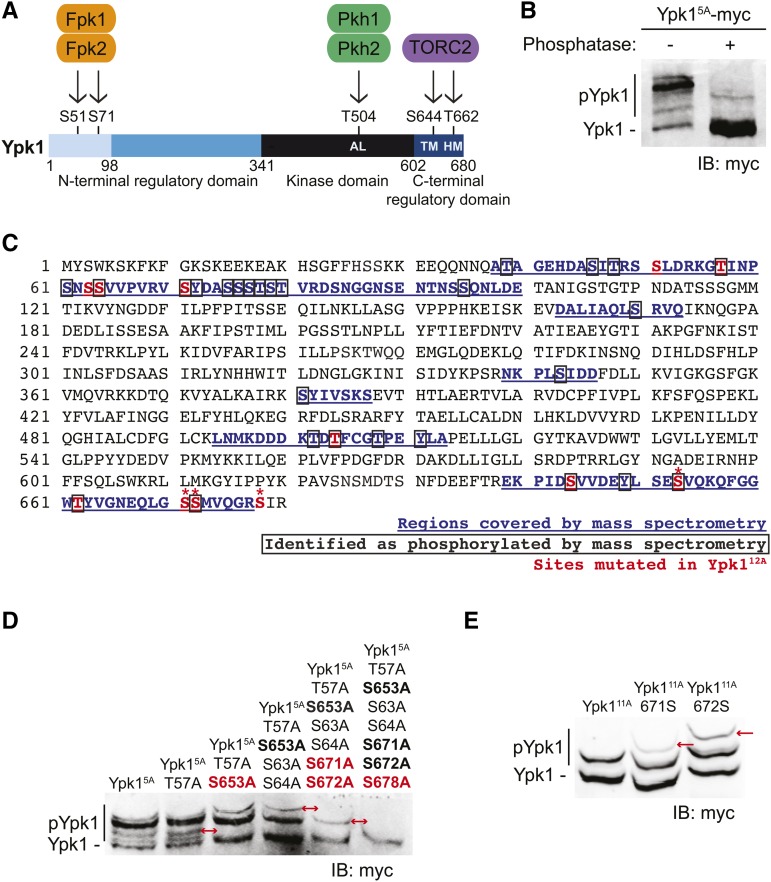
Figure 1.
Ypk1 is phosphorylated at four previously uncharacterized C-terminal sites. (A) Primary structure of Ypk1 depicted schematically. Catalytic domain and N- and C-terminal regulatory elements indicated. Two N-terminal residues phosphorylated by Fpk1 and, less efficiently, by Fpk2 also shown. Shading reflects percent sequence identity between Ypk1 (680 residues) and the corresponding segment in its paralog Ypk2 (677 residues): 1–98, 22% (faint blue); 99–341, 62% (medium blue); 342–602, 90% (black); and, 603–680, 73% (dark blue). AL, activation loop Thr, phosphorylated by Pkh1 and, less efficiently, by Pkh2; HM, hydrophobic motif Thr, phosphorylated by TORC2; TM, turn motif Ser, phosphorylated by TORC2. (B) WT cells (BY4741) expressing Ypk15A-myc from a CEN plasmid (pFR246) were grown to midexponential phase, harvested, lysed, and samples of the resulting extract incubated in the absence or presence of phosphatase. These samples were then resolved by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-myc mAb 9E10. (C) Ypk1 was isolated from yeast extracts by immunoprecipitation; converted to peptide fragments by protease digestion, from which phospho-peptides were enriched; and then analyzed by MS, as described in Materials and Methods. Sequences recovered, blue underlined; phosphorylation sites, boxed residues; sites mutated in Ypk112A [Ypk1(S51A T57A S63A S64A S71A T504A S644A S653A T662A S671A S672A S678)]; see also rightmost lane in (D)], red; and, new TORC2-dependent phosphorylation sites confirmed by band shift, *. (D) WT cells (BY4741) expressing Ypk15A-myc (pFR246) or derivatives of Ypk15A-myc lacking the additional indicated sites; Ypk16A-myc (pFR249), Ypk17A-myc (pFR252), Ypk19A-myc (pFR255), Ypk111A-myc (pFR264), or Ypk112A-myc (pJEN9); were examined as in (B) without any phosphatase treatment. (E) WT cells (BY4741) expressing Ypk111A-myc (pFR264) or derivatives of Ypk111A-myc in which the indicated additional phosphorylation site was restored, Ypk111A 671S-myc (pKL28) or Ypk111A 672S-myc (pKL29), were examined as in (D). IB, immunoblot. In (D) and (E), red arrows indicate the change in the migration pattern caused by the indicated mutation(s).