Abstract
Lactic acid bacteria produce diverse functional metabolites in fermented foods. However, little is known regarding the metabolites and the fermentation process in kimchi. In this study, the culture broth from Leuconostoc lactis, a lactic acid bacterium isolated from kimchi, was analysed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and identified by the MS-DIAL program. The MassBank database was used to analyse the metabolites produced during fermentation. A mass spectrum corresponding to 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA) was validated based on a collision-induced dissociation (CID) fragmentation pattern with an identified m/z value of 131.07. HICA production by lactic acid bacteria was monitored and showed a positive correlation with hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenases (HicDs), which play a key role in the production of HICA from leucine and ketoisocaproic acid. Interestingly, the HICA contents of kimchi varied with Leuconostoc and Lactobacillus content during the early stage of fermentation, and the addition of lactic acid bacteria enhanced the HICA content of kimchi. Our results suggest that HICA production in kimchi is dependent on the lactic acid bacterial composition.
Introduction
Fermentation improves the long-term storage of food and increases the contents of active metabolites, thereby contributing to human health1. Various studies have shown that fermented foods exhibit enhanced health-promoting effects. Kimchi is a representative fermented vegetable-containing food product with health-promoting activity. Kimchi improves lipid profiles by lowering low-density lipoprotein levels and has been reported to exert antioxidant and anti-obesity effects1–4. Kimchi contains a variety of bacteria, among which Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae are the dominant lactic acid bacterial families. The antibacterial activities and probiotic features of lactic acid bacteria from kimchi have been extensively characterized5, 6. In addition, lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi exhibit antioxidant, immunomodulatory, antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-adipogenic activities7–12. Moreover, exopolysaccharides, vitamins, phenolic compounds, γ-amino butyric acid, mannitol, and organic acids from kimchi have been reported to originate from lactic acid bacteria13–20.
The unique process of kimchi fermentation depends mainly on the physiological and biochemical traits of metabolite processing by the bacteria, with bacterial population changes contributing to the flavour and taste of kimchi through the conversion of raw materials into organic acids, sugars, and diverse components. The identification of metabolites from kimchi is necessary to elucidate these fermentation mechanisms. The metabolites in kimchi from the bacterial associations have not been characterized. Research has focused on the molecules that originate from the raw materials used to produce kimchi, such as cabbage, garlic, pepper21. Therefore, it would be of great interest to characterize metabolite conversion by bacteria during kimchi fermentation.
To identify these molecules, a bacterial culture was subjected to ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) coupled with TripleTOF technology using IDA (information-dependent acquisition) mode, and the resultant mass spectrum was analysed with the MassBank mass-spectral database using MS-DIAL software22. A mono-isotopic parent ion peak at m/z 131.07 and fragment masses at m/z 85.06 and 69.03 had the highest MS2 similarities and were identified as 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA). HICA is reported to be a leucine metabolite of Lactobacillus sp. We therefore characterized and analysed HICA production by lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi and monitored HICA production in relation to the bacterial composition during kimchi fermentation.
Results
Identification of 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid from lactic acid bacteria
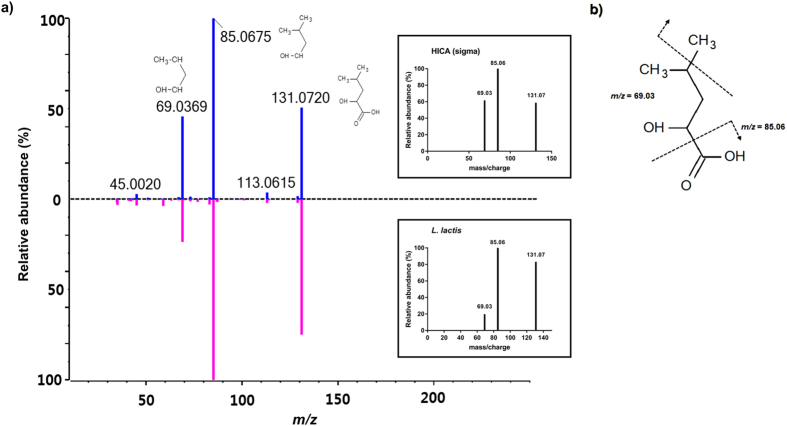
To investigate the metabolites of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi, we first attempted to identify the metabolites of Leuconostoc lactis using a UPLC system coupled to mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The untargeted acquisition of metabolome data was processed by the MS-DIAL program with the MassBank database22. In the resulting spectrum, one molecule had an m/z value of 131.07 with fragment ions of m/z 85.06 and 69.03; these had the highest MS2 similarities, exactly matching the known MS/MS fragmentation patterns for HICA in MassBank (http://www.massbank.jp/en/ database.html) and METLIN (https://metlin.scripps.edu/metabo_advanced.php). To confirm the identity of the compound, collision-induced dissociation was performed to characterize the identified ion and compare the molecule with pure HICA (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The identified compound exhibited the same retention time and fragmentation pattern as pure HICA in product-ion MS mode (Fig. 1). The fragment ions at m/z 85.06 and 69.03 corresponded to neutral losses of 46.01 and 62.04 Da, respectively, from the precursor ion (m/z 131.07).
