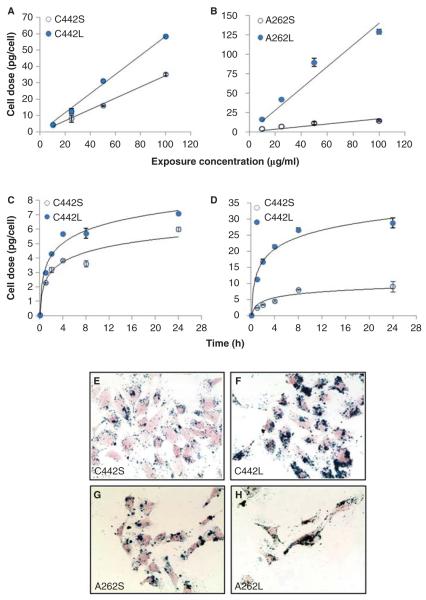
Figure 3.
Exposure- and time-dependent delivery of IONP agglomerates to cultured mouse C10 lung epithelial cells. Cells were treated with the indicated media concentrations of carboxylated (A) or amine-modified (B) IONPs for 4 h and total cell-associated IONPs were determined by magnetic particle detection, as described in the section “Materials and methods”. Solid lines represent a linear fit to the data (C442S, y = 0.3447x, R2 = 0.9942; C442L: y = 0.5865x, R2 = 0.994; A262S, y = 0.1682x, R2 = 0.9357; A262L: y = 1.4064x, R2 = 0.9267). The temporal patterns of cell association of carboxylated (C) and amine-modified (D) IONPs was determined after exposure to 10 μg/ml concentration and measured at the times indicated. Solid lines represent a logarithmic fit to the data (C442S, R2 = 0.9503; C442L, R2 = 0.9811; A262S, R2 = 0.9002; A262L, R2 = 0.9788). Panels E–H: Representative images of C10 cells after 4 h exposure to 10 μg/ml of small and large agglomerates of carboxylated IONPs (panels E, F) or aminated IONPS (panels G, H). Iron oxide is stained with Prussian blue and cells are stained with Nuclear Fast Red.