Figure 6. Structural insights into mechanisms of action of the P252R FGFR1c Pfeiffer syndrome mutation, the S99N FGF9 mutation in multiple synostoses syndrome (SYNS) patients, and the N143T FGF9 substitution in mice with Elbow knee synostosis (Eks).
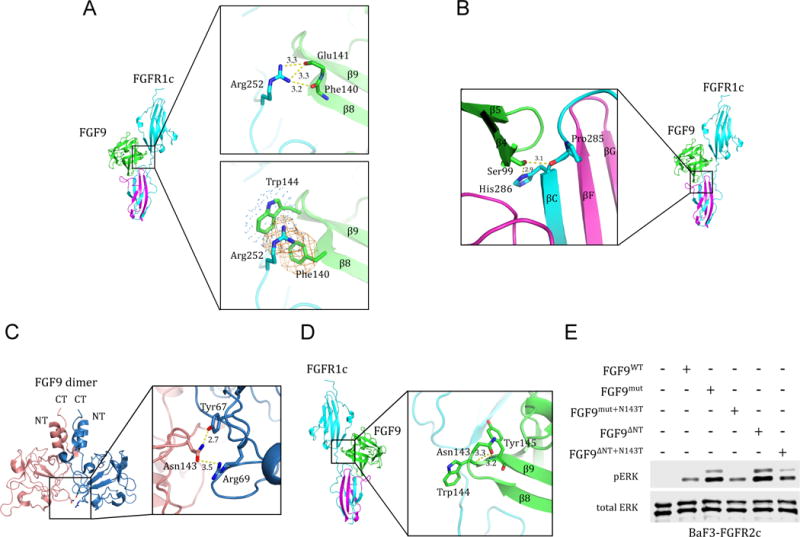
(A) Molecular basis for the robust increase in FGF9 binding affinity of pathogenic FGFR1-3 variants harboring Pro->Arg mutations in their D2-D3 linker region. The upper box shows the conserved hydrogen bonds between the side chain of the mutated Arg-252 residue in the D2-D3 linker of FGFR1c and the backbone carbonyl oxygens of Phe-140, Glu-141, and Glu-142 in FGF9 core region. The lower box depicts the FGF9 subfamily-specific π-cation and hydrophobic interactions (rendered as orange mesh and blue dots, respectively) between the side chain of the mutated Arg-252 residue and Phe-140 and Trp-144 of FGF9. (B) Structural basis for the loss-of-function effects of the S99N FGF9 mutation identified in multiple synostoses syndrome (SYNS) patients. Hydrogen bonds between Ser-99 of FGF9 and D3 of FGFR1c are depicted as dashed yellow lines. (C) The FGF9 N143T mutation found in Elbow knee synostosis (Eks) mice is a loss-of-function mutation. Cartoon presentation of the autoinhibited FGF9 dimer (PDB ID: 1IHK) (Plotnikov et al., 2001) with a close-up view of the dimer interface mediated by Asn-143. Asn-143 on one of the FGF9 molecules (pink) and Tyr-67, Arg-69 on the other FGF9 (blue) molecule are shown as sticks. Hydrogen bonds are depicted by dashed yellow lines and their lengths are given in Å. (D) FGF9-FGFR1c structure model showing the location of Asn-143 of FGF9 in the complex. Dashed yellow lines represent the hydrogen bonds between the side chain of Asn-143 and the backbone amide nitrogen of Trp-144 and Tyr-154 that facilitate formation of β8-β9 turn. (E) Comparison of the activities of FGF9WT, FGF9mut, FGF9ΔNT, and derivatives of FGF9mut and FGF9ΔNT carrying the N143T mutation (FGF9mut+N143T and FGF9ΔNT+N143T). BaF3-FGFR2c cells were stimulated with 500 pM of each ligand and FGFR2c activation was assessed by blotting total cell lysates with phospho-Erk1/2 antibodies. Bottom blot: Detection of total ERK protein as a sample loading control. See also Figure S1.