Figure 1.
Identification of HICA from lactic acid bacteria using ultra-performance liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionization time-of-flight MS. (a) Comparison of fragment-ion mass spectra of HICA with [M-H]− at m/z 131.07 as the precursor ion. The fragment ion at m/z 131.07 at 1.4 min from HICA was obtained from a commercial supplier (the upper panel) or L. lactis (the lower panel). (b) Structural schematic of ionized HICA, which divided into three major fragments when the collision energy was −20 eV.
Analysis of hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenases (HicDs)
To investigate HicDs, which catalyse the conversion to HICA, the amino acid sequences of HicDs were obtained from the protein sequence collection in UniProt (http://www.uniprot.org/). Leuconostoc lactis and Leuconoostoc mesenteroides each have 1 annotated HicD protein. Pediococcus pentosaceus and Lactobacillus sakei do not have any proteins corresponding to HicDs, while Lactobacillus brevis has two and Lactobacillus plantarum has 2–4 HicD proteins (Table 1).
Table 1.
HICA production and HicD proteins of lactic acid bacteria.
| Strains | HICD detection1 | Gene/Protein2 |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus brevis | ⊚ | |
| L. brevis ATCC 27350 | ldhD-3/C2D5N4 | |
| HMPREF0496_0286/C2CYB4 | ||
| Pediococcus pentosaceus | ○ | na |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | ⊚ | |
| L. plantarum WCFS1 | hicD1/F9UTU9 | |
| hicD2/F9UN38 | ||
| hicD3/F9UQQ1 | ||
| L. plantarum 16 | Lp16_0961/R9X0G7 | |
| Lp16_1847/R9X4I9 | ||
| Lp16_0312/R9WYL0 | ||
| L. plantarum EDG-AQ4 | N692_14205/T5JVU0 | |
| N692_07995/T5JPG7 | ||
| N692_09230/T5JNS8 | ||
| L. plantarum JCM 1149 | hiD2/D7V8C8 | |
| hiD3/D7VB10 | ||
| L. plantarum DSM 16365 | FD10_GL001795/A0A0R1UA88 | |
| FD10_GL001842/A0A0R1UFN3 | ||
| FD10_GL000167/A0A0R1UV40 | ||
| FD10_GL002915/A0A0R1UXZ3 | ||
| Leuconostoc lactis | ⊚ | |
| L. lactis ATCC 19256 | AN225_00170/A0A0Q0YB06 | |
| Lactobacillus sakei | ○ | na |
| Leuconostoc mesenteroides | ⊚ | |
| L. mesenteroides J18 | MI1_00275/A0A0N1S1U2 | |
| L. mesenteroides ATCC 19254 | HMPREF0555_1660/C2KLZ4 | |
| L. mesenteroides P45 | LH61_00190/A0A095BJX0 | |
| L. mesenteroides subsp. dextranicum | WZ78_04955/A0A0K9JDI8 |
1HICD was identified and measured using UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS/MS (○: > 20 μg/ml, ⊚: > 150 μg/ml).
2Gene/Protein IDs were obtained from the UniProt (http://www.uniprot.org/) protein database.
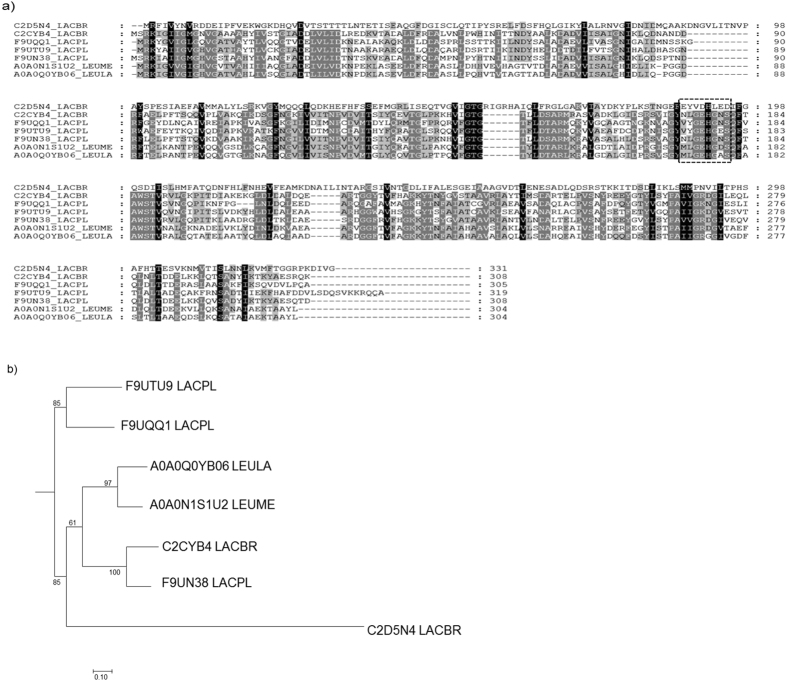
We compared the HicDs among the lactic acid bacteria and were able to classify them into Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc groups (Supplementary Fig. S1 and Fig. 2). For further investigation, we selected strains with reliable reference genomes (L. plantarum WCFS123, L. mesenteroides J1824, L. brevis ATCC 27350, and L. lactis ATCC 19256) and aligned their HicD amino acid sequences using the ClustalW multi-alignment program to compare the core regions of the amino acid sequences (Fig. 2). The active domain was analysed by performing a ProSite scan-motif search (http://prosite.expasy.org/), which identified LGEHGNS as the proton-donor active site (Fig. 2a). The HicD amino acid sequences with the UniProt accession numbers A0A0N1S1U2 (L. mesenteroides J18) and A0A0Q0YB06 (L. lactis ATCC 19256) exhibited 75.33% similarity, whereas F9UN38 (L. plantarum WCFS1) and C2CYB4 (L. brevis ATCC 27350) exhibited 74.68% similarity. The other HicDs exhibited 40–55% similarities, except for C2D5N4 (L. brevis ATCC 27350), which showed 11% similarity.
Figure 2.
Comparison of hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenases from lactic acid bacteria. (a) Alignments of hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenases of lactic acid bacteria. The boxed region indicates the proton-donor active site. (b) Phylogenetic trees constructed from hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase protein sequences showing phylogenetic relationships. (LACPL: Lactobacillus plantarum; LEULA: Leuconostoc lactis: LEUME: Leuconostoc mesenteroides; LACBR: Lactobacillus brevis).
Quantification of HICA and hicD gene expression
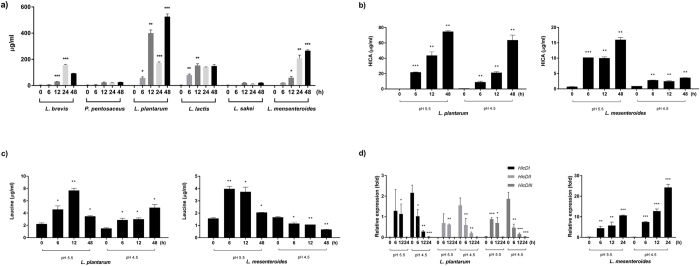
For quantification of HICA content, a bacterial culture extract was analysed by UPLC combined with electrospray ionization time-of-flight MS (UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS/MS). Quantification of HICA was achieved by comparing the peak area of l-norvaline (internal standard) with the areas of relevant peaks from extracted-ion chromatograms (internal standard, m/z 116 > 116; HICA, m/z 131 > 85). The HICA content of L. plantarum reached 526 ± 20.9 μg/ml at 48 h (P = 0.00078) after cultivation, whereas L. lactis and L. mesenteroides produced 153.1 ± 13.7 (P = 0.004) and 266.9 ± 5.9 μg/ml (P = 0.0002) at 12 and 48 h, respectively (Fig. 3a). HICA content began to increase at 6 or 12 h with the growth of lactic acid bacteria. L. plantarum possesses three HicD proteins, and it produced approximately two fold more HICA than L. lactis or L. mesenteroides (Fig. 3a). However, although L. brevis possesses two HicD proteins, its HICA production was the lowest among the four lactic acid bacteria studied. This may be because one of its HicD proteins (C2D5N4) exhibited low similarity to the other HicDs (Fig. 2a and b). The HICA contents of L. plantarum and L. mesenteroides were positively correlated with the intracellular leucine content (Fig. 3b and c). In addition, the HICA content of L. mesenteroides increased despite growth suppression at pH 5.5 (Fig. 3b).
Figure 3.
Confirmation of the HICA and leucine contents from lactic acid bacteria and the expression of hicD genes according to growth and MRS conditions. (a) Comparison of HICA production by six lactic acid bacteria, including Lactobacillus brevis, P. pentosaceus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Leuconostoc lactis, Lactobacillus sakei, and Leuconostoc mesenteroides. (b,c) Comparison of the change in HICA production and intracellular leucine content induced by Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides in MRS broths of pH 5.5 and 4.5 adjusted with lactic acid solution. (d) The transcription levels of the 2-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase genes in Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides in MRS broths of pH 5.5 and 4.5 were determined via qRT-PCR. The mRNA expression values were normalized by the transcription levels in bacteria cultivated in MRS pH 6.2 according to growth time. Asterisks indicate significant differences (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05).
hicD gene expression from lactic acid bacteria was measured using quantitative real-time PCR. Bacteria were cultivated in MRS broth in which the original pH of 6.2 was adjusted to 4.5–5.5 with lactic acid. hicD gene expression increased as bacterial growth increased or as pH decreased (Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. S3). The three hicD homologues of L. plantarum all showed similar gene expression patterns. While L. brevis possesses two hicD genes, HMPREF0496_0286 (C2CYB4) did not exhibit an increase in gene expression with increasing bacterial growth (Supplementary Fig. S3).
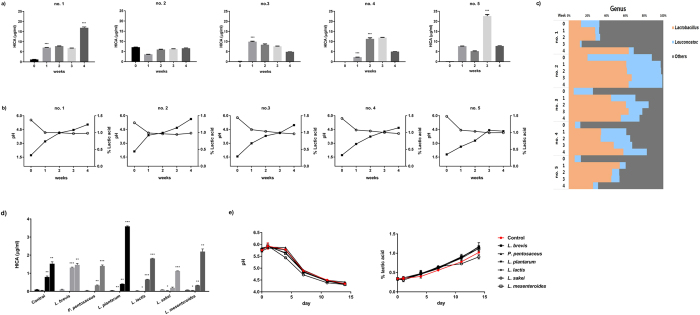
Next, we measured the HICA contents of kimchi obtained from a local market. The HICA contents of the kimchi samples began to increase after approximately 2 weeks and then decreased over a 3–4-week period. Kimchi HICA content ranged from 7.1 ± 0.1 to 22.6 ± 0.4 μg/ml during the period from 2 weeks to 4 weeks (Fig. 4a).
Figure 4.
Properties of kimchi producing HICA obtained from a local market or treated with lactic acid bacteria starter. (a) Quantification of HICA production in commercial kimchi. The HICA content was determined after LC-MS/MS separation and analysis in multiple-reaction monitoring mode with measurements of the product ion. All kimchi samples were purchased from a local market. (b) Changes in pH and acidity in commercial kimchi. (c) Comparison of bacterial communities among commercial kimchi. Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae are dominant. (d) Quantification of HICA production in kimchi treated with lactic acid bacteria for 0, 4, 7, and 14 days. (e) Measurements of the pH and acidity of starter-inoculated kimchi. Asterisks indicate significant differences (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05).
To investigate the association between HICA content and the kimchi microbiota, we examined the kimchi microbiota using metagenomic techniques and measured the acidity of each kimchi sample. As shown in Fig. 4b, acidity increased during kimchi fermentation, with all kimchi samples showing a similar pattern in which acidity increased from approximately 0.3% at the initial time point to approximately 1.2% after 4 weeks of fermentation. The overall HICA contents of kimchi increased (P < 0.05) after 1 week of fermentation, except for in one kimchi sample (no. 2), which nonetheless showed a similar acidity to those of the other kimchi samples. The microbiota of the kimchi was dominated by the Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc genera, in accordance with the presence of fermentation (Fig. 4c). Two kimchi samples (no. 1 and 2) showed relatively high abundances of lactic acid bacteria and higher HICA contents (1.2–7.1 μg/ml) than the other kimchi samples (0.1–0.2 μg/ml) at the initial time point (0 W).
To determine whether the addition of lactic acid bacteria contributes to the production of HICA in kimchi, we inoculated 107 CFU/g bacteria into kimchi. Kimchi inoculated with L. plantarum and L. mesenteroides showed higher contents of HICA (2.2–3.5 μg/ml) (P < 0.01) than control kimchi samples (1.1–1.5 μg/ml) (Fig. 4d). The pH and acidity of inoculated kimchi were not dependent on HICA content (Fig. 4e).
Discussion
In this study, we identified HICA from bacterial cultures of L. lactis, L. plantarum, L. brevis, and L. mesenteroides through an untargeted metabolomics approach. The amino acid derivative HICA (also known as leucic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-methylvaleric acid, and 2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid) is a protein-fermentation product of bacteria, such as lactobacilli. In addition, mammalian cells can metabolize HICA and use the metabolite for protein synthesis25. However, the generation of HICA in fermented vegetables and the lactic acid bacteria responsible for HICA production in fermented foods have not been investigated thoroughly.
A previous report showed that the Lactobacillus amylovorus DSM19280 (cereal isolate), Lactobacillus brevis R2Δ (porcine isolate), and Lactobacillus reuteri R29 strains produce HICA and characterized their antifungal activities26. HICA exhibits mild fungicidal or antibiotic activity against Candida, Aspergillus, Staphylococcus, and Fusobacterium 27, 28 and also shows activity against Enterococcus faecalis isolated from human teeth29. In a murine model, HICA attenuated inflammatory responses during Candida infection25. HICA can increase protein synthesis and improve muscle recovery after immobilization-induced atrophy30. The induction of protein synthesis is believed to occur through the activation of mammalian mTOR signalling, which is also activated during the innate inflammatory responses induced by bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses30.
HICA is formed by the transamination of leucine to 2-ketoisocaproic acid (KICA), followed by a reduction reaction of 2-KICA to 2-HICA, which is the end product of the leucine catabolism pathway. HicD is required for the latter reaction27. HICA is a typical constituent of human plasma, naturally circulating at a concentration of 0.25 ± 0.02 mmol/L31, and is found in muscle generally considered to have anti-catabolic activity30. HICA is also detectable in urine32 and other biological fluids33–35. HICA can inhibit various matrix metalloproteinase enzymes that are responsible for degrading connective and protein tissues36.
HICA production during bacterial growth was measured in multiple-reaction monitoring (MRM) mode during LC-MS/MS analysis. HICA production ranged from 153.1 to 526 μg/ml in L. lactis, L. plantarum, L. brevis, and L. mesenteroides. HICA production was lower in L. sakei and P. pentosaceus 21.4 and 26.1 μg/ml, respectively), which do not have HicDs.
These results agree well with both the numbers and similarities of HicDs in the bacterial strains. HicD was not identified in P. pentosaceus and L. sakei, and these two lactic acid bacteria strains showed reduced HICA production during growth. However, HicD belongs to the family of lactate dehydrogenases (Table S1), suggesting basal expression of HICA even in the absence of HicDs.
Previously, changes in the microbiota during kimchi fermentation were well characterized, and it was shown that Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae are the dominant microbial families in kimchi, with Lactobacillus species present during the later stages of fermentation and Leuconostoc species found during the early stages of kimchi fermentation6, 37. Even with varying degrees of acidity among the lactic acid bacteria, all cultures were acidic, and this increased in parallel with bacterial growth.
Therefore, we studied HICA production in kimchi and microbial populations to evaluate HICA production during kimchi fermentation. The HICA content in kimchi began to increase after 1 week, with the exception of that in kimchi sample no. 2 (Fig. 4b). Kimchi samples no. 1 and 2 had higher HICA contents at the starting time point but had low acidity and were composed predominantly of Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc (Fig. 4c). Nonetheless, HICA contents were consistent with changes in the microbiota despite the low acidity. Moreover, HICA contents in kimchi with added lactic acid bacteria support this finding. HICA contents were highest in the kimchi samples with L. mesenteroides and L. plantarum (Fig. 4d).
Acidity is used as a standard to evaluate the progress of fermentation in kimchi and other fermented foods, as acidity increases with the duration of kimchi fermentation. Leucine and ketoisocarproic acid are the main substrates in the HICA catabolic pathway in bacteria. Isovaleric acid is the final product of leucine oxidization, while reduction promotes the final product of isocaproic acid38. Acidic stress in L. rhamnosus and L. reuteri results in an increase in ABC-type dipeptide/oligopeptide transporter (dpp/opp) expression, which plays an important role in amino acid transport39, 40. A study into the L. casei amino acid uptake system suggested that leucine is transported by a proton drive motive force. Reductions in the proton motive force due to inhibitors or changes in pH decrease leucine transport41. In this study, we observed an increase in intracellular leucine, and this was positively correlated with HICA production (Fig. 3b,c). The fact that hicD expression was also increased at lower pH ranges supports the idea that the kimchi fermentation environment might be positively influenced by HICA production by lactic acid bacteria (Fig. 3d), especially by Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc during the initial kimchi fermentation process.
In conclusion, we found that the production of HICA as a leucine metabolite differed among lactic acid bacteria. These differences were mainly due to the core HicDs present in the lactic acid bacteria and to environmental stress during fermentation. These results also suggest the possible use of HICA as an indicator for fermented foods with lactic acid bacteria or related industrial processes.
Materials and Methods
Medium and bacterial culture conditions
All bacteria were isolated from homemade kimchi and identified by 16 S rDNA sequencing42. The identified 16 S rRNA gene sequences were deposited in NCBI GenBank under accession nos. KT759681 (Leuconostoc mesenteroides WiKim19), KX890131 (Pediococcus pentosaceus WiKim20), KX886794 (Lactobacillus brevis WiKim47), KX886799 (Lactobacillus lactis WiKim48), and KX886806 (Lactobacillus sakei WiKim49). Lactobacillus plantarum WiKim18 was reported previously43. All bacteria were cultivated in de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth.
Preparation of samples and standard solutions
Bacterial culture samples were collected at 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours after incubation at 30 °C and were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min; l-norvaline was added as an internal standard (final concentration: 100 μg/ml). The samples were extracted using a Sep-Pak C18 Light cartridge (Waters, Milford, MA, USA). Finally, the collected samples were lyophilized in a Speed-Vac and resuspended with distilled water for LC-MS/MS analysis. To prepare standard solutions, a stock solution of HICA was diluted serially to concentrations of 100, 300, 500, 800, and 1000 μM in 10 ml MRS broth. l-Norvaline was used as an internal standard at a concentration of 100 μg/ml in 10 ml MRS broth or bacterial culture supernatant. HICA and the internal standard were obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and used to generate standard curves for subsequent quantification. All solvents were LC-MS grade and were purchased from J. T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ, USA).
UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS/MS conditions, HICA identification, and quantification
A TripleTOF 5600 plus instrument (SCIEX, Redwood City, CA, USA) coupled with an Acquity UPLC system (Waters) was used to characterize the metabolites and quantify the HICA contents of bacteria and kimchi. MS results were obtained at m/z 50–2000 in electrospray-negative mode with a spray voltage of −4.5 kV at a scan rate of 10 spectra/s. A reversed-phase column (Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column 2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm particle size; Waters) was used to separate the compounds. The mobile phase consisted of distilled water (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) containing 10 mM ammonium acetate at a flow rate of 0.5 ml/min. The UPLC gradient program was as follows: (1) 95% solvent A from 0 to 0.5 min, (2) a linear gradient from 70% to 45% over 18.4 min, (3) 10% solvent A for 5 min. The total run time was 30 min per sample, and the injection volume was 2 μl. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data were processed using SCIEX PeakView 1.2 and MultiQuant 2.1 software (ABsciex). Peak picking and alignment were performed using MS-DIAL (ver. 1.98)22. Representative MS/MS spectra were exported in abf format for MS-DIAL, and compound identification was performed against MS/MS libraries including MassBank (MassBank_MSMS_Neg_Rev173_vs1)44 and ReSpect (Respect_20120925_ESI_Negative_MSMS)45. HICA from lactic acid bacteria and kimchi was quantified in MRM mode, using the following transitions: HICA, m/z 131.0 > 85.0; l-norvaline, m/z 116.
HicD sequence analysis
The amino acid sequences of HicD proteins from lactic acid bacteria were obtained from UniProt46 for L. brevis ATCC 27350 (C2CYB4, C2D5N4), P. pentosaceus (na), L. plantarum WCFS1 (F9UTU9, F9UN38, F9UQQ1), L. lactis ATCC 1956 (A0A0Q0YB06), L. sakei (na), and L. mesenteroides J18 (A0A0N1S1U2). The amino acid sequences were aligned and compared using the ClustalW program. Amino acid sequence similarities were analysed, and phylogenetic trees were generated using the CLC Genomics Workbench v7.5 program (Qiagen, Redwood City, CA, USA).
Quantitative real-time PCR of hicD expression
hicD gene expression levels from lactic acid bacteria were measured using quantitative real-time PCR. The bacteria were cultivated in MRS broth. The pH of the MRS broth (pH 6.2) was adjusted to pH 4.5–5.5 with lactic acid. The bacterial cells were harvested and lysed for total RNA extraction using TRIzol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was generated and RT-PCR was performed using TOPreal™ qPCR 2X PreMix (Enzynomics, Daejeon, Republic of Korea). Relative expression levels were calculated and normalized to that of the 16 S rRNA gene. Primers were designed based on nucleotide sequences from L. lactis A0A0Q0YB06 (AN225_0017); L. brevis C2D5N4 and C2CYB4 (ldhD3 and HMPREF0496_0286, respectively); L. mesenteroides A0A0N1S1U2 (MI1_00275); and L. plantarum F9UTU9, F9UN38, and F9UQQ1 (hicd1, hicd2, and hicd3, respectively) (Table S2).
Comparison and analysis of metagenomic data
Metagenomic DNA was isolated from commercial kimchi and analysed by sequencing at Chunlab, Inc. (Seoul, Korea) using an Illumina MiSeq sequencing system (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
The taxonomic classification for each read was determined using the EzTaxon-e database (http://eztaxon-e.ezbiocloud.net). The richness and diversity of samples were confirmed by Chao1 estimation and the Shannon diversity index at a 3% distance. To compare operational taxonomic units (OTUs) among samples, shared OTUs were identified by XOR analysis using the CL community program (Chunlab Inc., Seoul, Korea).
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grant from the World Institute of Kimchi (KE1601-1, KE1701-2), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
Author Contributions
B.P., H.H., and J.L. designed the study. B.P., H.H., S.H., and S.S. performed the experiments. B.P. and H.H. performed the LC-MS analysis. J.J. and S.L. performed the metagenomics analysis. All authors contributed to data interpretation. J.L. supervised the experimental work and data analysis. B.P., H.H., and J.L. contributed to manuscript generation. All authors read, reviewed, and approved the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Boyeon Park and Hyelyeon Hwang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at doi:10.1038/s41598-017-10948-0
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Park S, Bae JH. Fermented food intake is associated with a reduced likelihood of atopic dermatitis in an adult population (Korean national health and nutrition examination survey 2012–2013) Nutr Res. 2016;36:125–133. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Choi IH, et al. Kimchi, a fermented vegetable, improves serum lipid profiles in healthy young adults: randomized clinical trial. J Med Food. 2013;16:223–229. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Park KY, Jeong JK, Lee YE, Daily JW., 3rd Health benefits of kimchi (Korean fermented vegetables) as a probiotic food. J Med Food. 2014;17:6–20. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2013.3083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kim BK, Choi JM, Kang SA, Park KY, Cho EJ. Antioxidative effects of Kimchi under different fermentation stage on radical-induced oxidative stress. Nutr Res Pract. 2014;8:638–643. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2014.8.6.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ji K, Jang NY, Kim YT. Isolation of lactic acid bacteria showing antioxidative and probiotic activities from kimchi and infant feces. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;25:1568–1577. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1501.01077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jung JY, et al. Metagenomic analysis of kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented food. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77:2264–2274. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02157-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Han EJ, Lee NK, Choi SY, Paik HD. Short communication: Bacteriocin KC24 produced by Lactococcus lactis KC24 from kimchi and its antilisterial effect in UHT milk. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96:101–104. doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-5884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park JE, Oh SH, Cha YS. Lactobacillus brevis OPK-3 isolated from kimchi inhibits adipogenesis and exerts anti-inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. J Sci Food Agric. 2014;94:2514–2520. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hong YF, Kim H, Kim HR, Gim MG, Chung DK. Different immune regulatory potential of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus sakei isolated from kimchi. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;24:1629–1635. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1406.06062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thakur K, Tomar SK, De S. Lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory for riboflavin production. Microb Biotechnol. 2016;9:441–451. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shobharani P, Nanishankar VH, Halami PM, Sachindra NM. Antioxidant and anticoagulant activity of polyphenol and polysaccharides from fermented Sargassum sp. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;65:542–548. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Varsha KK, et al. 2,4-Di-tert-butyl phenol as the antifungal, antioxidant bioactive purified from a newly isolated Lactococcus sp. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015;211:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Binh TT, Ju WT, Jung WJ, Park RD. Optimization of gamma-amino butyric acid production in a newly isolated Lactobacillus brevis. Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36:93–98. doi: 10.1007/s10529-013-1326-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Di Cagno R, et al. Synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by Lactobacillus plantarum DSM19463: functional grape must beverage and dermatological applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;86:731–741. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Caggianiello G, Kleerebezem M, Spano G. Exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria: from health-promoting benefits to stress tolerance mechanisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:3877–3886. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Franciosi E, et al. Biodiversity and gamma-aminobutyric acid production by lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional alpine raw cow’s milk cheeses. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:625740. doi: 10.1155/2015/625740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Santos MM, Piccirillo C, Castro PM, Kalogerakis N. & Pintado, M. E. Bioconversion of oleuropein to hydroxytyrosol by lactic acid bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;28:2435–2440. doi: 10.1007/s11274-012-1036-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jeong SH, Jung JY, Lee SH, Jin HM, Jeon CO. Microbial succession and metabolite changes during fermentation of dongchimi, traditional Korean watery kimchi. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013;164:46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jung JY, et al. Effects of Leuconostoc mesenteroides starter cultures on microbial communities and metabolites during kimchi fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012;153:378–387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.11.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lim HS, Cha IT, Roh SW, Shin HH, Seo MJ. Enhanced production of gamma-aminobutyric acid by optimizing culture conditions of Lactobacillus brevis HYE1 isolated from kimchi, a Korean fermented food. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;27:450–459. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1610.10008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Patra JK, Das G, Paramithiotis S, Shin HS. Kimchi and other widely consumed traditional fermented foods of Korea: A review. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1493. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tsugawa H, et al. MS-DIAL: data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat Methods. 2015;12:523–526. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Siezen RJ, et al. Complete resequencing and reannotation of the Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 genome. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:195–196. doi: 10.1128/JB.06275-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jung JY, Lee SH, Lee SH, Jeon CO. Complete genome sequence of Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides strain J18, isolated from kimchi. J Bacteriol. 2012;194:730–731. doi: 10.1128/JB.06498-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nieminen MT, et al. DL-2-hydroxyisocaproic acid attenuates inflammatory responses in a murine Candida albicans biofilm model. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014;21:1240–1245. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00339-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Axel C, et al. Antifungal activities of three different Lactobacillus species and their production of antifungal carboxylic acids in wheat sourdough. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100:1701–1711. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-7051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sakko M, et al. 2-Hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA): a new potential topical antibacterial agent. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;39:539–540. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sakko M, et al. 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid is fungicidal for Candida and Aspergillus species. Mycoses. 2014;57:214–221. doi: 10.1111/myc.12145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sakko M, Tjaderhane L, Sorsa T, Hietala P, Rautemaa R. 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA) is bactericidal in human dental root canals ex vivo. Int Endod J. 2017;50:455–463. doi: 10.1111/iej.12639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lang CH, et al. Chronic alpha-hydroxyisocaproic acid treatment improves muscle recovery after immobilization-induced atrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013;305:E416–428. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00618.2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hoffer LJ, Taveroff A, Robitaille L, Mamer OA, Reimer ML. Alpha-keto and alpha-hydroxy branched-chain acid interrelationships in normal humans. J Nutr. 1993;123:1513–1521. doi: 10.1093/jn/123.9.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lancaster G, Mamer OA, Scriver CR. Branched-chain alpha-keto acids isolated as oxime derivatives: relationship to the corresponding hydroxy acids and amino acids in maple syrup urine disease. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1974;23:257–265. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90064-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mamer OA, Laschic NS, Scriver CR. Stable isotope dilution assay for branched chain alpha-hydroxy-and alpha-ketoacids: serum concentrations for normal children. Biomed Enbiron Mass Spectrom. 1986;13:553–558. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200131007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jakobs C, Sweetman L, Nyhan WL. Hydroxy acid metabolites of branched-chain amino acids in amniotic fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1984;140:157–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ehling S, Reddy TM. Direct analysis of leucine and its metabolites β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid, α-ketoisocaproic acid, and α-hydroxyisocaproic acid in human breast milk by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63:7567–7573. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mero AA, et al. Effects of alfa-hydroxy-isocaproic acid on body composition, DOMS and performance in athletes. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2010;7:1–1. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-7-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hong Y, Yang HS, Chang HC, Kim HY. Comparison of bacterial community changes in fermenting kimchi at two different temperatures using a denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;23:76–84. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1210.10002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Díaz-Pérez AL, Díaz-Pérez C, Campos-García J. Bacterial l-leucine catabolism as a source of secondary metabolites. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2015;15:1–29. doi: 10.1007/s11157-015-9385-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lee K, Lee HG, Pi K, Choi YJ. The effect of low pH on protein expression by the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus reuteri. Proteomics. 2008;8:1624–1630. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200700663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Koponen J, et al. Effect of acid stress on protein expression and phosphorylation in Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J Proteomics. 2012;75:1357–1374. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Strobel HJ, Russell JB, Driessen AJ, Konings WN. Transport of amino acids in Lactobacillus casei by proton-motive-force-dependent and non-proton-motive-force-dependent mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:280–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.280-284.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Park B, et al. Evaluation of ginsenoside bioconversion of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi. J Ginseng Res. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jang JY, et al. Draft genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum wikim18, isolated from Korean kimchi. Genome Announc. 2014;2:e00467–13. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00467-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Horai H, et al. MassBank: a public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J Mass Spectrom. 2010;45:703–714. doi: 10.1002/jms.1777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sawada Y, et al. RIKEN tandem mass spectral database (ReSpect) for phytochemicals: a plant-specific MS/MS-based data resource and database. Phytochemistry. 2012;82:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.UniProt C. UniProt: a hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D204–212. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.